Abstract
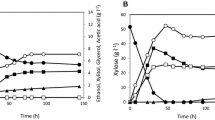
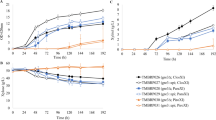
In order to better understand the differences in xylose metabolism between natural xylose-utilizing Pichia stipitis and metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we constructed a series of recombinant S. cerevisiae strains with different xylose reductase/xylitol dehydrogenase/xylulokinase activity ratios by integrating xylitol dehydrogenase gene (XYL2) into the chromosome with variable copies and heterogeneously expressing xylose reductase gene (XYL1) and endogenous xylulokinase gene (XKS1). The strain with the highest specific xylose uptake rate and ethanol productivity on pure xylose fermentation was selected to compare to P. stipitis under oxygen-limited condition. Physiological and enzymatic comparison showed that they have different patterns of xylose metabolism and NADPH generation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- XR:
-
Xylose reductase
- XDH:
-
Xylitol dehydrogenase
- XK:
-
Xylulokinase
- G6PDH:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IDP:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bruinenberg PM (1986) The NADP(H) redox couple in yeast metabolism. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 52:411–429
Bruinenberg PM, van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1983) An enzymic analysis of NADPH production and consumption in Candida utilis. J Gen Microbiol 129:965–971
Caspeta L, Shoaie S, Agren R, Nookaew I, Nielsen J (2012) Genome-scale metabolic reconstructions of Pichia stipitis and Pichia pastoris and in silico evaluation of their potentials. BMC Syst Biol 6:24
Ekino K, Hayashi H, Moriyama M, Matsuda M, Goto M, Yoshino S, Furukawa K (2002) Engineering of polyploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae for secretion of large amounts of fungal glucoamylase. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5693–5697
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hagerdal B (2000) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Eliasson A, Hofmeyr JS, Pedler S, Hahn-Hagerbal B (2001) The xylose reductase/xylitol dehydrogenase/xylulokinase ratio affects product formation in recombinant xylose-utilising Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:288–297
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (1991) Applications of high efficiency lithium acetate transformation of intact yeast cells using single-stranded nucleic acids as carrier. Yeast 7:253–263
Grabowska D, Chelstowska A (2003) The ALD6 gene product is indispensable for providing NADPH in yeast cells lacking glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. J Biol Chem 278:13984–13988
Guo C, He P, Lu D, Shen A, Jiang N (2006) Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene coding d-xylulokinase (CmXYL3) from Candida maltosa. J Appl Microbiol 101:139–150
Jeffries TW (1983) Utilization of xylose by bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 27:1–32
Jeffries TW (2006) Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:320–326
Jeffries TW, Kurtzman CP (1994) Strain selection, taxonomy, and genetics of xylose-fermenting yeasts. Enzyme Microb Technol 16:922–932
Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aerts A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, Jin YS, Passoth V, Richardson PM (2007) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat Biotechnol 25:319–326
Jeppsson M, Johansson B, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2002) Reduced oxidative pentose phosphate pathway flux in recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains improves the ethanol yield from xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1604–1609
Jeppsson M, Johansson B, Jensen PR, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2003) The level of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity strongly influences xylose fermentation and inhibitor sensitivity in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Yeast 20:1263–1272
Jin YS, Alper H, Yang YT, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Improvement of xylose uptake and ethanol production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae through an inverse metabolic engineering approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8249–8256
Khattab SM, Watanabe S, Saimura M, Kodaki T (2011) A novel strictly NADPH-dependent Pichia stipitis xylose reductase constructed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:634–637
Krahulec S, Klimacek M, Nidetzky B (2012) Analysis and prediction of the physiological effects of altered coenzyme specificity in xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase during xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 158:192–202
Krizkova L, Jelokova J (1991) A rapid and simple method for DNA preparation from Candida utilis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 36:406–407
Lee WJ, Kim MD, Ryu YW, Bisson LF, Seo JH (2002) Kinetic studies on glucose and xylose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:186–191
Lighthelm ME, Prior BA, Preez JC, Brandt V (1988) An investigation of d-{1-13C} xylose metabolism in Pichia stipitis under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:293–296
Liu EAHY (2010) Construction of a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain by combined approaches of genetic engineering, chemical mutagenesis and evolutionary adaptation. Biochem Eng J 48:204–210
Matsushika A, Oguri E, Sawayama S (2010) Evolutionary adaptation of recombinant shochu yeast for improved xylose utilization. J Biosci Bioeng 110:102–105
Minard KI, Jennings GT, Loftus TM, Xuan D, McAlister-Henn L (1998) Sources of NADPH and expression of mammalian NADP+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 273:31486–31493
Parachin NS, Bengtsson O, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2010) The deletion of YLR042c improves ethanolic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 27:741–751
Pearce AK, Booth IR, Brown AJ (2001) Genetic manipulation of 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels affects the extent to which benzoic acid inhibits the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiology 147:403–410
Tantirungkij M, Nakashima N, Seki T, Yoshida H (1993) Construction of xylose-assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 75:83–88
Toivari MH, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttila M (2001) Conversion of xylose to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae: importance of xylulokinase (XKS1) and oxygen availability. Metab Eng 3:236–249
Traff-Bjerre KL, Jeppsson M, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2004) Endogenous NADPH-dependent aldose reductase activity influences product formation during xylose consumption in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 21:141–150
van den Berg MA, Steensma HY (1997) Expression cassettes for formaldehyde and fluoroacetate resistance, two dominant markers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 13:551–559
Wahlbom CF, van Zyl WH, Jonsson LJ, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Otero RR (2003) Generation of the improved recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB 3400 by random mutagenesis and physiological comparison with Pichia stipitis CBS 6054. FEMS Yeast Res 3:319–326
Walfridsson M, Anderlund M, Bao X, Hahn-Hagerdal B (1997) Expression of different levels of enzymes from the Pichia stipitis XYL1 and XYL2 genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its effects on product formation during xylose utilisation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:218–224
Watanabe S, Saleh AA, Pack SP, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein engineered NADP+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 130:316–319
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2004CB719702) and the National Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. We thank Dr. Blanca Valle for reading and revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Jiang, N. Physiological and enzymatic comparison between Pichia stipitis and recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae on xylose fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 541–547 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1208-x