Abstract
Introduction
Starfish are recognized as interesting source of natural steroid products with pharmaceutical potential. Polar steroid metabolites of starfish have unique chemical structures and exhibit various biological activities but their biological functions are controversial.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to investigate the response of polar steroid metabolome of the starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera on various environmental factors and stresses.
Methods
Here we first have applied MS-based environmental metabolomics to elucidate the metabolic changes of polar steroid metabolome of starfish. Using HPLC–ESI–Q/TOF–MS approach followed by statistical analysis including principal component analysis and partial least squares discriminant analysis for data classification and potential biomarkers selection, we investigated the changes induced by feeding, injury, variations in water temperature and salinity, and oxygen deficiency.
Results
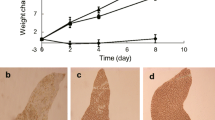
According to multivariate and univariate statistical analysis the responses to feeding, injury and water heating were better expressed than the others and have some similarity in their action on the steroid metabolome of the starfish P. pectinifera. Most constituents of asterosaponin pool were reduced and most constituents of polyhydroxysteroid and related glycoside pool were increased at that.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that various metabolic changes in polar steroid constituents of P. pectinifera are induced by feeding and stresses. We believe that these responses are connected with biological multifunctionality of these compounds.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
Bundy, J. G., Davey, M. P., & Viant, M. R. (2009). Environmental metabolomics: A critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics, 5(1), 3–21.
Cevallos-Cevallos, J. M., Reyes-De-Corcuera, J. I., Etxeberria, E., Danyluk, M. D., & Rodrick, G. E. (2009). Metabolomic analysis in food science: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20(11–12), 557–566.
Demeyer, M., De Winter, J., Caulier, G., Eeckhaut, I., Flammang, P., & Gerbaux, P. (2014). Molecular diversity and body distribution of saponins in the sea star Asterias rubens by mass spectrometry. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 168, 1–11.
Demeyer, M., Wisztorski, M., Decroo, C., De Winter, J., Caulier, G., Hennebert, E., et al. (2015). Inter- and intra-organ spatial distributions of sea star saponins by MALDI imaging. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 407(29), 8813–8824.
Dong, G., Xu, T., Yang, B., et al. (2011). Chemical constituents and bioactivities of starfish. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 8(5), 740–791.
Durbin, B. P., Hardin, J. S., Hawkins, D. M., & Rocke, D. M. (2002). A variance-stabilizing transformation for gene-expression microarray data. Bioinformatics, 18, S105–S110.
Fang, Z. Z., & Gonzalez, F. J. (2014). LC–MS-based metabolomics: An update. Archives of Toxicology, 88(8), 1491–1502.
Franco, C. F., Santos, R., & Coelho, A. V. (2014). Proteolytic events are relevant cellular responses during nervous system regeneration of the starfish Marthasterias glacialis. Journal of Proteomics, 99, 1–25.
Goulitquer, S., Potin, P., & Tonon, T. (2012). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to elucidate functions in marine organisms and ecosystems. Marine Drugs, 10(4), 849–880.
Harvey, C., Garneau, F.-X., & Himmelman, J. H. (1987). Chemodetection of the predatory seastar Leptasterias polaris by the whelk Buccinum undatum. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 40(1–2), 79–86.
Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., Kalinovsky, A. I., Dmitrenok, P. S., Prokof’eva, N. G., & Stonik, V. A. (2001). New steroid glycosides from the starfish Asterias rathbuni. Journal of Natural Products, 64(7), 945–947.
Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., Kalinovsky, A. I., et al. (2000). Hemolytic polar steroidal constituents of the starfish Aphelasterias japonica. Journal of Natural Products, 63(8), 1178–1181.
Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., Malyarenko, T. V., Kalinovsky, A. I., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Stonik, V. A. (2013). Biosynthesis of polar steroids from the Far Eastern starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera. Cholesterol and cholesterol sulfate are converted into polyhydroxylated sterols and monoglycoside asterosaponin P1 in feeding experiments. Steroids, 78(12–13), 1183–1191.
Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., & Stonik, V. A. (2011). Steroid glycosides from marine organisms. Steroids, 76(5), 425–454.
Kamleh, M. A., Dow, J. A. T., & Watson, D. G. (2009). Applications of mass spectrometry in metabolomic studies of animal model and invertebrate systems. Briefings in Functional Genomics & Proteomics, 8(1), 28–48.
Kessner, D., Chambers, M., Burke, R., Agus, D., & Mallick, P. (2008). ProteoWizard: Open source software for rapid proteomics tools development. Bioinformatics, 24(21), 2534–2536.
Kicha, A. A., Ivanchina, N. V., Gorshkova, I. A., Ponomarenko, L. P., Likhatskaya, G. N., & Stonik, V. A. (2001a). The distribution of free sterols, polyhydroxysteroids and steroid glycosides in various body components of the starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 128(1), 43–52.
Kicha, A. A., Ivanchina, N. V., Kalinovsky, A. I., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Stonik, V. A. (2001b). Sulfated steroid compounds from the starfish Aphelasterias japonica of the Kuril population. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 50(4), 724–727.
Lankadurai, B. P., Nagato, E. G., & Simpson, M. J. (2013). Environmental metabolomics: An emerging approach to study organism responses to environmental stressors. Environmental Reviews, 21(3), 180–205.
Mackie, A. M., Lasker, R., & Grant, P. T. (1968). Avoidance reactions of a mollusc Buccinum undatum to saponin-like surface-active substances in extracts of the starfish Asterias rubens and Marthasterias glacialis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 26, 415–428.
