Abstract
Purpose
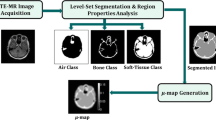
The aim of this study is to generate a four-class magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based attenuation map (μ-map) for attenuation correction of positron emission tomography (PET) data of the head area using a novel combination of short echo time (STE)/Dixon-MRI and a dedicated image segmentation method.
Procedures
MR images of the head area were acquired using STE and two-point Dixon sequences. μ-maps were derived from MRI images based on a fuzzy C-means (FCM) clustering method along with morphologic operations. Quantitative assessment was performed to evaluate generated MRI-based μ-maps compared to X-ray computed tomography (CT)-based μ-maps.
Results
The voxel-by-voxel comparison of MR-based and CT-based segmentation results yielded an average of more than 95 % for accuracy and specificity in the cortical bone, soft tissue, and air region. MRI-based μ-maps show a high correlation with those derived from CT scans (R 2 > 0.95).
Conclusions
Results indicate that STE/Dixon-MRI data in combination with FCM-based segmentation yields precise MR-based μ-maps for PET attenuation correction in hybrid PET/MRI systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heiss W-D (2009) The potential of PET/MR for brain imaging. Eur J Nucl Med 36(1):105–112
Pichler BJ, Kolb A, Nägele T, Schlemmer H-P (2010) PET/MRI: paving the way for the next generation of clinical multimodality imaging applications. J Nucl Med 51(3):333–336
Zaidi H, Del Guerra A (2011) An outlook on future design of hybrid PET/MRI systems. Med Phys 38:5667
Joshi U, Raijmakers PG, Riphagen II et al (2007) Attenuation-corrected vs. nonattenuation-corrected 2-deoxy-2-[f-18] fluoro-d-glucose-positron emission tomography in oncology, a systematic review. Mol Imaging Biol 9(3):99–105
Turkington TG (2000) Attenuation correction in hybrid positron emission tomography [abstract]. Semin Nucl Med Elsevier 30:255–267
Akbarzadeh A, Ay M, Ahmadian A et al (2013) MRI-guided attenuation correction in whole-body PET/MR: assessment of the effect of bone attenuation. Ann Nucl Med 27(2):152–62
Rezaei A, Defrise M, Bal G et al (2012) Simultaneous reconstruction of activity and attenuation in time-of-flight pet. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(12):2224–2233
Rezaei A, Defrise M, Nuyts J (2014) Ml-reconstruction for tof-pet with simultaneous estimation of the attenuation factors. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(7):1563–1572
Keereman V, Mollet P, Berker Y et al (2013) Challenges and current methods for attenuation correction in PET/MR. Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 26(1):81–98
Zaidi H, Montandon M-L, Slosman DO (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging-guided attenuation and scatter corrections in three-dimensional brain positron emission tomography. Med Phys 30:937
Fei B, Yang X, Wang H (2009) An MRI-based attenuation correction method for combined PET/MRI applications [abstract]. SPIE Med Imaging Int Soc Opt Photon 27:7262
Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V et al (2007) MR-based PET attenuation correction–method and validation [abstract]. IEEE NSS-MIC 2007 49:1875–1883
Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V et al (2008) MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI: a novel approach combining pattern recognition and atlas registration. J Nucl Med 49(11):1875–1883
Malone IB, Ansorge RE, Williams GB et al (2011) Attenuation correction methods suitable for brain imaging with a PET/MRI scanner: a comparison of tissue atlas and template attenuation map approaches. J Nucl Med 52(7):1142–1149
Martinez-Möller A, Souvatzoglou M, Delso G et al (2009) Tissue classification as a potential approach for attenuation correction in whole-body PET/MRI: evaluation with PET/CT data. J Nucl Med 50(4):520–526
Schulz V, Torres-Espallardo I, Renisch S et al (2011) Automatic, three-segment, MR-based attenuation correction for whole-body PET/MRI data. Eur J Nucl Med 38(1):138–152
Navalpakkam BK, Braun H, Kuwert T, Quick HH (2013) Magnetic resonance–based attenuation correction for pet/mr hybrid imaging using continuous valued attenuation maps. Invest Radiol 48(5):323–332
Keereman V, Van Holen R, Mollet P, Vandenberghe S (2011) The effect of errors in segmented attenuation maps on PET quantification. Med Phys 38(11):6010–6019
Andersen FL, Ladefoged CN, Beyer T et al (2014) Combined PET/MR imaging in neurology: MR-based attenuation correction implies a strong spatial bias when ignoring bone. Neuroimage 84:206–216
Catana C, van der Kouwe A, Benner T et al (2010) Toward implementing an MRI-based pet attenuation-correction method for neurologic studies on the MR-PET brain prototype. J Nucl Med 51(9):1431–1438
Keereman V, Fierens Y, Broux T et al (2010) MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI using ultrashort echo time sequences. J Nucl Med 51(5):812–818
Berker Y, Franke J, Salomon A et al (2012) Mri-based attenuation correction for hybrid PET/MRI systems: a 4-class tissue segmentation technique using a combined ultrashort-echo-time/Dixon MRI sequence. J Nucl Med 53(5):796–804
Buerger C, Aitken A, Tsoumpas C et al (2011) Investigation of 4D PET attenuation correction using ultra-short echo time mr [abstract]. IEEE NSS-MIC 2011, IEEE 3558–3561
Khateri P, Rad HS, Fathi A, Ay MR (2012) Generation of attenuation map for MR-based attenuation correction of PET data in the head area employing 3D short echo time MR imaging. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res Sect A 702: 133–136
Khateri P, Rad HS, Jafari AH, Ay MR (2014) A novel segmentation approach for implementation of MRAC in head PET/MRI employing short-TE MRI and 2-point Dixon method in a fuzzy c-means framework. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 734:171–174
Fahey FH, Palmer MR, Strauss KJ et al (2007) Dosimetry and adequacy of CT-based attenuation correction for pediatric PET: phantom study 1. Radiology 243(1):96–104
Xia T, Alessio AM, De Man B et al (2012) Ultra-low dose CT attenuation correction for PET/CT. Phys Med Biol 57(2):309
Valentin J (2007) The 2007 recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection: user’s edition. Int Comm Radiol Prot 37: 2-4
Serra J (1982) Image analysis and mathematical morphology. Academic, London
ICRU (1989) International commission on radiation units and measurements, report no. 44
Bezrukov I, Schmidt H, Mantlik F et al (2013) MR-based attenuation correction methods for improved pet quantification in lesions within bone and susceptibility artifact regions. J Nucl Med 54(10):1768–1774
Keereman V (2011) MRI-based attenuation correction for emission tomography [Thesis]
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences under grant no. 25095.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khateri, P., Saligheh Rad, H., Jafari, A.H. et al. Generation of a Four-Class Attenuation Map for MRI-Based Attenuation Correction of PET Data in the Head Area Using a Novel Combination of STE/Dixon-MRI and FCM Clustering. Mol Imaging Biol 17, 884–892 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0849-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0849-1