Abstract
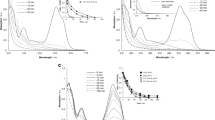
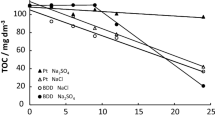
The electrochemical degradation of the Reactive Red 141 azo dye was done using a one-compartment filter-press flow cell with a boron-doped diamond anode. The response surface methodology (with a central composite design) was used to investigate the effect of current density (10–50 mA cm−2), pH (3–11), NaCl concentration ([NaCl]) (0–2.34 g L–1), and temperature (15–55 °C) on the system’s performance. The charge required for 90 % decolorization (Q 90), the fraction of chemical oxygen demand removal after 6 min of electrolysis (COD6), and the fraction of total organic carbon removal after 90 min of electrolysis (TOC90) were used to model the obtained results. The lowest values of Q 90 were attained at pH <4 in the presence of higher values of [NaCl] (>1.5 g L−1), due to the electrogeneration of active chlorine, present mainly as HClO. The value of COD6 was not affected by the solution pH, but increased with [NaCl] up to 1.5 g L−1. Higher temperatures (>40 °C) led to a decrease in COD6, as a consequence of side reactions. Higher values of TOC90, which can be reached only with strong oxidants (such as ·OH and Cl·), were efficiently attained at low [NaCl] values (<0.7 g L−1) in acidic solutions that inhibit the formation of ClO3 − and ClO4 −. Finally, the obtained results allow inferring that most probably the mineralization of the dye starts with an attack on the chromophore group, followed by the degradation of intermediate species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade, L. S., Tasso, T. T., Silva, D. L., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2009). On the performances of lead dioxide and boron-doped diamond electrodes in the anodic oxidation of simulated wastewater containing the Reactive Orange 16 dye. Electrochimica Acta, 54, 2024–2030.
Anglada, A., Urtiaga, A., Ortiz, I., Mantzavinos, D., & Diamadopoulos, E. (2011). Boron-doped diamond anodic treatment of landfill leachate: evaluation of operating variables and formation of oxidation by-products. Water Research, 45, 828–838.
Aquino, J. M., Irikura, K., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2010). A comparison of electrodeposited Ti/β-PbO2 and Ti-Pt/β-PbO2 anodes in the electrochemical degradation of the Direct Yellow 86 dye. Quimica Nova, 33, 2124–2129.
Aquino, J. M., Pereira, G. F., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2011). Electrochemical degradation of a real textile effluent using boron-doped diamond or β-PbO2 as anode. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 1275–1282.
Aquino, J. M., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2010a). Electrochemical degradation of the Acid Blue 62 dye on a β-PbO2 anode assessed by the response surface methodology. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 40, 1751–1757.
Aquino, J. M., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2010b). Electrochemical degradation of the Reactive Red 141 dye on a β-PbO2 anode assessed by the response surface methodology. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 21, 324–330.
Aquino, J. M., Rodrigo, M. A., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Sáez, C., & Cañizares, P. (2012). Influence of the supporting electrolyte on the electrolyses of dyes with conductive-diamond anodes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 184, 221–227.
Baker, J. R., Milke, M. W., & Mihelcic, J. R. (1999). Relationship between chemical and theoretical oxygen demand for specific classes of organic chemicals. Water Research, 33, 327–334.
Cañizares, P., Beteta, A., Sáez, C., Rodríguez, L., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2008). Use of electrochemical technology to increase the quality of the effluents of bio-oxidation processes. A case studied. Chemosphere, 72, 1080–1085.
Cañizares, P., Gadri, A., Lobato, J., Nasr, B., Paz, R., Rodrigo, M. A., et al. (2006). Electrochemical oxidation of azoic dyes with conductive-diamond anodes. Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research, 45, 3468–3473.
Cañizares, P., Lobato, J., Paz, R., Rodrigo, M. A., & Sáez, C. (2005). Electrochemical oxidation of phenolic wastes with boron-doped diamond anodes. Water Research, 39, 2687–2703.
Cañizares, P., Louhichi, B., Gadri, A., Nasr, B., Paz, R., Rodrigo, M. A., et al. (2007). Electrochemical treatment of the pollutants generated in an ink-manufacturing process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 552–557.
Cañizares, P., Martínez, L., Paz, R., Sáez, C., Lobato, J., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2006). Treatment of Fenton-refractory olive oil mill wastes by electrochemical oxidation with boron-doped diamond anodes. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 81, 1331–1337.
Cañizares, P., Sáez, C., Sánchez-Carretero, A., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2009). Synthesis of novel oxidants by electrochemical technology. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 39, 2143–2149.
Carneiro, P. A., Oliveira, D. P., Umbuzeiro, G. A., & Zanoni, M. V. B. (2010). Mutagenic activity removal of selected disperse dye by photoeletrocatalytic treatment. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 40, 485–492.
Chen, B., Zhang, M., Chang, C., Ding, Y., Chen, W., & Hsueh, C. (2011). Deciphering azo dye decolorization characteristics by indigenous Proteus hauseri: chemical structure. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42, 327–333.
Chen, G. (2004). Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 38, 11–41.
Cheng, C. Y., & Kelsall, G. H. (2007). Models of hypochlorite production in electrochemical reactors with plate and porous anodes. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 37, 1203–1217.
Costa, C. R., Montilla, F., Morallón, E., & Olivi, P. (2010). Electrochemical oxidation of acid black 210 dye on the boron-doped diamond electrode in the presence of phosphate ions: effect of current density, pH, and chloride ions. Electrochimica Acta, 54, 7048–7055.