Mackie, A. M., Singh, H. T., & Owen, J. M. (1977). Studies on the distribution, biosynthesis and function of steroidal saponins in echinoderms. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Comparative Biochemistry, 56(1), 9–14.
Micallef, L., & Rodgers, P. (2014). eulerAPE: Drawing area-proportional 3-Venn diagrams using ellipses. PLoS ONE, 9(7), e101717.
Miller, M. G. (2007). Environmental metabolomics: A SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats). Journal of Proteome Research, 6(2), 540–545.
Minale, L., Riccio, R., & Zollo, F. (1993). Steroidal oligoglycosides and polyhydroxysteroids from Echinoderms. Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe, 62, 75–308.
Naruse, M., Suetomo, H., Matsubara, T., Sato, T., Yanagawa, H., Hoshi, M., & Matsumoto, M. (2010). Acrosome reaction-related steroidal saponin, Co-ARIS, from the starfish induces structural changes in microdomains. Development Biology, 347(1), 147–153.
Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2008). Systems biology—metabonomics. Nature, 455(7216), 1054–1056.
Palyanova, N. V., Pankova, T. M., Starostina, M. V., Kicha, A. A., Ivanchina, N. V., & Stonik, V. A. (2013). Neuritogenic and neuroprotective effects of polar steroids from the Far East starfishes Patiria pectinifera and Distolasterias nipon. Marine Drugs, 11(5), 1440–1455.
Patti, G. J., Yanes, O., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). Metabolomics: The apogee of the omics trilogy. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 13(4), 263–269.
Pluskal, T., Castillo, S., Villar-Briones, A., & Oresic, M. (2010). MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 395.
Popov, R. S., Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., Malyarenko, T. V., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Stonik, V. A. (2014). Metabolite profiling of polar steroid constituents in the Far Eastern starfish Aphelasterias japonica using LC–ESI MS/MS. Metabolomics, 10(6), 1152–1168.
Popov, R. S., Ivanchina, N. V., Kicha, A. A., Malyarenko, T. V., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Stonik, V. A. (2016). LC-ESI MS/MS profiling of polar steroid metabolites of the Far Eastern starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera. Metabolomics, 12(2), 21.
Quinones, M. P., & Kaddurah-Daouk, R. (2009). Metabolomics tools for identifying biomarkers for neuropsychiatric diseases. Neurobiology of Diseases, 35(2), 165–176.
Sandvoss, M., Weltring, A., Preiss, A., Levsen, K., & Wuensch, G. (2001). Combination of matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and direct on-line liquid chromatography–nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy–tandem mass spectrometry as a new efficient approach for the rapid screening of natural products: application to the total asterosaponin fraction of the starfish Asterias rubens. Journal of Chromatography A, 917(1–2), 75–86.
Shao, Y., Li, C., Chen, X., Zhang, P., Li, Y., Li, T., & Jiang, J. (2015). Metabolomic responses of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus to thermal stresses. Aquaculture, 435, 390–397.
Spratlin, J. L., Serkova, N. J., & Eckhardt, S. G. (2009). Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(2), 431–440.
Stonik, V. A. (2001). Marine polar steroids. Russ. Chemical Reviews, 70(8), 673–715.
Stonik, V. A., Ivanchina, N. V., & Kicha, A. A. (2008). New polar steroids from starfish. Natural Products Communications, 3(10), 1587–1610.
Storey, J. D., & Tibshirani, R. (2003). Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(16), 9440–9445.
Theodoridis, G. A., Gika, H. G., Want, E. J., & Wilson, I. D. (2012). Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 711, 7–16.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Veselkov, K. A., Vingara, L. K., Masson, P., et al. (2011). Optimized preprocessing of ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry urinary metabolic profiles for improved information recovery. Analytical Chemistry, 83(15), 5864–5872.
Viant, M. R. (2007). Metabolomics of aquatic organisms: the new ‘omics’ on the block. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 332, 301–306.
Viant, M. R. (2008). Recent developments in environmental metabolomics. Molecular BioSystems, 4(10), 980–986.
Viant, M. R., & Sommer, U. (2013). Mass spectrometry based environmental metabolomics: A primer and review. Metabolomics, 9, 144–158.
Voogt, P. A., & Huiskamp, R. (1979). Sex-dependence and seasonal variation of saponins in the gonads of the starfish Asterias rubens: Their relation to reproduction. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 62, 1049–1055.
Xia, J. G., Mandal, R., Sinelnikov, I. V., Broadhurst, D., & Wishart, D. S. (2012). MetaboAnalyst 2.0—a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(W1), W127–W133.
Xia, J. G., Sinelnikov, I. V., Han, B., & Wishart, D. S. (2015). MetaboAnalyst 3.0—making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(W1), W251–W257.
Zhang, A. H., Sun, H., Wang, P., Han, Y., & Wang, X. J. (2012). Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst, 137(2), 293–300.
Zhou, B., Xiao, J. F., Tuli, L., & Ressom, H. W. (2012). LC-MS-based metabolomics. Molecular BioSystems, 8(2), 470–481.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Grant No. 14-04-00341-a from the RFBR. We sincerely thanks to Vasily A. Avilov for help in data preprocessing and Dr. Valery G. Voinov for his assistance in editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popov, R.S., Ivanchina, N.V., Kicha, A.A. et al. LC–MS-based metabolome analysis on steroid metabolites from the starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera in conditions of active feeding and stresses. Metabolomics 12, 106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1048-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1048-z