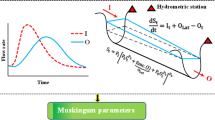
Abstract
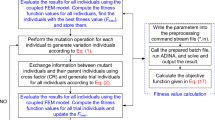
The Muskingum method is one of the most utilized lumped flood routing model in which calibration of its parameters provides an active area of research in water resources engineering. Although various techniques and versions of Muskingum model have been presented to estimate the parameters of different versions of Muskingum model, more rigorous approaches and models are still required to improve the computational precision of calibration process. In this study, a new hybrid technique was proposed for Muskingum parameter estimation which combines the Modified Honey Bee Mating Optimization (MHBMO) and Generalized Reduced Gradient (GRG) algorithms. According to the conducted literature-review on the improvement of Muskingum flood routing models, a new six-parameter Muskingum model was proposed. The hybrid technique was successfully applied for parameter estimation of this new version of Muskingum model for three case studies selected from literature. The obtained results were compared with those of other methods using several common performance evaluation criteria. The new hybrid method with the new proposed Muskingum model perform the best among all the considered approaches based on most of utilized criteria. The new Muskingum model significantly reduces the SSQ value for the double-peak case study. Finally, the achieved results demonstrate that not only the hybrid MHBMO-GRG algorithm overcomes the shortcomings of both phenomenon-mimicking and mathematical optimization techniques, but also the presented Muskingum model is appeared to be the most reliable version of Muskingum model comparing with other considered models in this research.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzali S (2016) Variable-parameter Muskingum model. Iranian J Sci Technol, Trans Civil Eng 40(1):59–68
Afzali SH, Darabi A, Niazkar M (2016) Steel frame optimal design using MHBMO algorithm. Int J Steel Struct 16(2):455–465
Barati R (2011) Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using Nelder-Mead Simplex algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 16(11):946–954
Barati R (2012) Discussion of parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using Parameter-Setting-Free Harmony Search by Zong Woo Geem
Barati R (2013) Application of Excel Solver for parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum models. KSCE J Civil Eng 17(5):1139–1148
Barati R (2014) Discussion of parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a Hybrid Harmony Search algorithm by Halil Karahan, Gurhan Gurarslan, and Zong Woo Geem. J Hydrol Eng 19(4):842–845
Chow VT (1959) Open channel hydraulics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Chu HJ, Chang LC (2009) Applying Particle Swarm Optimization to parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model. J Hydrol Eng 14(9):1024–1027
Das A (2004) Parameter estimation for Muskingum models. J Irrig Drain Eng 130(2):140–147
Easa SM (2013a) Improved nonlinear Muskingum model with variable exponent parameter. J Hydrol Eng 18(12):1790–1794
Easa SM (2013b) New and improved four-parameter non-linear Muskingum model. Proc ICE-Water Manag 167(5):288–298
Easa SM (2014) Versatile Muskingum flood model with four variable parameters. Proc ICE-Water Manag 168(3):139–148
Easa SM (2015) Evaluation of nonlinear Muskingum model with continuous and discontinuous exponent parameters. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering pp 1–10, doi:10.1007/s12205-015-0154-1
Easa SM, Barati R, Shahheydari EJN, Barati T (2014) Discussion: New and improved four-parameter non-linear Muskingum model. Proc ICE-Water Manag 167(10):612–615
Gavilan G, Houck MH (1985) Optimal Muskingum river routing. In: Computer applications in water resources, ASCE, pp 1294–1302
Geem ZW (2006) Parameter estimation for the nonlinear Muskingum model using the BFGS technique. J Irrig Drain Eng 132(5):474–478
Geem ZW (2010) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using Parameter-Setting-Free Harmony Search. J Hydrol Eng 16(8):684–688
Gill MA (1978) Flood routing by the Muskingum method. J Hydrol 36(3):353–363
