Abstract
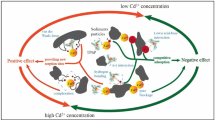
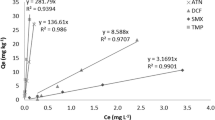
Metal cations could enhance the sorption of tetracyclines but sometimes the effects are negligible. It is still not clear how these metals produce different effects. In this study, the sorption of chlortetracycline (CTC), tetracycline (TC), and oxytetracycline (OTC) was performed in the presence of Cd (II) to reveal the unknown mechanisms with two river sediments. It is found that Cd (II) could enhance the sorption of TCs on sediment SS, while it is negligible on sediment SY. For different tetracyclines, the enhancement effect by Cd (II) was more significant for CTC, while it is inferior for OTC and TC. Sorption isotherms of Cd (II) under strong and weak background electrolyte and pH decrease of sorption solutions indicate specific sorption is major on SY and cation exchange is significant on SS. Consequently, specific sorption is unfavorable for the enhanced sorption of TCs in the presence of Cd (II) because it is not favorable for the sorption of Cd-TCs by complexation and cation exchange. By the theoretical calculations, it is found that the significant enhancement of CTC is due to the higher electron affinity of Cd-CTC complex than the others to the surface groups. In conclusion, TCs sorption will not be affected by Cd (II) on sediments or soils with strong specific sorption characters of Cd (II).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avisar, D., Primor, O., Gozlan, I., & Mamane, H. (2010). Sorption of sulfonamides and tetracyclines to montmorillonite clay. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 209(1–4), 439–450.
Bu, Q., Wang, B., Huang, J., Deng, S., & Yu, G. (2013). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 189–211. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.040.
Chang, B.-V., & Ren, Y.-L. (2015). Biodegradation of three tetracyclines in river sediment. Ecological Engineering, 75, 272–277. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.11.039.
Chen, Z., Sun, L., Luo, A., He, Y., Zhang, Y., & Li, Y. (2015). Photoluminescent materials for highly toxic metals sensing: from downconversion to upconversion. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 6–7, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.teac.2015.04.001.
Fernández-Calviño, D., Bermúdez-Couso, A., Arias-Estévez, M., Nóvoa-Muñoz, J. C., Fernández-Sanjurjo, M. J., Álvarez-Rodríguez, E., et al. (2015). Competitive adsorption/desorption of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline on two acid soils: stirred flow chamber experiments. Chemosphere, 134, 361–366. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.098.
Floroiu, R. M., Davis, A. P., & Torrents, A. (2001). Cadmium adsorption on aluminum oxide in the presence of polyacrylic acid. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(2), 348–353.
Ghandour, M. A., Azab, H. A., Hassan, A., & Ali, A. M. (1992). Potentiometric studies on the complexes of tetracycline (TC) and oxytetracyclin (OTC) with some metal ions. Chemical Monthly, 123(1–2), 51–58. doi:10.1007/BF01045296.
Gulbis, J., & Everett, G. W., Jr. (1976). Metal binding characteristics of tetracycline derivatives in DMSO solution. Tetrahedron, 32(8), 913–917. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(76)85048-X.
Huang, B., Li, Z., Huang, J., Chen, G., Nie, X., Ma, W., et al. (2015). Aging effect on the leaching behavior of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, and Cd) in red paddy soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(15), 11467–11477. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4386-x.
Jezowska-Bojczuk, M., Lambs, L., Kozlowski, H., & Berthon, G. (1993). Metal ion-tetracycline interactions in biological fluids. 10. Structural investigations on copper (II) complexes of tetracycline, oxytetracycline, chlortetracycline, 4-(dedimethylamino) tetracycline, and 6-desoxy-6-demethyltetracycline and discussion of their binding modes. Inorganic Chemistry, 32(4), 428–437. doi:10.1021/ic00056a015.
Jia, D.-A., Zhou, D.-M., Wang, Y.-J., Zhu, H.-W., & Chen, J.-L. (2008). Adsorption and cosorption of Cu (II) and tetracycline on two soils with different characteristics. Geoderma, 146(1–2), 224–230. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.05.023.
Li, T., Di, Z., Yang, X., & Sparks, D. L. (2011). Effects of dissolved organic matter from the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii on sorption of zinc and cadmium by different soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(3), 1616–1622.
Li, Y., Pan, T., Miao, D., Chen, Z., & Tao, Y. (2015). Sorption–desorption of typical tetracyclines on different soils: environment hazards analysis with partition coefficients and hysteresis index. Environmental Engineering Science, 32(10), 865–871. doi:10.1089/ees.2014.0325.
Meng, B., Liu, J., Li, Y., & Shi, X. (2015). Speciation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surfacial sediments of Lianshui River in Beijing. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(5), 964–972 (in Chinese).
