Abstract
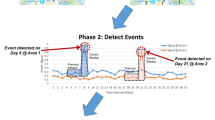
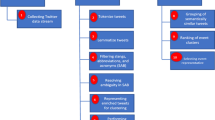
Social media sites contain a considerable amount of data for natural calamities events, such as earthquakes, snowstorms, mud-rock flows. With the increasing amount of social media data, an important task is to discover and retrieve sub-events over time. Especially in emergency situations, rescue and relief activities can be enhanced by identifying and retrieving sub-events of a natural hazard event. However, the existing event detection techniques in news-related reports cannot effectively work for social media data due to the unstructured of social network data. In this paper, we propose a new natural hazard sub-events discovery model SED (Sub-Events Discovery), which adopts multifarious features to detect sub-events. Moreover, in order to retrieve the sub-events over a specific event, we introduce a novel SER (Sub-Event Retrieval) algorithm from time-stamped social media data. Our novel approach SER makes use of automatically obtained messages from external search engines in the entire process. For purpose of determining the periodical convergence time for natural hazard event, our method provides online sub-events retrieval and sub-events discovery to meet the further needs. Next the improved estimation standards with timestamp are utilized in our experiments to verify the effectiveness and efficiency of SED model and SER algorithm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, W., Chundi, P.: Extracting hot spots of topics from time-stamped documents. Data Knowl. Eng. 70(7), 642–660 (2011)
Dhekar, A., Durga, T.: Sub-event detection during natural hazards using features of social media data. In: WWW (Companion Volume). 783–788 Springer (2013)
Emilio, F., Pasquale, D.M., Giacomo, F., Robert, B.: Web data extraction, applications and techniques: a survey. Knowl.-Based Syst. 70, 301–323 (2014)
Feng, H., Qian, X.M.: Mining user-contributed photos for personalized product recommendation. Neurocomputing. 129, 409–420 (2014)
Ganguly, D., Leveling, J., Jones, G.J.F.: An LDA-smoothed relevance model for document expansion: a case study for spoken document retrieval. In: SIGIR. 1057–1060 ACM (2013)
George, T.: Optimizing word segmentation tasks using ant colony metaheuristics. Lit. Linguist. Comput. 29(2), 234–254 (2014)
Gossen, T., Nürnberger, A.: Specifics of information retrieval for young users: a survey. Inf. Process. Manag. 49(4), 739–756 (2013)
Han, X.P., Zhao, J.: Named entity disambiguation by leveraging Wikipedia semantic knowledge. In: CIKM. 215–224 ACM (2009)
Han, Y.H., Chen, J.J., Cao, X.C., Xu, C.F., Shen, H.Q.: Feature selection with spatial path coding for multimedia analysis. Inf. Sci. 281, 523–535 (2014)
He, Y., Tan, J.X.: Study on SINA micro-blog personalized recommendation based on semantic network. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(10), 4797–4804 (2015)
Ittoo, A., Bouma, G.: Minimally-supervised extraction of domain-specific part-whole relations using wikipedia as knowledge-base. Data Knowl. Eng. 85, 57–79 (2013)
Kaleel, S.B., Abhari, A.: Cluster-discovery of twitter messages for event detection and trending. J. Comput. Sci. 6, 47–57 (2015)
Karimzadehgan, M., Zhai, C.X.: Improving retrieval accuracy of difficult queries through generalizing negative document language models. In: CIKM. 27–36 ACM (2011)
King, A., Huffaker, B., Dainotti, A., Claffy, K.: A coordinated view of the temporal evolution of large-scale internet events. Computing 96(1), 53–65 (2014)
Kotov, A., Agichtein, E.: The importance of being socially-savvy: quantifying the influence of social networks on microblog retrieval. In: CIKM. 1905–1908 ACM (2013)
Lin, C.X., Zhao, B., Mei, Q., and Han. J.: Pet: a statistical model for popular events tracking in social communities. In: KDD. 929–938 ACM (2010)
Metzler, D., Cai, C.X., Hovy, E.H.: Structured event retrieval over Microblog archives. In: HLT-NAACL. 646–655 NAACL (2012)
Pohl, D., Bouchachia, A., Hellwagner, H.: Automatic sub-event detection in emergency management using social media. In: WWW (Companion Volume). 683–686 Springer (2012)
Qian, X.M., Hua, X.S., Tang, Y.Y., Mei, T.: Social image tagging with diverse semantics. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(12), 2493–2508 (2014)