Haddad OB, Hamedi F, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Orouji H, Mariño MA (2015a) Application of a hybrid optimization method in Muskingum parameter estimation. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering p 04015026
Haddad OB, Hamedi F, Orouji H, Pazoki M, Loáiciga HA (2015b) A re-parameterized and improved nonlinear Muskingum model for flood routing. Water Resour Manag 29(9):3419–3440
Hamedi F, Haddad O, Orouji H (2015) Discussion of application of Excel Solver for parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum models by Reza Barati. KSCE J Civil Eng 1(19):340–342
Hirpurkar P, Ghare AD (2014) Parameter estimation for the nonlinear forms of the Muskingum model. J Hydrol Eng 20(8):04014,085
Hosseini SM (2009) Application of spreadsheets in developing flexible multiple-reach and multiple-branch methods of Muskingum flood routing. Comput Appl Eng Educ 17(4):448–454
Karahan H (2014) Discussion of improved nonlinear Muskingum model with variable exponent parameter by Said M. Easa. J Hydrol Eng 19(10):07014,007
Karahan H, Gurarslan G, Geem ZW (2013) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid Harmony Search algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 18(3):352–360
Karahan H, Gurarslan G, Geem ZW (2015) A new nonlinear Muskingum flood routing model incorporating lateral flow. Eng Optim 47(6):737–749
Kim JH, Geem ZW, Kim ES (2001) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using Harmony Search. JAWRA J Amer Water Resour Assoc 37(5):1131–1138
Latt ZZ (2015) Application of feedforward artificial neural network in Muskingum flood routing: a black-box forecasting approach for a natural river system. Water Resour Manag 29(14):4995–5014
Luo J, Xie J (2010) Parameter estimation for nonlinear Muskingum model based on Immune Clonal Selection Algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 15(10):844–851
McCarthy GT (1938) The unit hydrograph and flood routing. In: Proceeding of the Conference of North Atlantic Division. U.S. Army Corps of Engineer District, Wahsington, DC
Moghaddam A, Behmanesh J, Farsijani A (2016) Parameters estimation for the new four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum model using the Particle Swarm Optimization. Water Resour Manag 30(7):2143–2160
Mohan S (1997) Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using Genetic Algorithm. J Hydraul Eng 123(2):137–142
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2015a) Assessment of Modified Honey Bee Mating Optimization for parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models. J Hydrol Eng 20(4):04014,055
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2015b) Optimum design of lined channel sections. Water Resour Manag 29(6):1921–1932
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2016) Streamline performance of Excel in stepwise implementation of numerical solutions. Comput Appl Eng Educ 24(4):555–566
O’Donnel T (1985) A direct three-parameter Muskingum procedure incorporating lateral inflow. Hydrol Sci J 30(4):479–496
Tung YK (1985) River flood routing by nonlinear Muskingum method. J Hydraul Eng 111(12):1447–1460
Vatankhah AR (2014) Discussion of parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid Harmony Search algorithm by Halil Karahan, Gurhan Gurarslan, and Zong Woo Geem. J Hydrol Eng 19(4):839–842
Viessman W, Lewis GL (2003) Introduction to Hydrology, 5th edn. Prentice Hall India (P) Limited
Wilson EM (1974) Engineering hydrology. Macmillan Education LTD, Hampshire, United Kingdom
Xu DM, Qiu L, Chen SY (2011) Estimation of nonlinear Muskingum model parameter using Differential Evolution. J Hydrol Eng 17(2):348–353
Yoon J, Padmanabhan G (1993) Parameter estimation of linear and nonlinear Muskingum models. J Water Resour Plan Manag 119(5):600–610
Yuan X, Wu X, Tian H, Yuan Y, Adnan RM (2016) Parameter identification of nonlinear Muskingum model with backtracking search algorithm. Water Resour Manag 30(8):2767–2783
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niazkar, M., Afzali, S.H. Application of New Hybrid Optimization Technique for Parameter Estimation of New Improved Version of Muskingum Model. Water Resour Manage 30, 4713–4730 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1449-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1449-9