Abstract
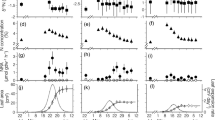
Tree canopies are believed to act as a sink of atmospheric ammonia (NH3). However, few studies have compared the uptake efficiency of different tree species. This study assessed the uptake of 15N-labelled NH3 at 5, 20, 50 and 100 ppbv by leaves and twigs of potted silver birch, European beech, pedunculate oak and Scots pine saplings in June, August and September 2008. Additionally, foliar uptake of 13C-labelled carbon dioxide (13CO2) and leaf stomatal characteristics were determined per species and treatment date and the relation with 15NH3 uptake and estimated stomatal 15NH3 uptake were assessed. Both 15NH3 and 13CO2 uptake were affected by tree species and treatment date, but only 15NH3 uptake was influenced by the applied NH3 concentration. Depending on the treatment date, 15NH3 uptake by leaves and twigs was highest at 5 (September), 20 (June) or 50 (August) ppbv. Birch, beech and oak leaves showed the highest uptake in August, while for pine needles this was in June and, except at 5 ppbv in June, the 15NH3 uptake was always higher for the deciduous species than for pine. For all species except beech 13CO2 uptake was highest in August and on every treatment date the 13CO2 uptake by leaves of deciduous species was significantly higher than by pine needles. Leaf characteristics and 13CO2 uptake did not provide a strong explanation for the observed differences in 15NH3 uptake. This study shows that on the short-term a high interspecific variability exists in NH3 uptake, which depends on the time in the growing season.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasamaa, K., & Sober, A. (2011). Stomatal sensitivities to changes in leaf water potential, air humidity, CO2 concentration and light intensity, and the effect of abscisic acid on the sensitivities in six temperate deciduous tree species. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 71, 72–78.
Adriaenssens, S., Staelens, J., Wuyts, K., De Schrijver, A., Van Wittenberghe, S., Wuytack, T., et al. (2011). Foliar nitrogen uptake from wet deposition and the relation with leaf wettability and water storage capacity. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 219, 43–57.
Asman, W. A. H., Sutton, M. A., & Schjoerring, J. K. (1998). Ammonia: emission, atmospheric transport and deposition. New Phytologist, 139, 27–48.
Balasooriya, B. L. W. K., Samson, R., Mbikwa, F., Vitharana, U. W. A., Boeckx, P., & Van Meirvenne, M. (2009). Biomonitoring of urban habitat quality by anatomical and chemical leaf characteristics. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 65, 386–394.
Bowman, W. D., Cleveland, C. C., Halada, L., Hresko, J., & Baron, J. S. (2008). Negative impact of nitrogen deposition on soil buffering capacity. Nature Geoscience, 1, 767–770.
Brodribb, T., & Hill, R. S. (1997). Imbricacy and stomatal wax plugs reduce maximum leaf conductance in Southern Hemisphere conifers. Australian Journal of Botany, 45, 657–668.
Bruckner, G., Gebauer, G., & Schulze, E. D. (1993). Uptake of NH3–N-15 by Picea abies in closed-chamber experiments. Isotopenpraxis, 29, 71–76.
Burkhardt, J. (2010). Hygroscopic aerosols on leaves: nutrients or desiccants? Ecological Monographs, 80, 369–399.
Burkhardt, J., & Eiden, R. (1994). Thin water films on coniferous needles. Atmospheric Environment, 28, 2001–2011.
Dail, D. B., Hollinger, D. Y., Davidson, E. A., Fernandez, I., Sievering, H. C., Scott, N., et al. (2009). Distribution of nitrogen-15 tracers applied to the canopy of a mature spruce-hemlock stand, Howland, Maine, USA. Oecologia, 160, 589–599.
de Vries, W., Solberg, S., Dobbertin, M., Sterba, H., Laubhann, D., van Oijen, M., et al. (2009). The impact of nitrogen deposition on carbon sequestration by European forests and heathlands. Forest Ecology and Management, 258, 1814–1823.
