Abstract
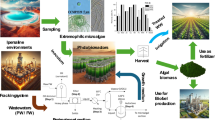
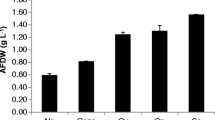
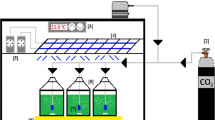
This paper discusses the possibility of including the culturing of microalgae within a conventional wastewater treatment sequence by growing them on the blackwater (BW) from biosolid dewatering to produce biomass to feed the anaerobic digester. Two photobioreactors were used: a 12 L plexiglas column for indoor, lab-scale tests and a 85 L plexiglas column for outdoor culturing. Microalgae (Chlorella sp. and Scenedesmus sp.) could easily grow on the tested blackwater. The average specific growth rate in indoor and outdoor batch tests was satisfactory, ranging between 0.14 and 0.16 day−1. During a continuous test performed under outdoor conditions from May to November, in which the off-gas from the combined heat and power unit was used as the CO2 source, an average biomass production of 50 mgTSS L−1 day−1 was obtained. However, statistical analyses confirmed that microalgal growth was affected by environmental conditions (temperature and season) and that it was negatively correlated with the occurrence of nitrification. Finally, the biochemical methane potential of the algal biomass was slightly higher than that from waste sludge (208 mLCH4 gVS−1 vs. 190 mLCH4 gVS−1).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acién, F. G., Fernández, J. M., Magán, J. J., & Molina, E. (2012). Production cost of a real microalgae production plant and strategies to reduce it. Biotechnology Advances, 30(6), 1344–1353. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.02.005.
Anthonisen, A. C., Srinath, E. G., Loehr, R. C., & Prakasam, T. B. S. (1976). Inhibition of nitrification and nitrous acid compounds. Water Environment Federation, 48(5), 835–852. doi:10.2307/25038971.
APHA. (2005). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (21st ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association.
Arbib, Z., Ruiz, J., Álvarez-Díaz, P., Garrido-Pérez, C., Perales, J. A. (2014) Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Research, 49, 465–474.
Arcila, J. S., & Buitrón, G. (2016). Microalgae-bacteria aggregates: effect of the hydraulic retention time on the municipal wastewater treatment, biomass settleability and methane potential. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 91, 2862–2870. doi:10.1002/jctb.4901.
Bahr, M., Díaz, I., Dominguez, A., González Sánchez, A., & Muñoz, R. (2014). Microalgal-biotechnology as a platform for an integral biogas upgrading and nutrient removal from anaerobic effluents. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(1), 573–581. doi:10.1021/es403596m.
Bchir, F. S., Gannoun, H., Herry, S. E., & Hamdi, M. (2011). Optimization of Spongiochloris sp. biomass production in the abattoir digestate. Bioresource Technology, 102(4), 3869–3876. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.036.
Bizzotto, E. C., Villa, S., & Vighi, M. (2009). POP bioaccumulation in macroinvertebrates of alpine freshwater systems. Environmental Pollution, 157(12), 3192–3198. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.06.001.
Blier, R., Lalibert, G., & De Notie, J. (1995). Tertiary treatment of cheese factory anaerobic effluent with Phormidium bohneri and Micractinum pusillum. Bioresource Technology, 52, 151–155.
Borowitzka, M. A., & Moheimani, N. R. (2013). In M. A. Borowitzka & N. R. Moheimani (Eds.), Algae for Biofuels and Energy. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5479-9.
Chen, R., Li, R., Deitz, L., Liu, Y., Stevenson, R. J., & Liao, W. (2012). Freshwater algal cultivation with animal waste for nutrient removal and biomass production. Biomass and Bioenergy, 39, 128–138. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.12.045.
Chinnasamy, S., Bhatnagar, A., Hunt, R. W., & Das, K. C. (2010). Microalgae cultivation in a wastewater dominated by carpet mill effluents for biofuel applications. Bioresource Technology, 101(9), 3097–3105. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.026.
Chisti, Y. (2007). Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnology Advances, 25(3), 294–306. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001.
Cho, S., Lee, N., Park, S., Yu, J., Luong, T. T., Oh, Y.-K., & Lee, T. (2013). Microalgae cultivation for bioenergy production using wastewaters from a municipal WWTP as nutritional sources. Bioresource Technology, 131, 515–520. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.176.
Craggs, R., Sutherland, D., & Campbell, H. (2012). Hectare-scale demonstration of high rate algal ponds for enhanced wastewater treatment and biofuel production. Journal of Applied Phycology, 24(3), 329–337. doi:10.1007/s10811-012-9810-8.
De-Bashan, L. E., & Bashan, Y. (2010). Immobilized microalgae for removing pollutants: review of practical aspects. Bioresource Technology, 101(6), 1611–1627. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.043.
El Hamouri, B. (2012) Rethinking natural, extensive systems for tertiary treatment purposes: The high-rate algae pond as an example. Desalination and Water Treatment, 4(1–3), 128–134.
