Abstract
Purpose
The aims of this study were to determine the frequencies of swallowing and swallowing associated with arousals during sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and to determine whether these were associated with the severity of OSA and differed according to the preceding breathing route.
Methods
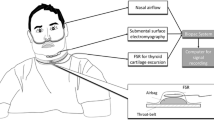
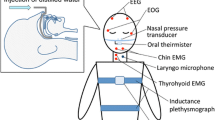
Standard audio-video polysomnography including an evaluation of swallowing-related elevation of the thyroid cartilage and breathing route (i.e., nasal or oronasal) was undertaken in an academic sleep laboratory. Fifty-six patients were analyzed (13 non-OSA patients, 17 mild, 10 moderate, and 16 severe OSA).
Results
The frequency of swallowing per hour of sleep was significantly higher in the severe OSA patients when compared to mild OSA patients (mild OSA, 3.1/h and severe OSA, 8.4/h). This was mainly due to the significantly higher frequency of swallowing associated with a respiratory event-related arousal in the severe OSA patients when compared to non- and mild OSA patients (non-OSA, 0.6/h; mild OSA, 1.0/h; severe OSA, 6.0/h), especially when swallowing was preceded by oronasal breathing (non-OSA, 0.2/h; mild OSA, 0.4/h; severe OSA, 4.2/h).
Conclusions
Swallowing frequency during sleep can increase with increasing OSA severity in most OSA patients. These events are predominately associated with respiratory event-related arousals and are more frequent when preceded by oronasal breathing. The observed swallowing under high ventilatory needs may compromise the maintenance of the pharynx as a conduit for airflow in OSA patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathew OP (1988) Regulation of breathing pattern during feeding: role of suck, swallow, and nutrients. In: Mathew OP, Sant’Ambrogio G (eds) Respiratory function of the upper airway. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 535–560
The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep 22:667–689
Bowes G, Phillipson EA (1984) Arousal responses to respiratory stimuli during sleep. In: Saunders NA, Sullivan CE (eds) Sleep and breathing. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 137–161
Wilson SL, Thach BT, Brouillette RT, Abu-Osba YK (1981) Coordination of breathing and swallowing in human infants. J Appl Physiol 50:851–858
Menon AP, Schefft GL, Thach BT (1984) Frequency and significance of swallowing during prolonged apnea in infants. Am Rev Respir Dis 130:969–973
Don GW, Waters KA (2003) Influence of sleep state on frequency of swallowing, apnea, and arousal in human infants. J Appl Physiol 94:2456–2464
Nixon GM, Charbonneau I, Kermack AS, Brouillette RT, McFarland DH (2008) Respiratory-swallowing interactions during sleep in premature infants at term. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 160:76–82
Lear CSC, Flanagan JB Jr, Moorrees CFA (1965) The frequency of deglutition in man. Arch Oral Biol 10:83–100
Lichter I, Muir RC (1975) The pattern of swallowing during sleep. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 38:427–432
Freidin N, Fisher MJ, Taylor W et al (1991) Sleep and nocturnal acid reflux in normal subjects and patients with reflux oesophagitis. Gut 32:1275–1279
Miyawaki S, Lavigne GJ, Pierre M, Guitard F, Montplaisir JY, Kato T (2003) Association between sleep bruxism, swallowing-related laryngeal movement, and sleep positions. Sleep 26:461–465
Dubé C, Rompré PH, Manzini C, Guitard F, de Grandmont P, Lavigne GJ (2004) Quantitative polygraphic controlled study on efficacy and safety of oral splint devices in tooth-grinding subjects. J Dent Res 83:398–403
Sato K, Nakashima T (2006) Human adult deglutition during sleep. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 115:334–339
Sato K, Nakashima T (2009) Sleep-related deglutition in patients with sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118:30–36
Tsuda H, Lowe AA, Chen H, Fleetham JA, Ayas NT, Almeida FR (2011) The relationship between mouth opening and sleep stage-related sleep disordered breathing. J Clin Sleep Med 7:181–186
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson A, Quan SF (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications, 1st edn. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester
Bonnet M, Carley D, Carskadon M et al (1992) EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples: a preliminary report from the sleep disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association Sleep 15:173–184
Miller AJ (1982) Deglutition. Physiol Rev 62:129–184
Mathew OP, Abu-Osba YK, Thach BT (1982) Genioglossus muscle responses to upper airway pressure changes: afferent pathways. J Appl Physiol 52:445–450
Gleeson K, Zwillich CW, Braier K, White DP (1986) Breathing route during sleep. Am Rev Respir Dis 134:115–120
Fitzpatrick MF, Driver HS, Chatha N, Voduc N, Girard AM (2003) Partitioning of inhaled ventilation between the nasal and oral routes during sleep in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol 94:883–890
Madronio MR, Di Somma E, Stavrinou R et al (2004) Older individuals have increased oro-nasal breathing during sleep. Eur Respir J 24:71–77
Kirkness JP, Madronio M, Stavrinou R, Wheatley JR, Amis TC (2005) Surface tension of upper airway mucosal lining liquid in obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Sleep 28:457–463
Koutsourelakis I, Vagiakis E, Roussos C, Zakynthinos S (2006) Obstructive sleep apnoea and oral breathing in patients free of nasal obstruction. Eur Respir J 28:1222–1228
Bachour A, Maasilta P (2004) Mouth breathing compromises adherence to nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Chest 126:1248–1254
Ruhle KH, Nilius G (2008) Mouth breathing in obstructive sleep apnea prior to and during nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Respiration 76:40–45
Verma M, Seto-Poon M, Wheatley JR, Amis TC, Kirkness JP (2006) Influence of breathing route on upper airway lining liquid surface tension in humans. J Physiol 574:859–866
Nguyen AT, Jobin V, Payne R, Beauregard J, Naor N, Kimoff RJ (2005) Laryngeal and velopharyngeal sensory impairment in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 28:585–593
Beal M, Chesson A, Garcia T, Caldito G, Stucker F, Nathan CO (2004) A pilot study of quantitative aspiration in patients with symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea: comparison to a historic control group. Laryngoscope 114:965–968
Huxley EJ, Viroslav J, Gray WR, Pierce AK (1978) Pharyngeal aspiration in normal adults and patients with depressed consciousness. Am J Med 64:564–568
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the sleep technologists for their assistance in data collection, Mrs. Mary Wong for her assistance in the software and statistical analysis, Miss Sandra Harrison for her assistance in the preparation of experimental equipments, and Miss Adrian Carney for her editorial assistance in the final preparation of this manuscript. The first author was supported as a postdoctoral fellow, in part, by MITACS ACCELERATE BC.
Conflict of interest
The first author was supported as a postdoctoral fellow, in part, by MITACS ACCELERATE BC. None of the authors have any conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The institution at which the work was performed was the Faculty of Dentistry and University of British Columbia Hospital Sleep Disorder Program
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, K., Lowe, A.A., Ayas, N.T. et al. Swallowing and breathing patterns during sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 19, 377–384 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1031-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1031-8