Deborde, M., & von Gunten, U. (2008). Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment—kinetics and mechanisms: a critical review. Water Research, 42, 13–51.
Domínguez, J. R., González, T., Palo, P., Sánchez-Martín, J., Rodrigo, M. A., & Sáez, C. (2012). Electrochemical degradation of a real pharmaceutical effluent. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 2685–2694.
Eaton, A. D., Clesceri, L. S., & Greenberg, A. E. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington: American Public Healthy Association.
Férnandez, C., Larrechi, M. S., & Callao, M. P. (2010). An analytical overview of processes for removing organic dyes from wastewater effluents. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29, 1202–1211.
Ghernaout, D., Naceur, M. W., & Aouabed, A. (2011). On the dependence of chlorine by-products generated species formation of the electrode material and applied charge during electrochemical water treatment. Desalination, 270, 9–22.
Grebel, J. E., Pignatello, J. J., & Mitch, W. A. (2010). Effect of halide ions and carbonates on organic contaminant degradation by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes in saline waters. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 6822–6828.
Hessel, C., Allegre, C., Maisseu, M., Charbit, F., & Moulin, P. (2007). Guidelines and legislation for dye house effluents. Journal of Environmental Management, 83, 171–180.
Jara, C. C., & Fino, D. (2010). Cost optimization of the current density for electroxidation wastewater processes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 160, 497–502.
Kapalka, A., Fóti, G., & Comninellis, C. (2009). The importance of electrode material in environmental electrochemistry formation and reactivity of free hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 54, 2018–2023.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Brillas, E. (2009). Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 87, 105–145.
Montanaro, D., & Petrucci, E. (2009). Electrochemical treatment of Remazol Brilliant Blue on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chemical Engineering Journal, 153, 138–144.
Myers, R. H., Montgomery, D. C., & Anderson-Cook, C. M. (2009). Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Muthukumar, M., Sargunamani, D., & Selvakumar, N. (2005). Statistical analysis of the effect of aromatic, azo and sulphonic acid groups on decolouration of acid dye effluents using advanced oxidation processes. Dyes and Pigments, 65, 151–158.
Pandey, A., Singh, P., & Iyengar, L. (2007). Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 59, 73–84.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2005). Application of diamond electrodes to electrochemical processes. Electrochimica Acta, 51, 191–199.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2008). Removal of colour and COD from wastewater containing Acid Blue 22 by electrochemical oxidation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 83–88.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2009). Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chemical Reviews, 109, 6541–6569.
Panizza, M., Kapalka, A., & Comninellis, C. (2008). Oxidation of organic pollutants on BDD anodes using modulated current electrolysis. Electrochimica Acta, 53, 2289–2295.
Peralta-Hernández, J. M., Méndez-Tovar, M., Guerra-Sánchez, R., Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Nava, J. L. (2012). A brief review on environmental application of boron doped diamond electrodes as a new way for electrochemical incineration of synthetic dyes. International Journal of Electrochemistry. doi:10.1155/2012/154316.
Pereira, G. F., Andrade, L. S., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2012). Electrochemical determination of bisphenol A using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 82, 3–8.
Pereira, G. F., Rocha-Filho, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2012). Electrochemical degradation of bisphenol A using a flow reactor with a boron-doped diamond anode. Chemical Engineering Journal, 198–199, 282–288.
Polcaro, A. M., Vacca, A., Mascia, M., Palmas, S., & Ruiz, J. R. (2009). Electrochemical treatment of waters with BDD anodes: kinetics of the reactions involving chlorides. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 39, 2083–2092.
Prasad, R., Kumar, R., & Srivastava, S. (2008). Design of optimum response surface experiments for electro-coagulation of distillery spent wash. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 191, 5–13.
Rajkumar, D., & Kim, J. G. (2006). Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B136, 203–212.
Rodrigo, M. A., Cañizares, P., Sánchez-Carretero, A., & Sáez, C. (2010). Use of conductive-diamond electrochemical oxidation for wastewater treatment. Catalysis Today, 151, 173–177.
Rodriguez, J., Rodrigo, M. A., Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2009). Electrochemical oxidation of Acid Yellow 1 using diamond anode. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 39, 2285–2289.
Sáez, C., Panizza, M., Rodrigo, M. A., & Cerisola, G. (2007). Electrochemical incineration of dyes using a boron-doped diamond anode. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 82, 575–581.
Sánchez-Carretero, A., Sáez, C., Cañizares, P., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2011). Electrochemical production of perchlorates using conductive diamond electrolyses. Chemical Engineering Journal, 166, 710–714.
Song, S., Fan, J., He, Z., Zhan, L., Liu, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2010). Electrochemical degradation of azo dye C.I. Reactive Red 195 by anodic oxidation on Ti/SnO2–Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 55, 3606–3613.
Urbansky, E. T. (2001). Total organic carbon analyzers as tools for measuring carbonaceous matter in natural waters. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 102–112.
Umbuzeiro, G. A., Freeman, H. S., Warren, S. H., Oliveira, D. P., Terao, Y., Watanabe, T., et al. (2005). The contribution of azo dyes to the mutagenic activity of the Cristais River. Chemosphere, 60, 55–64.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Junta de Comunidades de Castilla La Mancha, Spain (project PEII11-0097-2026). The Brazilian agencies CNPq and CAPES (scholarship for J. M. Aquino) are gratefully acknowledged. Dystar is also acknowledged for supplying the dye sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 2.10 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aquino, J.M., Rocha-Filho, R.C., Rodrigo, M.A. et al. Electrochemical Degradation of the Reactive Red 141 Dye Using a Boron-Doped Diamond Anode. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1397 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1397-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1397-9