Abstract
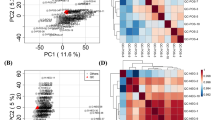
The diagnosis of respiratory chain deficiencies (RCDs) is complicated and the need for a diagnostic biomarker or biosignature has been widely expressed. In this study, the metabolic profile of a selected group of 29 RCD patients, with a predominantly muscle disease phenotype, and 22 controls were investigated using targeted and untargeted analyses of three sub-sections of the human metabolome, including urinary organic acids and amino acids [measured by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS)], as well as acylcarnitines (measured by electrospray ionization tandem MS). Although MS technologies are highly sensitive and selective, they are restrictive by being applied only to sub-sections of the metabolome; an untargeted nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy approach was therefore also included. After data reduction and pre-treatment, a biosignature comprising six organic acids (lactic, succinic, 2-hydroxyglutaric, 3-hydroxyisobutyric, 3-hydroxyisovaleric and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acids), six amino acids (alanine, glycine, glutamic acid, serine, tyrosine and α-aminoadipic acid) and creatine, was constructed from uni- and multivariate statistical analyses and verified by cross-validation. The results presented here provide the first proof-of-concept that the metabolomics approach is capable of defining a biosignature for RCDs. We postulate that the composite of organic acids ≈ amino acids > creatine > betaine > carnitines represents the basic biosignature for RCDs. Validated through a prospective study, this could offer an improved ability to assign individual patients to a group with defined RCD characteristics and improve case selection for biopsy procedures, especially in infants and children.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, A. J., Colburn, W. A., DeGruttola, V. G., DeMets, D. L., Downing, G. J., Hoth, D. F., et al. (2001). Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 69(3), 89–95.
Barker, M., & Rayens, W. (2003). Partial least squares for discrimination. Journal of Chemometrics, 17(3), 166–173.
Bijlsma, S., Bobeldijk, I., Verheij, E. R., Ramaker, R., Kochhar, S., Macdonald, I. A., et al. (2006). Large-scale human metabolomics studies: A strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Analytical Chemistry, 78(2), 567–574.
Brereton, R. G. (2003). Chemometrics—data analysis for the laboratory and chemical plant. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Calvo, S. E., & Mootha, V. K. (2010). The mitochondrial proteome and human disease. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 11, 25–44.
Chong, I. G., & Jun, C. H. (2005). Performance of some variable selection methods when multicollinearity is present. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 78(1–2), 103–112.
Chung, Y., Rider, L., Bell, J., Summers, R. M., Zemel, L. S., Rennebohm, R. M., et al. (2005). Muscle metabolites, detected in urine by proton spectroscopy, correlate with disease damage in juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis Care & Research, 53(4), 565–570.
Ellis, S., & Steyn, H. (2003). Practical significance (effect sizes) versus or in combination with statistical significance (p-values). Management Dynamics, 12(4), 51–53.
Elstner, M., & Turnbull, D. M. (2011). Transcriptome analysis in mitochondrial disease. Brain Research Bulletin,. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.07.018.
Engelke, U. F. H., Liebrand-van Sambeek, M. L. F., de Jong, J. G., Leroy, J. G., Morava, E., Smeitink, J. A., et al. (2004). N-acetylated metabolites in urine: Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study on patients with inborn errors of metabolism. Clinical Chemistry, 50(1), 58–66.
Engelke, U. F. H., Moolenaar, S. H., Hoenderop, S. M. G. C., van der Morava, E., Graaf, M., Heerschap, A., et al. (2007). Handbook of 1 H-NMR spectroscopy in inborn errors of metabolism: body fluid NMR spectrum and in vivo MR spectroscopy. Amsterdam: SPS Publications.
Ferrara, C. T., Wang, P., Neto, E. C., Stevens, R. D., Bain, J. R., Wenner, B. R., et al. (2008). Genetic networks of liver metabolism revealed by integration of metabolic and transcriptional profiling. PLoS Genetics, 4(3), e1000034.
Fluss, R., Faraggi, D., & Reiser, B. (2005). Estimation of the youden index and its associated cutoff point. Biometrical Journal, 47(4), 458–472.
Frankenhaeuser, M., Lundberg, U., Von Wright, M. R., Von Wright, J., & Sedvall, G. (1986). Urinary monoamine metabolites as indices of mental stress in healthy males and females. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behaviour, 24(6), 1521–1525.
Giak-Sim, K., Carpenter, K., Hammond, J., Christodoulou, J., & Wilcken, B. (2002). Quantitative fibroblast acylcarnitine profiles in mitochondrial fatty acid [beta]-oxidation defects: Phenotype/metabolite correlations. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 76(4), 327–334.
Haas, R. H., Parikh, S., Falk, M. J., Saneto, R. P., Wolf, N. I., Darin, N., et al. (2008). The in-depth evaluation of suspected mitochondrial disease. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 94(1), 16–37.
Hu, F. B. (2011). Metabolic profiling of diabetes: From black-box epidemiology to systems epidemiology. Clinical Chemistry, 57(9), 1224–1226.