Duyzer, J. H., Verhagen, H. L. M., Weststrate, J. H., & Bosveld, F. C. (1992). Measurement of the dry deposition flux of NH3 on to coniferous forest. Environmental Pollution, 75, 3–13.
Erisman, J. W., & Draaijers, G. (2003). Deposition to forests in Europe: most important factors influencing dry deposition and models used for generalisation. Environmental Pollution, 124, 379–388.
Fangmeier, A., Hadwigerfangmeier, A., Vandereerden, L., & Jager, H. J. (1994). Effects of atmospheric ammonia on vegetation—a review. Environmental Pollution, 86, 43–82.
Farquhar, G. D., & Sharkey, T. D. (1982). Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 33, 317–345.
Farquhar, G. D., Firth, P. M., Wetselaar, R., & Weir, B. (1980). On the gaseous exchange of ammonia between leaves and the environment—determination of the ammonia compensation point. Plant Physiology, 66, 710–714.
Ferm, M. (1998). Atmospheric ammonia and ammonium transport in Europe and critical loads: a review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 51, 5–17.
Fitter, A. H., & Peat, H. J. (1994). The ecological flora database. Journal of Ecology, 82, 415–425.
Gaige, E., Dail, D. B., Hollinger, D. Y., Davidson, E. A., Fernandez, I. J., & Sievering, H. (2007). Changes in canopy processes following whole-forest canopy nitrogen fertilization of a mature spruce-hemlock forest. Ecosystems, 10, 1133–1147.
Gessler, A., Rienks, M., & Rennenberg, H. (2000). NH3 and NO2 fluxes between beech trees and the atmosphere—correlation with climatic and physiological parameters. New Phytologist, 147, 539–560.
Gessler, A., Rienks, M., & Rennenberg, H. (2002). Stomatal uptake and cuticular adsorption contribute to dry deposition of NH3 and NO2 to needles of adult spruce (Picea abies Karst.) trees. New Phytologist, 156, 179–194.
Grundmann, G. L., Lensi, R., & Chalamet, A. (1993). Delayed NH3 and N2O uptake by maize leaves. New Phytologist, 124, 259–263.
Gundersen, P., Schmidt, I. K., & Raulund-Rasmussen, K. (2006). Leaching of nitrate from temperate forests—effects of air pollution and forest management. Environmental Reviews, 14, 1–57.
Hanstein, S., Mattsson, M., Jaeger, H. J., & Schjoerring, J. K. (1999). Uptake and utilization of atmospheric ammonia in three native Poaceae species: leaf conductances, composition of apoplastic solution and interactions with root nitrogen supply. New Phytologist, 141, 71–83.
Harrison, A. F., Schulze, E.-D., Gebauer, G., & Bruckner, G. (2000). Canopy uptake and utilization of atmospheric pollutant nitrogen. In: E.-D. Schulze, Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling in European Forest Ecosystems, Ecological Studies, pp. 171–188.
Hill, P. W., Raven, J. A., & Sutton, M. A. (2002). Leaf age-related differences in apoplastic NH +4 concentration, pH and the NH3 compensation point for a wild perennial. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53, 277–286.
Husted, S., & Schjoerring, J. K. (1996). Ammonia flux between oilseed rape plants and the atmosphere in response to changes in leaf temperature, light intensity, and air humidity—interactions with leaf conductance and apoplastic NH +4 and H+ concentrations. Plant Physiology, 112, 67–74.
Jones, M. R., Leith, I. D., Fowler, D., Raven, J. A., Sutton, M. A., Nemitz, E., et al. (2007). Concentration-dependent NH3 deposition processes for mixed moorland semi-natural vegetation. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 2049–2060.
Jones, M. R., Raven, J. A., Leith, I. D., Cape, J. N., Smith, R. I., & Fowler, D. (2008). Short-term flux chamber experiment to quantify the deposition of gaseous N-15-NH3 to Calluna vulgaris. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 148, 893–901.