Parolo, M. E., Avena, M. J., Pettinari, G. R., & Baschini, M. T. (2012). Influence of Ca2+ on tetracycline adsorption on montmorillonite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 368(1), 420–426. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.10.079.
Phillips, I. R. (1999). Copper, lead, cadmium, and zinc sorption by waterlogged and air-dry soil. Journal of Soil Contamination, 8(3), 343–364. doi:10.1080/10588339991339379.
Pils, J. R. V., & Laird, D. A. (2007). Sorption of tetracycline and chlortetracycline on K- and Ca-saturated soil clays, humic substances, and clay-humic complexes. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(6), 1928–1933.
Sassman, S. A., & Lee, L. S. (2005). Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(19), 7452–7459. doi:10.1021/es0480217.
Scalmani, G., & Frisch, M. J. (2010). Continuous surface charge polarizable continuum models of solvation. I. General formalism. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 132(11), 114110. doi:10.1063/1.3359469.
Schindler, P. W., Fürst, B., Dick, R., & Wolf, P. U. (1976). Ligand properties of surface silanol groups. I. surface complex formation with Fe3+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 55, 469–475.
Teixidó, M., Granados, M., Prat, M. D., & Beltrán, J. L. (2012). Sorption of tetracyclines onto natural soils: data analysis and prediction. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(8), 3087–3095.
Waller, C. W., Hutchings, B. L., Broschard, R. W., Goldman, A. A., Stein, W. J., Wolf, C. F., et al. (1952). Degradation of aureomycin. VII.1 aureomycin and anhydroaureomycin. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 74(19), 4981–4982. doi:10.1021/ja01139a539.
Wan, Y., Bao, Y., & Zhou, Q. (2010). Simultaneous adsorption and desorption of cadmium and tetracycline on cinnamon soil. Chemosphere, 80(7), 807–812. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.066.
Wang, D., Sui, Q., Zhao, W., Lv, S., Qiu, Z., & Yu, G. (2014). Pharmaceutical and personal care products in the surface water of China: a review. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 743–751 (in Chinese).
Wessels, J. M., Ford, W. E., Szymczak, W., & Schneider, S. (1998). The complexation of tetracycline and anhydrotetracycline with Mg2+ and Ca2+: a spectroscopic study. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 102(46), 9323–9331. doi:10.1021/jp9824050.
Xu, G., Liu, J., Pei, S., Gao, M., Hu, G., & Kong, X. (2015). Sediment properties and trace metal pollution assessment in surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(15), 11634–11647. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4393-y.
Zhang, Z., Sun, K., Gao, B., Zhang, G., Liu, X., & Zhao, Y. (2011). Adsorption of tetracycline on soil and sediment: effects of pH and the presence of Cu (II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190(1–3), 856–862. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.017.
Zhang, Q.-Q., Ying, G.-G., Pan, C.-G., Liu, Y.-S., & Zhao, J.-L. (2015). Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(11), 6772–6782. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b00729.
Zhao, Y., Jinju, G., Xiaorong, W., Xueyuan, G., & Shixiang, G. (2011). Tetracycline adsorption on kaolinite: pH, metal cations and humic acid effects. Ecotoxicology, 20(5), 1141–1147. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0665-6.
Zhao, Y., Gu, X., Gao, S., Geng, J., & Wang, X. (2012). Adsorption of tetracycline (TC) onto montmorillonite: cations and humic acid effects. Geoderma, 183(3), 12–18.
Zhao, Y., Tan, Y., Guo, Y., Gu, X., Wang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Interactions of tetracycline with Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) and their cosorption behavior in soils. Environmental Pollution, 180(3), 206–213.
Zhu, G., Guo, Q., Chen, T., Marc, P., Yang, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2013). Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Nansha River in Beijing. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(8), 2148–2153 (in Chinese).
Zou, X., Zhang, C., Ning, J., Wei, L., & Yang, S. (2012). Behaviors of copper ions different in concentration in sorption-desorption by soils—and existence of weak-specific—adsorption state. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49(5), 892–900.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (Grant No. 8142020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Table S1 Calibration curves for TCs. Table S2 Freundlich parameters for the sorption isotherms of TCs as affected by Cd (II). Fig. S1 possible configurations of TCs. Fig. S2 sediment dispersions in triangular flasks and containers. Fig. S3 TC sorption isotherms in triangular flasks and centrifuge tubes. Fig. S4 FTIR spectra of sediments and sediments after sorption of TC and Cd (II). (DOC 2133 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Li, G., Sun, L. et al. Tetracyclines Sorption in the Presence of Cadmium on River Sediments: the Effects of Sorption Mechanism and Complex Properties. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2982-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2982-0