Fernández, I., Acién, F. G., Berenguel, M., & Guzmán, J. L. (2014). First principles model of a tubular photobioreactor for microalgal production. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53, 11121–11136. doi:10.1021/ie501438r.
Ficara, E., Uslenghi, A., Basilico, D., & Mezzanotte, V. (2014). Growth of microalgal biomass on supernatant from biosolid dewatering. Water Science and Technology, 69, 896–902. doi:10.2166/wst.2013.805.
Fouilland, E., Vasseur, C., Leboulanger, C., Le Floc’h, E., Carré, C., Marty, B., et al. (2014). Coupling algal biomass production and anaerobic digestion: production assessment of some native temperate and tropical microalgae. Biomass and Bioenergy, 70, 564–569. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.08.027.
Franchino, M., Comino, E., Bona, F., & Riggio, V. a. (2013). Growth of three microalgae strains and nutrient removal from an agro-zootechnical digestate. Chemosphere, 92(6), 738–744. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.023.
Ge, S., & Champagne, P. (2016). Nutrient removal, microalgal biomass growth, harvesting and lipid yield in response to centrate wastewater loadings. Water Research, 88, 604–612. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.054.
Ge, S., Champagne, P., Plaxton, W. C., Leite, G. B., & Marazzi, F. (2016). Microalgal cultivation with waste streams and metabolic constraints to triacylglycerides accumulation for biofuel production. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining. doi:10.1002/bbb.
Gonzales, L. E. , Canizares R. O. , Baena S. (1997). Efficiency of ammonia and phosphprus removal from a colombian agroindustrial wastewater by the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus dimorphus. Bioresource technology, 60, 259–262.
González, C., Marciniak, J., Villaverde, S., García-Encina, P. A., & Muñoz, R. (2008). Microalgae-based processes for the biodegradation of pretreated piggery wastewaters. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80(5), 891–898. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1571-6.
González-Fernández, C., Molinuevo-Salces, B., & García-González, M. C. (2011). Nitrogen transformations under different conditions in open ponds by means of microalgae-bacteria consortium treating pig slurry. Bioresource Technology, 102(2), 960–966. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.052.
Green, F. B., Lundquist, J. T., & Oswald, W. J. (1995). Energetics of advanced integrated wastewater pond systems. Water Science and Technology, 31(12), 9–20.
Harrel, F., & Dupont, C. (2015). Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous. R package version 3.17-1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Hmisc
Li, Y., Horsman, M., Wang, B., Wu, N., & Lan, C. Q. (2008). Effects of nitrogen sources on cell growth and lipid accumulation of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 81(4), 629–936. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1681-1.
Lourie, E., Patil, V., & Gjengedal, E. (2010). Efficient purification of heavy-metal-contaminated water by microalgae-activated pine bark. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 210(1–4), 493–500. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0275-6.
Makulla, A. (2000). Fatty acid composition of Scenedesmus obliquus: correlation to dilution rates. Limnologica - Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 30, 162–168. doi:10.1016/S0075-9511(00)80011-0.
Marcilhac, C., Sialve, B., Pourcher, A. M., Ziebal, C., Bernet, N., & Béline, F. (2014). Digestate color and light intensity affect nutrient removal and competition phenomena in a microalgal-bacterial ecosystem. Water Research, 64, 278–287. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.012.
Marcilhac, C., Sialve, B., Pourcher, A.-M., Ziebal, C., Bernet, N., & Béline, F. (2015). Control of nitrogen behaviour by phosphate concentration during microalgal-bacterial cultivation using digestate. Bioresource Technology, 175, 224–230. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.022.
Monlau, F., Sambusiti, C., Ficara, E., Aboulkas, A., Barakat, A., & Carrère, H. (2015). New opportunities for agricultural digestate valorization: current situation and perspectives. Energy & Environmental Science, 2600–2621. doi:10.1039/C5EE01633A.
Mooij, P. R., Stouten, G. R., Tamis, J., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & Kleerebezem, R. (2013). Survival of the fattest. Energy & Environmental Science, 6(12), 3404. doi:10.1039/c3ee42912a.
Muñoz, R., & Guieysse, B. (2006). Algal-bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: a review. Water Research, 40(15), 2799–2815. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.011.
Mussgnug, J. H., Klassen, V., Schlüter, A., & Kruse, O. (2010). Microalgae as substrates for fermentative biogas production in a combined biorefinery concept. Journal of Biotechnology, 150(1), 51–56. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.07.030.
Nielsen, S. L., Enríquez, S., Duarte, C. M., & Sand–Jensen, K. (1996). Scaling maximum growth rates across photosynthetic organisms. Functional Ecology, 10, 167–175.
OECD (2006) Test n 311. Anaerobic biodegradability of organic compounds in digested sludge by measurement of gas production
Olguín, E. J., Hernández, B., Araus, A., Camacho, R., González, R., Ramírez, M. E., et al. (1994). Simultaneous high-biomass protein production and nutrient removal using Spirulina maxima in sea water supplemented with anaerobic effluents. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 10(5), 576–578. doi:10.1007/BF00367671.