Krupa, S. V. (2003). Effects of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) on terrestrial vegetation: a review. Environmental Pollution, 124, 179–221.
Lindberg, S. E., Lovett, G. M., Richter, D. D., & Johnson, D. W. (1986). Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of major ions in a forest. Science, 231, 141–145.
Loubet, B., & Cellier, P. (2001). Experimental assessment of atmospheric ammonia dispersion and short range dry deposition in a maize canopy. Water Air and Soil Pollution: Focus 1, 157–166.
Ma, B. L., Subedi, K. D., & Costa, C. (2005). Comparison of crop-based indicators with soil nitrate test for corn nitrogen requirement. Agronomy Journal, 97, 462–471.
Magnani, F., Mencuccini, M., Borghetti, M., Berbigier, P., Berninger, F., Delzon, S., et al. (2007). The human footprint in the carbon cycle of temperate and boreal forests. Nature, 447, 848–850.
Massad, R. S., Nemitz, E., & Sutton, M. A. (2010). Review and parameterisation of bi-directional ammonia exchange between vegetation and the atmosphere. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 10359–10386.
Mattsson, M., & Schjoerring, J. K. (2003). Senescence-induced changes in apoplastic and bulk tissue ammonia concentrations of ryegrass leaves. New Phytologist, 160, 489–499.
Millard, P., & Proe, M. F. (1993). Nitrogen uptake, partitioning and internal cycling in Picea sitchensis (Bong) Carr as influenced by nitrogen supply. New Phytologist, 125, 113–119.
Morikawa, H., Higaki, A., Nohno, M., Takahasi, M., Kamada, M., Nakata, M., et al. (1998). More than a 600-fold variation in nitrogen dioxide assimilation among 217 plant taxa. Plant Cell and Environment, 21, 180–190.
Nadelhoffer, K. J., Emmett, B. A., Gundersen, P., Kjonaas, O. J., Koopmans, C. J., Schleppi, P., et al. (1999). Nitrogen deposition makes a minor contribution to carbon sequestration in temperate forests. Nature, 398, 145–148.
Neirynck, J., & Ceulemans, R. (2008). Bidirectional ammonia exchange above a mixed coniferous forest. Environmental Pollution, 154, 424–438.
Neirynck, J., Kowalski, A. S., Carrara, A., & Ceulemans, R. (2005). Driving forces for ammonia fluxes over mixed forest subjected to high deposition loads. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 5013–5024.
Neirynck, J., Kowalski, A. S., Carrara, A., Genouw, G., Berghmans, P., & Ceulemans, R. (2007). Fluxes of oxidised and reduced nitrogen above a mixed coniferous forest exposed to various nitrogen sources. Environmental Pollution, 149, 31–43.
Neirynck, J., Flechard, C. R., & Fowler, D. (2011). Long term (13 years) measurements of SO2 fluxes over a forest and their control by surface chemistry. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151, 1768–1780.
Paoletti, E., & Grulke, N. E. (2005). Does living in elevated CO2 ameliorate tree response to ozone? A review on stomatal responses. Environmental Pollution, 137, 483–493.
Papen, H., Gessler, A., Zumbusch, E., & Rennenberg, H. (2002). Chemolithoauthotrophic nitrifiers in the phyllosphere of a spruce ecosystem receiving high atmospheric nitrogen input. Current Microbiology, 44, 56–60.
Pearcy, R. W., Schulze, E. D., & Zimmerman, R. (1989). Measurement of transpiration and leaf conductance. In: R. W. Pearcy et al., Plant physiological ecology. Field methods and instrumentation, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 37-60.
Peuke, A. D., Jeschke, W. D., Dietz, K. J., Schreiber, L., & Hartung, W. (1998). Foliar application of nitrate or ammonium as sole nitrogen supply in Ricinus communis—I. Carbon and nitrogen uptake and inflows. New Phytologist, 138, 675–687.