Jacobsen, M., Mattow, J., Repsilber, D., & Kaufmann, S. H. E. (2008). Novel strategies to identify biomarkers in tuberculosis. Biological Chemistry, 389(5), 487–495.
Johnson, R. A., & Wichern, D. W. (1998). Applied multivariate statistical analysis (4th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Kell, D. B. (2004). Metabolomics and systems biology: making sense of the soup. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 7(3), 296–307.
Koene, S., & Smeitink, J. (2011). Mitochondrial medicine. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 34(2), 247–248.
Levine, R. J., & Conn, H. O. (1967). Tyrosine metabolism in patients with liver disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 46(12), 2012–2020.
Mancuso, M., Orsucci, D., Coppedè, F., Nesti, C., Choub, A., & Siciliano, G. (2009). Diagnostic approach to mitochondrial disorders: The need for a reliable biomarker. Current Molecular Medicine, 9(9), 1095–1107.
Martín-Hernández, E., García-Silva, M. T., Vara, J., Campos, Y., Cabello, A., Muley, R., et al. (2005). Renal pathology in children with mitochondrial diseases. Pediatric Nephrology, 20(9), 1299–1305.
Mels, C. M. C., van Rensburg, P. J., van der Westhuizen, F. H., Pretorius, P. J., & Erasmus, E. (2011). Increased excretion of C4-carnitine species after a therapeutic acetylsalicylic acid dose: Evidence for an inhibitory effect on short-chain fatty acid metabolism. ISRN Pharmacology,. doi:10.5402/2011/851870.
Morath, M., Okun, J., Müller, I., Sauer, S. W., Hörster, F., Hoffmann, G. F., et al. (2008). Neurodegeneration and chronic renal failure in methylmalonic aciduria—A pathophysiological approach. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 31(1), 35–43.
Odièvre, M., Lombes, A., Dessemme, P., Santer, R., Brivet, M., Chevallier, B., et al. (2002). A secondary respiratory chain defect in a patient with Fanconi–Bickel syndrome. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 25(5), 379–384.
Rauste-von Wright, M., & Frankenhaeuser, M. (1989). Females’ emotionality as reflected in the excretion of the dopamine metabolite HVA during mental stress. Psychological Reports, 64(3), 856–858.
Reinecke, F., Smeitink, J. A. M., & van der Westhuizen, F. H. (2009). OXPHOS gene expression and control in mitochondrial disorders. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Molecular Basis of Disease, 1792(12), 1113–1121.
Reinecke, C. J., Koekemoer, G., van der Westhuizen, F. H., Louw, R., Lindeque, J. Z., Mienie, L. J., et al. (2012). Metabolomics of urinary organic acids in respiratory chain deficiencies in children. Metabolomics, 8(2), 264–283.
Shaham, O., Slate, N. G., Goldberger, O., Xu, Q., Ramanathan, A., Souza, A. L., et al. (2010). A plasma signature of human mitochondrial disease revealed through metabolic profiling of spent media from cultured muscle cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 107(4), 1571–1575.
Smuts, I., Louw, R., Du Toit, H., Klopper, B., Mienie, L. J., & van der Westhuizen, F. H. (2010). An overview of a cohort of South African patients with mitochondrial disorders. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease,. doi:10.1007/s10545-009-9031-8.
Suomalainen, A. (2011). Biomarkers for mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 34(2), 1–6.
Suomalainen, A., Elo, J. M., Pietiläinen, K. H., Hakonen, A. H., Sevastianova, K., Korpela, M., et al. (2011). FGF-21 as a biomarker for muscle-manifesting mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies: A diagnostic study. The Lancet Neurology, 10(9), 806–818.
Sztajnkrycer, M. D. (2002). Valproic acid toxicity: Overview and management. Clinical Toxicology, 40(6), 789–801.
Thorburn, D. (2004). Mitochondrial disorders: Prevalence, myths and advances. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 27(3), 349–362.
Turnbull, D. (2011). A new biomarker for mitochondrial disease. The Lancet Neurology, 10(9), 777–778.
Wikoff, W. R., Pendyala, G., Siuzdak, G., & Fox, H. S. (2008). Journal of Clinical Investigation, 118(7), 2661–2669.
Wolf, N. I., & Smeitink, J. A. M. (2002). Mitochondrial disorders. Neurology, 59(9), 1402–1405.
Wong, L. J. C., Scaglia, F., Graham, B. H., & Craigen, W. J. (2010). Current molecular diagnostic algorithm for mitochondrial disorders. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 100(2), 111–117.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr M. Duran from the Laboratory for Genetic and Metabolic Diseases, Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, for his comments on the original manuscript. This study formed part of BioPAD Project BPP007, funded through the South African Department of Science and Technology. Additional financial support from North-West University is likewise acknowledged. S.W. Mason is a recipient of a Vrije Universiteit (VU) Amsterdam-National Research Foundation (NRF)-Desmond Tutu PhD Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smuts, I., van der Westhuizen, F.H., Louw, R. et al. Disclosure of a putative biosignature for respiratory chain disorders through a metabolomics approach. Metabolomics 9, 379–391 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0455-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0455-z