Abstract
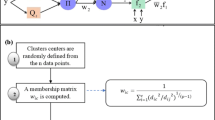
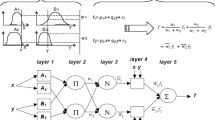
Flow as well as salt transport processes of coastal aquifers are dependent on the density variation of water, and are complicated and extremely non-linear in nature. Simulation of these complicated systems to an acceptable degree of accuracy using a suitable surrogate model can be useful to achieve computational efficiency in modelling. In this study, a Sugeno type Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) is developed to predict salinity concentrations at specified monitoring locations as a result of groundwater pumping. Fuzzy c-mean clustering (FCM) algorithm is used to develop the FIS. Heterogeneity of aquifer is incorporated by using different hydraulic conductivities at different layers of the aquifer. A numerical simulation model, FEMWATER is adopted to generate the required patterns of inputs and outputs for initial training of the developed FIS. The FIS analyzed different combinations of antecedent transient pumping values, and returns concentration values at different monitoring locations. The performance of the FIS for training and validation datasets is evaluated by comparing the outputs obtained from the numerical simulation model. The trained and validated FIS is utilized as an approximate simulator of the coupled flow and salt transport processes. It is then used to forecast salt concentrations at different monitoring locations. Performance evaluation results indicate that the developed FIS can be applied to forecast salt concentrations at specified monitoring locations. The FIS is able to simulate the complex physical processes of heterogeneous coastal aquifers, and can be suitable for incorporation in a coupled simulation-optimization technique to develop optimum pumping strategy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen DM, Schuurman N, Zhang Q (2007) Using fuzzy logic for modeling aquifer architecture. J Geogr Syst 9:289–310. doi:10.1007/s10109-007-0046-0
Altunkaynak A (2010) A predictive model for well loss using fuzzy logic approach. Hydrol Process 24:2400–2404. doi:10.1002/hyp.7642
Ayvaz MT, Karahan H, Aral MM (2007) Aquifer parameter and zone structure estimation using kernel-based fuzzy c-means clustering and genetic algorithm. J Hydrol 343:240–253. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.06.018
Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full W (1984) FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Compute Geosci 10:191–203. doi:10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7
Bhattacharjya R, Datta B (2005) Optimal management of coastal aquifers using linked simulation optimization approach. Water Resour Manag 19:295–320. doi:10.1007/s11269-005-3180-9
Bhattacharjya RK, Datta B, Satish MG (2007) Artificial neural networks approximation of density dependent saltwater intrusion process in coastal aquifers. J Hydrol Eng 12:273–282. doi:10.1061/(asce)1084-0699(2007)12:3(273)
Caniani D, Lioi DS, Mancini IM, Masi S (2015) Hierarchical classification of groundwater pollution risk of contaminated sites using fuzzy logic: a case study in the Basilicata Region (Italy). Water 7:2013–2036. doi:10.3390/w7052013
Cherkassky V (1998) Fuzzy inference systems: a critical review. In: Kaynak O, Zadeh LA, Türkşen B, Rudas IJ (eds) Computational intelligence: soft computing and fuzzy-neuro integration with applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 177–197. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-58930-0_10
Christelis V, Mantoglou A (2016) Pumping optimization of coastal aquifers assisted by adaptive metamodelling methods and radial basis functions. Water Resour Manag 30:1–15. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1337-3
Das A, Datta B (2001) Application of optimisation techniques in groundwater quantity and quality management. Sadhana 26:293–316. doi:10.1007/bf02703402
Doulgeris C, Zissis T (2014) 3D variable density flow simulation to evaluate pumping schemes in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manag 28:4943–4956. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0766-0
Emamgholizadeh S, Moslemi K, Karami G (2014) Prediction the groundwater level of Bastam Plain (Iran) by artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Water Resour Manag 28:5433–5446. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0810-0
Giambastiani BMS, Antonellini M, Oude Essink GHP, Stuurman RJ (2007) Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): A numerical model. J Hydrol 340:91–104. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.04.001
Gong YC, Zhang YX, Lan SS, Wang H (2016) A comparative study of artificial neural networks, support vector machines and adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system for forecasting groundwater levels near Lake Okeechobee. Fla Water Resour Manag 30:375–391. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-1167-8
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2009) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
He ZB, Wen XH, Liu H, Du J (2014) A comparative study of artificial neural network, adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and support vector machine for forecasting river flow in the semiarid mountain region. J Hydrol 509:379–386. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.054
Javadi A, Hussain M, Sherif M, Farmani R (2015) Multi-objective optimization of different management scenarios to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manag 29:1843–1857. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-0914-1
Kord M, Moghaddam AA (2014) Spatial analysis of Ardabil plain aquifer potable groundwater using fuzzy logic. J King Saud Univ - Sci 26:129–140. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2013.09.004
Kourakos G, Mantoglou A (2009) Pumping optimization of coastal aquifers based on evolutionary algorithms and surrogate modular neural network models. Adv Water Resour 32:507–521. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.01.001
Li H, Boufadel MC (2011) A tracer study in an Alaskan gravel beach and its implications on the persistence of the Exxon Valdez oil. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1261–1269. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.04.001
