Abstract
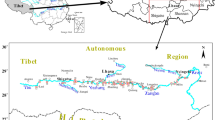
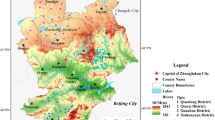
The Nandong Underground River System (NURS) is located in Southeast Yunnan Province, China. Groundwater in NURS plays a critical role in socio-economical development of the region. However, with the rapid increase of population in recent years, groundwater quality has degraded greatly. In this study, the analysis of 36 groundwater samples collected from springs in both rain and dry seasons shows significant spatial disparities and slight seasonal variations of major element concentrations in the groundwater. In addition, results from factor analysis indicate that NO −3 , Cl−, SO 2−4 , Na+, K+, and EC in the groundwater are mainly from the sources related to human activities while Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO −3 , and pH are primarily controlled by water–rock interactions in karst system with Ca2+ and HCO −3 somewhat from anthropogenic inputs. With the increased anthropogenic contaminations, the groundwater chemistry changes widely from Ca-HCO3 or Ca (Mg)-HCO3 type to Ca-Cl (+NO3) or Ca (Mg)-Cl (+NO3), and Ca-Cl (+NO3+SO4) or Ca (Mg)-Cl (+NO3+SO4) type. Concentrations of NO −3 , Cl−, SO 2−4 , Na+, and K+ generally show an indistinct grouping with respect to land use types, with very high concentrations observed in the groundwater from residential and agricultural areas. This suggests that those ions are mainly derived from sewage effluents and fertilizers. No specific land use control on the Mg2+ ion distribution is observed, suggesting Mg2+ is originated from natural dissolution of carbonate rocks. The distribution of Ca2+ and HCO −3 does not show any distinct land use control either, except for the samples from residential zones, suggesting the Ca2+ and HCO -3 mainly come from both natural dissolution of carbonate rocks and sewage effluents.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, L., Silva, B., Raphael, H., & Márcio, H. T. (1999). Environmental diagnosis, monitoring and research of heavy metals behavior methodology in soil-water-contaminant system in a contaminated area in Santa Gertrudes, Brazil. Hydrogeology and Land Use Management, 519–521.
Aravena, R., Auge, M., & Bucich, N. (1999). Evaluation of the origin of groundwater nitrate in the city La Plata-agentina, using isotope techniques. Hydrogeology and Land Use Management, 323–327.
Bohlke, J. K., & Horan, M. (2000). Strontium isotope geochemistry of groundwaters and streams affected by agriculture, Locust Grove, MD. Applied Geochemistry, 15, 599–609.
Chambel, A., & Duque, J. (1999). Hard rock aquifers of Alentejo region (south Portugal): contribution to the water and land use management. Hydrogeology and Land Use Management, 171–176.
Chan, H. J. (2001). Effect of land use and urbanization on hydrochemistry and contamination of groundwater from Taejon area, Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 253, 194–210.
Compton and Boone (2000). Long-term impacts of agriculture on soil carbon and nitrogen in New England. Forests Ecology, 81(8), 2314–2330.
Edmunds, W. M., Shand, P., Hart, P., & Ward, R. S. (2003). The natural (baseline) quality of groundwater: A UK pilot study. The Science of the Total Environment, 310(1–3), 25–35.
Fialho, A., Chambel, A., & Duque, J. (1999). Relation between geomorphology, land use and water management in the gneissic and migmatitic aquifer system of Evora (south Portugal). Hydrogeology and Land Use Management, 159–163.
Ford, D. C. (1993). Environmental change in karst areas. Environmental Geology, 21(3), 107–109.
Ganfopadhyay, S., Gupta, A., & Nachabe, M. H. (2001). Evaluation of ground water monitoring network by principal component analysis. GroundWater, 39(2), 181–191.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816.
Jiang, Y., Yuan, D., Zhang, C., Zhang, G., & He, R. (2008). Impact of land use change on groundwater quality in a typical karst watershed of southwest China. Hydrogeology Journal, 16(4), 727–735.
Jiang, Y., Li, L., Groves, C., Yuan, D., & Kambesis, P. (2009). Relationships between Rocky Desertification and spatial pattern of land use in typical karst area (Nandong), Southwest China. Environmental earth sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0083-8.
Kim, R. K., Lee, J., & Chang, H. W. (2003). Characteristics of organic matter as indicators of pollution from small-scale livestock and nitrate contamination of shallow groundwater in an agricultural area. Hydrological Processes, 17, 2485–2496.