Qian, X.M., Feng, H., Zhao, G.S., Mei, T.: Personalized recommendation combining user interest and social circle. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(7), 1763–1777 (2014)
Sakaki, T., Okazaki, M., Matsuo, Y.: Earthquake shakes Twitter users: real-time event detection by social sensors. In: WWW. 851–860 Springer (2010)
Salton, G., Wong, A., Yang, C.S.: A vector space model for automatic indexing. Commun. ACM 18(11), 613–620 (1975)
Schoefegger, K., Tammet, T., Granitzer, M.: A survey on socio-semantic information retrieval. Comput. Sci. Rev. 8, 25–46 (2013)
Shan, D.D., Zhao W.X., Chen, R.S., Shu, B.H., Wang, Z.Q., Yao J.J., Yan H.F., Li, X.M.: EventSearch: a system for event discovery and retrieval on multi-type historical data. In: KDD. 1564–1567 ACM (2012)
Suzanne, L., Iveel, J., Clawson, K.M., Nieto, M., Li, H., Direkoglu, C., O’Connor, N.E., Smeaton, A.F., Scotney, B.W., Wang, H., Liu, J.: An information retrieval approach to identifying infrequent events in surveillance video. In: ICMR. 223–230 ACM (2013)
Tang, J., Shao, L., Li, X.L.: Efficient dictionary learning for visual categorization. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 124, 91–98 (2014)
Tong, Y.X., Cao, C.C., Chen L.: TCS: efficient topic discovery over crowd-oriented service data. In: KDD. 861–870 ACM (2014)
Vavliakis, K.N., Symeonidis, A.L., Mitkas, P.A.: Event identification in web social media through named entity recognition and topic modeling. Data Knowl. Eng. 88, 1–24 (2013)
Verma, S., Vieweg, S., Corvey, W.J., Palen, L., Martin, J.H., Palmer, M., Schram, A., Anderson, K.M.: Natural language processing to the rescue? Extracting situational awareness Tweets during mass emergency. In: ICWSM. 49–57 AAAI (2011)
Vieweg, S., Hughes, A.L., Starbird, K., Palen, L.: Microblogging during two natural hazards events: what twitter may contribute to situational awareness. In: CHI. 1079--1088 ACM (2010)
Wu, X.N., Zeng, J., Yan, J.F., Liu, X.S.: Finding better topics: features, priors and constraints. In: PAKDD. (2), 296–310 Springer (2014)
Yang, Y., Ma, Z.G., Hauptmann, A.G., Sebe, N.: Feature selection for multimedia analysis by sharing information among multiple tasks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 15(3), 661–669 (2013)
Yang, Y., Nie, F.P., Xu, D., Luo, J.B., Zhuang, Y.T., Pan, Y.H.: A multimedia retrieval framework based on Semi-supervised ranking and relevance feedback. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(4), 723–742 (2012)
Yin, J., Lampert, A., Cameron, M., Robinson, B., Power, R.: Using social media to enhance emergency situation awareness. IEEE Intell. Syst. 27(6), 52–59 (2012)
Zhang, Z.F., Li, Q.D.: QuestionHolic: hot topic discovery and trend analysis in community question answering systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(6), 6848–6855 (2011)
Zhang, C., Baldwin, T., Ho, H., Kimelfeld, B., Li, Y.: Adaptive parser-centric text normalization. In: ACL. (1), 1159–1168 ACL (2013)
Zhang, H., Yuan, J.S., Gao, X.Y., Chen, Z.Y.: Boosting cross-media retrieval via visual-auditory feature analysis and relevance feedback. In: ACM Multimedia. 953–956 ACM (2014)
Zhong, Z.M., Li, C.H., Liu, Z.T., Dai, H.W.: Web news oriented event multi-elements retrieval. J. Softw. (Chin). 24(10), 2366–2378 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments. This research work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China “Research on High-order Collaboration, Real-time and Temporal Characteristics in Automatic Test of Safety-critical Systems” (NO.61300007), Self-conducted Exploratory Research Program from State Key Laboratory for Software Development Environment in China (NO.SKLSDE-2013ZX-11), Social Service Project in National Earthquake Response Support Service “International Rescue and Disposition System against Strong Earthquakes” (NO.SJZX-B11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Ma, S. & Liu, Y. Sub-event discovery and retrieval during natural hazards on social media data. World Wide Web 19, 277–297 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-015-0359-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-015-0359-8