Abstract
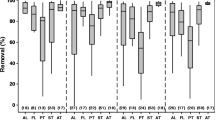
A comprehensive investigation of polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in wastewater was conducted in the second largest international metroplex area along the U.S. and Mexico (MX) border. Concentrations of PBDEs in wastewater and sludge were measured in four wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in El Paso, Texas and two WWTPs in Cd. Juarez, Chihuahua, MX. A green approach in sample preparation technique, called stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) coupled with thermal desorption and gas chromatography and mass spectrometry, was used which requires minimum amount of organic solvents and has good sensitivity at nanogram-per-liter levels for wastewater samples and nanograms per gram for waste sludge solids. Concentrations of PBDEs ranged from 30.2 to 342 ng L−1 in wastewater influents, from not detected to 209 ng L−1 in effluents, and from not detected to 1,303 ng g−1 in sludge. Among 27 PBDEs studied, BDE-47, BDE-99, and BDE-100 were the most commonly detected congeners in all samples. Further evaluation showed that secondary and tertiary treatments are highly effective at removing PBDEs from wastewater with percent removals ranging from 84 % to 100 %, while advanced primary treatment only removed 41–73 % of PBDEs. As a complement, the ambient air temperature change on PBDEs concentrations was evaluated finding that this factor did not have an influence on the PBDEs concentrations in WWTPs. The incomplete removal of PBDEs in WWTPs implicates a potential impact on the environmental and public health as a result of the continuous release of PBDEs from the WWTPs to the Rio Grande River and irrigation canals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. D., & MacRae, J. D. (2006). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish and wastewater samples from an area of the Penobscot River in Central Maine. Chemosphere, 62(7), 1153–1160.
Benijts, T., Vercammen, J., Dams, R., Tuan, H. P., Lambert, W., & Sandra, P. (2001). Stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–capillary gas chromatography–mass spectrometry applied to the analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls in human sperm. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 755(1–2), 137–142.
Bicchi, C., Iori, C., Rubiolo, P., & Sandra, P. (2002). Headspace sorptive extraction (HSSE), stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), and solid phase microextraction (SPME) applied to the analysis of roasted Arabica coffee and coffee brew. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(3), 449–459.
Blackman, A. & Michael, B. E., D. (2004). Maquiladoras, air pollution, and human health in Ciudad Juárez and El Paso. Resources for the Future Discussion Paper, 3–18.
Christensen, J. H., Groth, B. S., Vikelsøe, J. Vorkamp, K. (2003). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sewage sludge and wastewater, method development and validation. NERI Technical Report, No. 481, Denmark, National Environmental Research Institute, 8–28.
City of El Paso, Texas (2009). The Parks and Recreation Master Plan, Chapter 2, El Paso today. El Paso, TX.
Clarke, B., Porter, N., Symons, R., Marriott, P., Ades, P., Stevenson, G., & Blackbeard, J. (2008). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polybrominated biphenyls in Australian sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 73(6), 980–989.
David, F., Tienpont, P. & Sandra, P. (2003). Stir-bar sorptive extraction of trace organic compounds from aqueous matrices. Sample Preparation Perspectives. LC-GC Europe, 2–7.
Eljarrat, E., Marsh, G., Labandeira, A., & Barceló, D. (2008). Effect of sewage sludges contaminated with polybrominated diphenylethers on agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 71(6), 1079–1086.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2007). Brominated Diphenyl Ethers in Water Soil, Sediment and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS. www.epa.gov.
Gevao, B., Muzaini, S., & Helaleh, M. (2008). Occurrence and concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sewage sludge from three wastewater treatment plants in Kuwait. Chemosphere, 71(2), 242–247.
Hale, R., Alaee, M., Manchester-Neesvig, J., Stapleton, H., & Ikonomou, M. (2003). Polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in the North American environment. Environment International, 29(6), 771–779.
Hale, R. C., La Guardia, M. J., Harvey, E. P., Gaylor, M. O., Mainor, T. M., & Duf, W. H. (2001). Flame retardants: persistent pollutants in land-applied sludges. Nature, 412, 140–141.
Horii, Y., Reiner, J. L., Loganathan, B. G., Kumar, K. S., Sajwan, K., & Kannan, K. (2007). Occurrence and fate of polycyclic musks in wastewater treatment plants in Kentucky and Georgia, USA. Chemosphere, 68(11), 2011–2020.
Ikonomou, M. G., Rayne, S., Fischer, M., Fernandez, M. P., & Cretney, W. (2002). Occurrence and congener profiles of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in environmental samples from coastal British Columbia, Canada. Chemosphere, 46(5), 649–663.
Kinton, V. R., Whitecavage, J. A., Heiden, A. C. & Gil, C. (2004). Use of a mass spectral based chemical sensor to discriminate food and beverage samples: olive oils and wine as examples. Gerstel 1–10.
Knoth, W., Mann, W., Meyer, R., & Nebhuth, J. (2007). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sewage sludge in Germany. Chemosphere, 67(9), 1831–1837.
León, V. M., Álvarez, B., Cobollo, M. A., Muñoz, S., & Valor, I. (2003). Analysis of 35 priority semivolatile compounds in water by stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: I. Method optimisation. Journal of Chromatography A, 999(1–2), 91–101.
Llorca-Porcel, J., Martínez-Sánchez, G., Álvarez, B., Cobollo, M. A., & Valor, I. (2006). Analysis of nine polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water samples by means of stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 569(1–2), 113–118.
Medina, C. M., Pitarch, E., Lopez, J. F., Vazquez, C., & Hernande, F. (2008). Determination of PBDEs in human breast adipose tissues by gas chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390(5), 1343–1354.