Kim, J., Kim, R., Lee, J., Cheong, T., Yum, B., & Chang, H. (2005). Multivariate statistical analysis to identify the major factors governing groundwater quality in the coastal area of Kimje, South Korea. Hydrological Processes, 19, 1261–1276.
Lahermo, P., & Backman, B. (1999). Nitrates in groundwater in Finland: The most endangering quality problem. Hydrogeology and Land Use Management, 329–333.
LeGrand, H. E. (1984). Environmental problems in karst terrains. In A. Burger & L. Dubertret (Eds.), Hydrogeology of karstic terrains (pp. 189–194). Hanover: IAH International Contributions to Hydrogeology.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of ground water quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Negrel, P. (1999). Geochemical study of a Granitic Area—The Margeride Mountains, France: Chemical element behavior and 87Sr/86Sr constraints. Aquatic Geochemistry, 5(2), 125–165.
Negrel, P., & Pauwels, H. (2003). Interaction between the different water bodies in catchments in Brittany (France): Characterizing multiple sources in waters through isotopic tracing. Water Air Soil Pollution, 151, 261–285.
Negrel, P., & Petelet-Giraud, E. (2005). Strontium isotopes as tracers of groundwater-induced floods: The Somme case study (France). Journal of Hydrology, 305(1–4), 99–119.
Negrel, P., & Roy, S. (1998). Rain chemistry in the Massif Central (France). A strontium isotopic and major elements study. Applied Geochemistry, 13, 941–952.
Pacheco, F., & Van der Weijden, C. H. (1996). Contributions of water-rock interactions to the composition of groundwater in areas with a sizable anthropogenic input: a case study of the waters of the Fundao area, central Portugal. Water Resources Research, 32, 3553–3570.
Panda, U. C. P., Sundaray, S. K., Rath, P., Nayak, B. B., & Bhatta, D. (2006). Application of factor and cluster analysis for characterization of river and estuarine water systems—A case study: Mahanadi River (India). Journal of Hydrology, 331, 434–445.
Petelet-Giraud, E., Negrel, P., & Casanova, J. (2003). Variability of 87Sr/86Sr in water draining granite revealed after a double correction for atmospheric and anthropogenic inputs. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 48, 729–742.
Prohic, E. (1989). Pollution assessment in carbonate terrains. In: Hydrology of limestone terrains: Annotated bibliography of carbonate rock. International Contributions to Hydrogeology, 250–253.
Raghunath, R., Murthy, T. R. S., & Raghavan, B. R. (2002). The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: An example from Karnataka, India. Water Research, 36, 2437–2442.
Valdes, D., Dupont, J. P., Laignel, B., Ogier, S., Leboulanger, T., & Mahler, B. J. (2007). A spatial analysis of structural controls on Karst groundwater geochemistry at a regional scale. Journal of Hydrology, 340(1–4), 244–255.
Wakida, F. T., & Lerner, D. N. (2006). Potential nitrate leaching to groundwater from house building. Hydrological Processes, 20, 2077–2081.
Widory, D., Kloppmann, W., Chery, L., Bonnin, J., Rochdi, H., & Guinamant, J. L. (2004). Nitrate in groundwater: An isotopic multi-tracer approach. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 72(1–4), 165–188.
Witkowski, A. J. (1999). Change of sulphates concentrations in groundwater of Katowice regional water management council. Hydrogeology and Land Use Management. Bratislava, Slovak Republic, 575–580.
Wunderlin, D. A., Diaz, M. P., Ame, M. V., Pesce, S. F., Hued, A. C., & Bistoni, M. A. (2001). Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba-Argentina). Water Research, 35, 2881–2894.
Yuan, D. (2003). The geology environment and hydro-ecological problem of karst region. Land Resources in South of China, 1, 21–25. (in Chinese).
Zhang, C., & Yuan, D. (2004). Hydrochemical variation of typical karst subterranean basin and its relationship with landuse change. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(5), 134–137. (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2008CB417208); The China Environmental Health Project; Open foundation of Karst Dynamics Laboratory (No. kdl2008-06); Key Laboratory Cultivation Project: Guangxi Karst Dynamics Laboratory with the series number GuiKeNeng (No. 0842008). Thanks are given to Yinggang Li, Junbing Pu, and Qiong Xiao for their help in field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Yan, J. Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Contamination of Karst Groundwater from Nandong Underground River System, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 123–141 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0229-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0229-z