Lin HJ, Rechards DR, Talbot CA, Yeh GT, Cheng JR, Cheng HP, Jones NL (1997) A three-dimensional finite-element computer model for simulating density-dependent flow and transport in variable saturated media: Version 3.0 U S Army Engineering Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, Miss
Luyun R, Momii K, Nakagawa K (2011) Effects of recharge wells and flow barriers on seawater intrusion. Ground Water 49:239–249. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00719.x
MathWorks (2016) What is sugeno-type fuzzy inference? MATLAB documentation http://aumathworkscom/help/fuzzy/what-is-sugeno-type-fuzzy-inferencehtml Accessed 13 September 2016
Muhammetoglu A, Yardimci A (2006) A fuzzy logic approach to assess groundwater pollution levels below agricultural fields. Environ Monit Assess 118:337–354. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-1497-3
Oude Essink GHP (2001) Improving fresh groundwater supply—problems and solutions. Ocean Coast Manag 44:429–449. doi:10.1016/S0964-5691(01)00057-6
Oude Essink GHP, van Baaren ES, de Louw PGB (2010) Effects of climate change on coastal groundwater systems: a modeling study in the Netherlands. Water Resour Res:46. doi:10.1029/2009WR008719
Paniconi C, Khlaifi I, Lecca G, Giacomelli A, Tarhouni J (2001) Modeling and analysis of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of Eastern Cap-Bon. Tunis Transp Porous Media 43:3–28. doi:10.1023/a:1010600921912
Papadopoulou MP, Nikolos IK, Karatzas GP (2010) Computational benefits using artificial intelligent methodologies for the solution of an environmental design problem: saltwater intrusion. Water Sci Technol 62:1479–1490. doi:10.2166/wst.2010.442
Pebesma EJ, Heuvelink GBM (1999) Latin hypercube sampling of Gaussian random fields. Technometrics 41:303–312. doi:10.2307/1271347
Pillay N (2004) An investigation into the use of genetic programming for the induction of novice procedural programming solution algorithms in intelligent programming tutors dissertation. University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban
Pramada SK, Mohan S (2015) Stochastic simulation of seawater intrusion into freshwater aquifers. Aquat Procedia 4:87–94. doi:10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.013
Servan-Camas B, Tsai FTC (2009) Saltwater intrusion modeling in heterogeneous confined aquifers using two-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method. Adv Water Resour 32:620–631. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.02.001
Shiri J, Kisi O (2011) Comparison of genetic programming with neuro-fuzzy systems for predicting short-term water table depth fluctuations. Comput Geosci 37:1692–1701. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2010.11.010
Shu C, Ouarda TBMJ (2008) Regional flood frequency analysis at ungauged sites using the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. J Hydrol 349:31–43. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.10.050
Sobester A, Forrester AIJ, Toal DJJ, Tresidder E, Tucker S (2014) Engineering design applications of surrogate-assisted optimization techniques. Optim Eng 15:243–265. doi:10.1007/s11081-012-9199-x
Sreekanth J, Datta B (2010) Multi-objective management of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers using genetic programming and modular neural network based surrogate models. J Hydrol 393:245–256. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.08.023
Sreekanth J, Datta B (2011a) Comparative evaluation of genetic programming and neural network as potential surrogate models for coastal aquifer management. Water Resour Manag 25:3201–3218. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9852-8
Sreekanth J, Datta B (2011b) Optimal combined operation of production and barrier wells for the control of saltwater intrusion in coastal groundwater well fields. Desalin Water Treat 32:72–78. doi:10.5004/dwt.2011.2680
Sugeno M, Yasukawa T (1993) A fuzzy logic based approach to qualitative modeling. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 1:7–31. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.1993.390281
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its application to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 15:116–132. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399
Tam VT, Batelaan O, Le TT, Nhan PQ (2014) Three-dimensional hydrostratigraphical modelling to support evaluation of recharge and saltwater intrusion in a coastal groundwater system in Vietnam. Hydrogeol J 22:1749–1762. doi:10.1007/s10040-014-1185-2
Tu JV (1996) Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 49:1225–1231. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(96)00002-9
Vithanage M, Engesgaard P, Jensen KH, Illangasekare TH, Obeysekera J (2012) Laboratory investigations of the effects of geologic heterogeneity on groundwater salinization and flush-out times from a tsunami-like event. J Contam Hydrol 136:10–24. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.05.001
Voss CI, Souza WR (1987) Variable density flow and solute transport simulation of regional aquifers containing a narrow freshwater-saltwater transition zone. Water Resour Res 23:1851–1866. doi:10.1029/WR023i010p01851
Walther M, Bilke L, Delfs J-O, Graf T, Grundmann J, Kolditz O, Liedl R (2014) Assessing the saltwater remediation potential of a three-dimensional, heterogeneous, coastal aquifer system. Environ Earth Sci 72:3827–3837. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3253-2
Welty C, Gelhar LW (1991) Stochastic analysis of the effects of fluid density and viscosity variability on macrodispersion in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour Res 27:2061–2075. doi:10.1029/91WR00837
Welty C, Gelhar LW (1992) Simulation of large-scale transport of variable density and viscosity fluids using a stochastic mean model. Water Resour Res 28:815–827. doi:10.1029/91WR02931
Yang J, Graf T, Ptak T (2015) Sea level rise and storm surge effects in a coastal heterogeneous aquifer: a 2D modelling study in northern Germany. Grundwasser 20:39–51. doi:10.1007/s00767-014-0279-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, D.K., Datta, B. Fuzzy C-Mean Clustering Based Inference System for Saltwater Intrusion Processes Prediction in Coastal Aquifers. Water Resour Manage 31, 355–376 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1531-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1531-3