Abstract
Purpose
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep deprivation (SD) decreases cerebral sigma-1 receptor expression and causes cognitive deficits. Sigma-1 agonists are cognitive enhancers. Here, we investigate the effect of cutamesine treatment in the REM SD model.
Procedures
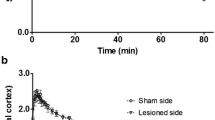
Sigma-1 receptor occupancy (RO) in the rat brain by cutamesine was determined using 1-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)]-4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazine ([11C]SA4503) and positron emission tomography (PET), and tissue cutamesine levels were measured by ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC)-MS. RO was calculated from a Cunningham-Lassen plot, based on the total distribution volume of [11C]SA4503 determined by Logan graphical analysis. Cognitive performance was assessed using the passive avoidance (PA) test.
Results
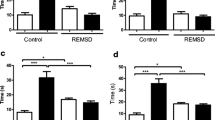
Cutamesine at a dose of 1.0 mg/kg reversed REM SD-induced cognitive deficit and occupied 92 % of the sigma-1 receptor population. A lower dose (0.3 mg/kg) occupied 88 % of the receptors but did not significantly improve cognition.
Conclusion
The anti-amnesic effect of cutamesine in this animal model may be related to longer exposure at a higher dose and/or drug binding to secondary targets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayashi T, Su TP (2007) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+) signaling and cell survival. Cell 131:596–610
Maurice T, Su TP (2009) The pharmacology of sigma-1 receptors. Pharmacol Ther 124:195–206
Su TP, Hayashi T, Maurice T et al (2010) The sigma-1 receptor chaperone as an inter-organelle signaling modulator. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31:557–566
Maurice T, Hiramatsu M, Kameyama T et al (1994) Behavioral evidence for a modulating role of sigma ligands in memory processes. II. Reversion of carbon monoxide-induced amnesia. Brain Res 647:57–64
Maurice T, Roman FJ, Su TP et al (1996) Beneficial effects of sigma agonists on the age-related learning impairment in the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). Brain Res 733:219–230
Maurice T, Hiramatsu M, Itoh J et al (1994) Behavioral evidence for a modulating role of sigma ligands in memory processes. I. Attenuation of dizocilpine (MK-801)-induced amnesia. Brain Res 647:44–56
Maurice T, Privat A (1997) SA4503, a novel cognitive enhancer with sigma1 receptor agonist properties, facilitates NMDA-receptor-dependent learning in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 328:9–18
Zou LB, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (1998) Sigma receptor ligands (+)-SKF10,047 and SA4503 improve dizocilpine-induced spatial memory deficits in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 355:1–10
Maurice T, Phan VL, Privat A (2001) The anti-amnesic effects of sigma1 (sigma1) receptor agonists confirmed by in vivo antisense strategy in the mouse. Brain Res 898:113–121
Noda A, Noda Y, Kamei H et al (2001) Phencyclidine impairs latent learning in mice: interaction between glutamatergic systems and sigma(1) receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:451–460
Hashimoto K, Fujita Y, Iyo M (2007) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of fluvoxamine: role of sigma-1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:514–521
Senda T, Matsuno K, Okamoto K et al (1996) Ameliorating effect of SA4503, a novel sigma 1 receptor agonist, on memory impairments induced by cholinergic dysfunction in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 315:1–10
Matsuno K, Senda T, Kobayashi T et al (1997) SA4503, a novel cognitive enhancer, with sigma-1 receptor agonistic properties. Behav Brain Res 83:221–224
Zvejniece L, Vavers E, Svalbe B et al (2014) The cognition-enhancing activity of E1R, a novel positive allosteric modulator of sigma-1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 171:761–771
Senda T, Matsuno K, Kobayashi T et al (1998) Ameliorative effect of SA4503, a novel cognitive enhancer, on the basal forebrain lesion-induced impairment of the spatial learning performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:129–134
Antonini V, Prezzavento O, Coradazzi M et al (2009) Anti-amnesic properties of (+/−)-PPCC, a novel sigma receptor ligand, on cognitive dysfunction induced by selective cholinergic lesion in rats. J Neurochem 109:744–754
Antonini V, Marrazzo A, Kleiner G et al (2011) Anti-amnesic and neuroprotective actions of the sigma-1 receptor agonist (−)-MR22 in rats with selective cholinergic lesion and amyloid infusion. J Alzheimers Dis 24:569–586
Maurice T, Su TP, Privat A (1998) Sigma1 (sigma 1) receptor agonists and neurosteroids attenuate B25-35-amyloid peptide-induced amnesia in mice through a common mechanism. Neuroscience 83:413–428
Behensky AA, Yasny IE, Shuster AM et al (2013) Stimulation of sigma receptors with afobazole blocks activation of microglia and reduces toxicity caused by amyloid-beta25-35. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 347:458–467