R Development Core Team (2011). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org.
Rennenberg, H., & Gessler, A. (1999). Consequences of N deposition to forest ecosystems—recent results and future research needs. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 116, 47–64.
Schjoerring, J. K., Husted, S., & Mattsson, M. (1998). Physiological parameters controlling plant–atmosphere ammonia exchange. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 491–498.
Schulze, E.-D., Beck, E., & Müller-Hohnenstein, K. (2005). Plant ecology. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Sparks, J. P. (2009). Ecological ramifications of the direct foliar uptake of nitrogen. Oecologia, 159, 1–13.
Stulen, I., Perez-Soba, M., De Kok, L. J., & Van der Eerden, L. (1998). Impact of gaseous nitrogen deposition on plant functioning. New Phytologist, 139, 61–70.
Sutton, M., Fowler, D., Burkhardt, J., & Milford, C. (1995). Vegetation atmosphere exchange of ammonia: canopy cycling and the impacts of elevated nitrogen inputs. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 85, 2057–2063.
Sutton, M. A., Burkhardt, J. K., Guerin, D., Nemitz, E., & Fowler, D. (1998). Development of resistance models to describe measurements of bi-directional ammonia surface–atmosphere exchange. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 473–480.
Thomas, R. Q., Canham, C. D., Weathers, K. C., & Goodale, C. L. (2010). Increased tree carbon storage in response to nitrogen deposition in the US. Nature Geoscience, 3, 13–17.
Vallano, D. M., & Sparks, J. P. (2007). Foliar δ15N values as indicators of foliar uptake of atmospheric nitrogen pollution. In: T.E. Dawson et al., Stable isotopes as indicators of ecological change, Elsevier, pp. 93–109.
Van Hove, L. W. A., & Adema, E. H. (1996). The effective thickness of water films on leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 30, 2933–2936.
Van Hove, L. W. A., Koops, A. J., Adema, E. H., Vredenberg, W. J., & Pieters, G. A. (1987). Analysis of the uptake of atmospheric ammonia by leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Atmospheric Environment, 21, 1759–1763.
Van Hove, L. W. A., Vankooten, O., Adema, E. H., Vredenberg, W. J., & Pieters, G. A. (1989). Physiological-effects of long-term exposure to low and moderate concentrations of atmospheric NH3 on poplar leaves. Plant Cell and Environment, 12, 899–908.
Verstraeten, A., Sioen, G., Neirynck, J., Coenen, S., & Roskams, P. (2008). Bosgezondheid in Vlaanderen. Bosvitaliteitsinventaris, meetnet Intensieve monitoring en meetstation luchtverontreiniging. Resultaten 2007. VMM, 2009. 'Zure regen' in Vlaanderen, Depositiemeetnet verzuring 2007, pp. 70.
VMM (2009). ‘Zure regen’ in Vlaanderen, Depositiemeetnet verzuring 2009, p. 70.
Wang, L., Xu, Y. C., & Schjoerring, J. K. (2011). Seasonal variation in ammonia compensation point and nitrogen pools in beech leaves (Fagus sylvatica). Plant and Soil, 343, 51–66.
Wyers, G. P., & Erisman, J. W. (1998). Ammonia exchange over coniferous forest. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 441–451.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge L. Willems, G. De bruyn, K. Van Nieuland, J. Vermeulen, K. Ceunen and A. De Mey for field and laboratory assistance. The first author is granted by a research project (G.0205.08N) of the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO) and the fourth author by the BIOHYPE project of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO). The second and third authors are funded as postdoctoral fellow of respectively FWO and the Special Research Fund of Ghent University (BOF) and the fifth author by a Ph.D. fellowship of the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT-Vlaanderen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adriaenssens, S., Staelens, J., Wuyts, K. et al. Canopy Uptake of 15NH3 by Four Temperate Tree Species and the Interaction with Leaf Properties. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 5643–5657 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1304-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1304-4