Osundeko, O., & Pittman, J. K. (2014). Implications of sludge liquor addition for wastewater-based open pond cultivation of microalgae for biofuel generation and pollutant remediation. Bioresource Technology, 152, 355–363. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.035.
Park, J. B. K., & Craggs, R. J. (2011). Nutrient removal in wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds with carbon dioxide addition. Water Science & Technology, 63(8), 1758. doi:10.2166/wst.2011.114.
Pittman, J. K., Dean, A. P., & Osundeko, O. (2011). The potential of sustainable algal biofuel production using wastewater resources. Bioresource Technology, 102(1), 17–25. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.035.
Posadas, E., Bochon, S., Coca, M., García-González, M. C., García-Encina, P. a., & Muñoz, R. (2014). Microalgae-based agro-industrial wastewater treatment: a preliminary screening of biodegradability. Journal of Applied Phycology. doi:10.1007/s10811-014-0263-0.
Prandini, J. M., da Silva, M. L. B., Mezzari, M. P., Pirolli, M., Michelon, W., & Soares, H. M. (2016). Enhancement of nutrient removal from swine wastewater digestate coupled to biogas purification by microalgae Scenedesmus spp. Bioresource Technology, 202, 67–75. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.082.
Prommuak, C., Pavasan, S., Quitain, A. T., Goto, M., & Shotipruk, A. (2013). Simultaneous production of biodiesel and free lutein from Chlorella vulgaris. Chemical Engineering & Tecnology, 36(5), 733–739.
Quiroz, C. E., Peebles, C., & Bradley, T. H. (2015). Scalability of combining microalgae-based biofuels with wastewater facilities: a review. Algal, 9, 160–169. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2015.03.001.
R core Team. (2015). R: A language and environment for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org
Roberts, K. P., Heaven, S., & Banks, C. J. (2016). Comparative testing of energy yields from micro-algal biomass cultures processed via anaerobic digestion. Renewable Energy, 87, 744–753. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2015.11.009.
Sambusiti, C., Rollini, M., Ficara, E., Musatti, A., Manzoni, M., & Malpei, F. (2014). Enzymatic and metabolic activities of four anaerobic sludges and their impact on methane production from ensiled sorghum forage. Bioresource Technology, 155, 122–128. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.055.
Shrestha, R. P., Haerizadeh, F., & Hildebrand, M. (2013). Handbook of microalgal culture. Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Applied Phycology and Biotechnology. doi:10.1002/9781118567166.
Sialve, B., Bernet, N., & Bernard, O. (2009). Anaerobic digestion of microalgae as a necessary step to make microalgal biodiesel sustainable. Biotechnology Advances, 27(4), 409–416. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.03.001.
Skorupskaite, V., Makareviciene, V., & Levisauskas, D. (2015). Optimization of mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae Chlorella sp. for biofuel production using response surface methodology. Algal Research, 7, 45–50. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2014.12.001.
Slegers, P. M., Lösing, M. B., Wijffels, R. H., van Straten, G., & van Boxtel, A. J. B. (2013). Scenario evaluation of open pond microalgae production. Algal Research, 2(4), 358–368. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2013.05.001.
Uggetti, E., Sialve, B., Latrille, E., & Steyer, J. P. (2014). Anaerobic digestate as substrate for microalgae culture: the role of ammonium concentration on the microalgae productivity. Bioresource Technology, 152, 437–443. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.036.
Vasseur, C., Bougaran, G., Garnier, M., Hamelin, J., Leboulanger, C., Le Chevanton, M., et al. (2012). Carbon conversion efficiency and population dynamics of a marine algae-bacteria consortium growing on simplified synthetic digestate: first step in a bioprocess coupling algal production and anaerobic digestion. Bioresource Technology, 119, 79–87. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.128.
Wang, M., & Park, C. (2015). Investigation of anaerobic digestion of Chlorella sp. and Micractinium sp. grown in high-nitrogen wastewater and their co-digestion with waste activated sludge. Biomass and Bioenergy, 80(813), 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.04.028.
Wang, B., Li, Y., Wu, N., & Lan, C. Q. (2008). CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79(5), 707–718. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1518-y.
Ward, A. J., Lewis, D. M., & Green, F. B. (2014). Anaerobic digestion of algae biomass: a review. Algal Research, 5, 204–214. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2014.02.001.
Weiland, R., & Hatcher, N. (2012). Stripping sour water: the effect of heat stable salts. Petroleum Technology Quarterly, 17, 105–109.
Xin, L., Hu, H., Ke, G., & Sun, Y. (2010). Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresource Technology, 101(14), 5494–5500. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.016.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bresso-Seveso Sud WWTP (Amiacque CAP holding) for hosting the experimentation and SEAM staff for helpful collaboration. We gratefully thank the reviewers for their time and efforts to improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marazzi, F., Ficara, E., Fornaroli, R. et al. Factors Affecting the Growth of Microalgae on Blackwater from Biosolid Dewatering. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3248-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3248-1