Moon, H. B., Yoon, S. P., Jung, R. H., & Choi, M. (2008). Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) as a source of sediment contamination by toxic organic pollutants and fecal sterols in a semi-enclosed bay in Korea. Chemosphere, 73(6), 880–889.
Mueller, K. E., Mueller-Spitz, S. R., Henry, H. F., Vonderheide, A. P., Soman, R. S., Kinkle, B. K., & Shann, J. R. (2006). Fate of pentabrominated diphenyl ethers in soil: abiotic sorption, plant uptake, and the impact of interspecific plant interaction. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(21), 6662–6667.
Nakada, N., Nyunoya, N., Nakamura, M., Hara, A., Iguchi, T., & Takada, H. (2004). Identification of estrogenic compounds in wastewater effluent. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23(12), 2807–2815.
North, K. D. (2004). Tracking polybrominated diphenyl ether releases in a wastewater treatment plant effluent, Palo Alto, California. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(17), 4484–4488.
Ochiai, N., Sasamoto, K., Kanda, H., Yamagami, T., David, F., Tienpont, B., & Sandra, P. (2005). Optimization of a multi-residue screening method for the determination of 85 pesticides in selected food matrices by stir bar sorptive extraction and thermal desorption GC–MS. Journal of Separation Science, 28(9-10), 1083–1092.
Ohta, S., Ishizuka, D., Nishimura, H., Teruyuki, N., Osamu, A., Yoshiko, S., Fumie, O., Takafumi, K., Masatoshi, N., & Hideaki, M. (2002). Comparison of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish, vegetables, and meats and levels in human milk of nursing women in Japan. Chemosphere, 46(5), 689–696.
Peng, X., Tang, C., Yu, Y., Tan, J., Huang, Q., Wu, J., Chen, S., & Mai, B. (2009). Concentrations, transport, fate, and releases of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environment International, 35(2), 303–309.
Prieto, A., Zuloaga, O., Usobiaga, A., Etxebarria, N., & Fernandez, L. A. (2008). Use of experimental design in the optimisation of stir bar sorptive extraction followed by thermal desorption for the determination of brominated flame retardants in water samples. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390(2), 739–748.
Ripp, J. (1996). Analytical detection limit guidance & laboratory guide for determining method detection limits. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. PUBL-TS-056-96 Laboratory Certification Program, 1–24.
Rocha-Gutierrez, B. & Lee, W.-Y. (2011). Determination and comparison of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment plants. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2011.585713
Sandra, P., Tienpont, B., & David, F. (2003). Multi-residue screening of pesticides in vegetables, fruits and baby food by stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–capillary gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1000(1–2), 299–309.
Sellström, U., Kierkegaard, A., de Wit, C., & Jansson, B. (1998). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in sediment and fish from a Swedish River. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17(6), 1065–1072.
Shin, M., Svoboda, M. L., & Falletta, P. (2007). Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) for the determination of polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) in sewage sludge. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 387(8), 2923–2929.
Siddiqi, M. A., Laessig, R. H., & Reed, K. D. (2003). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs): new pollutants—old diseases. Clinical Medicine & Research, 1(4), 281–290.
Silva, A. R. M., Portugal, F. C. M., & Nogueira, J. M. F. (2008). Advances in stir bar sorptive extraction for the determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in environmental water matrices: comparison between polyurethane and polydimethylsiloxane polymeric phases. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1209(1–2), 10–16.
Song, M., Chu, S., Letcher, R. J., & Seth, R. (2006). Fate, partitioning, and mass loading of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) during the treatment processing of municipal sewage. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(20), 6241–6246.
Stevens, J. L., Northcott, G. L., Stern, G. A., Tomy, G. T., & Jones, K. C. (2003). PAHs, PCBs, PCNs, organochlorine pesticides, synthetic musks, and polychlorinated n-alkanes in U.K. sewage sludge: survey results and implications. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(3), 462–467.
Stéphane, B., Kee, L. H., & Obbard, J. P. (2004). Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in marine biological tissues using microwave-assisted extraction. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1035(2), 291–294.
Tienpont, B., David, F., Benijts, T., & Sandra, P. (2003). Stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–capillary GC–MS for profiling and target component analysis of pharmaceutical drugs in urine. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 32(4–5), 569–579.
Tienpont, B., David, F., Desmet, K., & Sandra, P. (2002). Stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–capillary GC–MS applied to biological fluids. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 373(1-2), 46–55.
Vrkoslavová, J., Demnerová, K., Macková, M., Zemanová, T., Macek, T., Hajšlová, J., Pulkrabová, J., Hradková, P., & Stiborová, H. (2010). Absorption and translocation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by plants from contaminated sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 81(3), 381–386.
Woocay, A., & Walton, J. (2008). Multivariate analyses of water chemistry: surface and ground water interactions. Groundwater, 46(3), 437–449. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00404.x.
Xiao, Q., Hu, B., Duan, J., He, M., & Zu, W. (2007). Analysis of PBDEs in soil, dust, spiked lake water, and human serum samples by hollow fiber-liquid phase microextraction combined with GC–ICP–MS. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 18(10), 1740–1748.
Yamaguchi, C., & Lee, W.-Y. (2010). A cost effective, sensitive, and environmentally friendly sample preparation method for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in solid samples. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1217(44), 6816–6823.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the assistance provided by the wastewater treatment plant superintendents for collecting samples. Support from the Department of Chemistry and the Center for Environmental Resource Management at UTEP is gratefully recognized. This study was partially supported by CONACYT (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia), the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (Grant Number S11ES013339), and the National Institute of Health (NIH) SCORE Program (Project Number 2S06GM008012). The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not represent the official views of the funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha-Gutierrez, B., Lee, WY. Investigation of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Wastewater Treatment Plants Along the U.S.and Mexico Border: a Trans-boundary Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1398-8