Meunier J, Demeilliers B, Celerier A et al (2006) Compensatory effect by sigma1 (sigma1) receptor stimulation during alcohol withdrawal in mice performing an object recognition task. Behav Brain Res 166:166–176
Ishiwata K, Oda K, Sakata M et al (2006) A feasibility study of [11C]SA4503-PET for evaluating sigma 1 receptor occupancy by neuroleptics: the binding of haloperidol to sigma 1 and dopamine D 2-like receptors. Ann Nucl Med 20:569–573
Ishikawa M, Ishiwata K, Ishii K et al (2007) High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]SA4503. Biol Psychiatry 62:878–883
Ishikawa M, Sakata M, Ishii K et al (2009) High occupancy of sigma1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of donepezil: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]SA4503. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:1127–1131
Ramakrishnan NK, Visser AK, Schepers M et al (2014) Dose-dependent sigma-1 receptor occupancy by donepezil in rat brain can be assessed with 11C-SA4503 and microPET. Psychopharmacology 231:3997–4006
Palchykova S, Winsky-Sommerer R, Meerlo P et al (2006) Sleep deprivation impairs object recognition in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 85:263–271
Hagewoud R, Havekes R, Novati A et al (2010) Sleep deprivation impairs spatial working memory and reduces hippocampal AMPA receptor phosphorylation. J Sleep Res 19:280–288
Xu ZQ, Gao CY, Fang CQ et al (2010) The mechanism and characterization of learning and memory impairment in sleep-deprived mice. Cell Biochem Biophys 58:137–140
Aleisa AM, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA (2011) Post-learning REM sleep deprivation impairs long-term memory: reversal by acute nicotine treatment. Neurosci Lett 499:28–31
Esumi LA, Palma BD, Gomes VL et al (2011) Inflammatory markers are associated with inhibitory avoidance memory deficit induced by sleep deprivation in rats. Behav Brain Res 221:7–12
Colavito V, Fabene PF, Grassi-Zucconi G et al (2013) Experimental sleep deprivation as a tool to test memory deficits in rodents. Front Syst Neurosci 7:106
Naidoo N (2009) Cellular stress/the unfolded protein response: relevance to sleep and sleep disorders. Sleep Med Rev 13:195–204
Rothman SM, Herdener N, Frankola KA et al (2013) Chronic mild sleep restriction accentuates contextual memory impairments, and accumulations of cortical Abeta and pTau in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1529:200–208
Ramakrishnan N, Marosi K, Nyakas CJ, et al. (2014) Altered sigma-1 receptor expression in two animal models of cognitive impairment. Mol Imaging Biol (in press)
Kawamura K, Elsinga PH, Kobayashi T et al (2003) Synthesis and evaluation of (11)C- and (18)F-labeled 1-[2-(4-alkoxy-3-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazines as sigma receptor ligands for positron emission tomography studies. Nucl Med Biol 30:273–284
Schweinhardt P, Fransson P, Olson L et al (2003) A template for spatial normalisation of MR images of the rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 129:105–113
Julien-Dolbec C, Tropres I, Montigon O et al (2002) Regional response of cerebral blood volume to graded hypoxic hypoxia in rat brain. Br J Anaesth 89:287–293
Cunningham VJ, Rabiner EA, Slifstein M et al (2010) Measuring drug occupancy in the absence of a reference region: the Lassen plot re-visited. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:46–50
Lassen NA, Bartenstein PA, Lammertsma AA et al (1995) Benzodiazepine receptor quantification in vivo in humans using [11C]flumazenil and PET: application of the steady-state principle. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:152–165
Spira AP, Gamaldo AA, An Y et al (2013) Self-reported sleep and beta-amyloid deposition in community-dwelling older adults. JAMA Neurol 70:1537–1543
Matsuno K, Mita S (1998) SA4503: a novel sigma-1 receptor agonist. Cns Drug Rev 4:1
Ramakrishnan N, Reddy VP, Proost JH et al (2012) Population pharmacokinetics of cutamesine in rats using NONMEM, 11C-SA4503, and microPET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:S301–S302
Lever JR, Miller DK, Fergason-Cantrell EA et al (2014) Relationship between cerebral sigma-1 receptor occupancy and attenuation of cocaine’s motor stimulatory effects in mice by PD144418. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 351:153–163
Matsuno K, Nakazawa M, Okamoto K et al (1996) Binding properties of SA4503, a novel and selective sigma 1 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 306:271–279
Lever JR, Gustafson JL, Xu R et al (2006) Sigma1 and sigma2 receptor binding affinity and selectivity of SA4503 and fluoroethyl SA4503. Synapse 59:350–358
Acknowledgments
During the period of this research, NKR was supported by university funding (Ubbo Emmius Bursary Position).
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest concerning this paper can be reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishnan, N.K., Schepers, M., Luurtsema, G. et al. Cutamesine Overcomes REM Sleep Deprivation-Induced Memory Loss: Relationship to Sigma-1 Receptor Occupancy. Mol Imaging Biol 17, 364–372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0808-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0808-2