Abstract
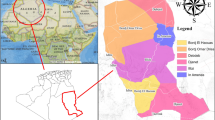
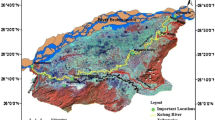
To overcome the shortcomings of the conventional variable fuzzy set assessment (VFSA) method in the dynamic water quality assessment, the functional data analysis (FDA) theory is introduced into VFSA method to develop a dynamic variable fuzzy set assessment (DVFSA) model. The procedure of DVFSA is: (1) generating continuous concentration curves through smoothing method, (2) calculating relative membership curves of indicators, (3) generating comprehensive relative membership curves, (4) making dynamic water quality assessment through calculating the ranking feature curve. DVFSA is the generalization of the conventional VFSA from discrete finite time points into continuous time domain through FDA method. DVFSA keeps the property of VFSA in fuzzy domain constructing and comprehensive classification recognizing; and absorbs the advantages of FDA in dealing with different sampling time and missing values, and representing the varying process of aquatic environment comprehensively and intuitively. Furthermore, DVFSA avoids the potential logical error by banning the least square optimization method in comprehensive relative membership generation. The dynamic water quality condition of Jiangdu hydro-junction in 2013 is assessed using DVFSA and the result shows that it belongs to classification “I” from January to April and “II” in other months. To further improve the water quality condition of Jiangdu hydro-junction, it is suggested to strengthen the environment protection in Lixiahe region and New Tongyang Canal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee T, Srivastava RK (2009) Application of water quality index for assessment of surface water quality surrounding integrated industrial estate-Pantnagar. Water Sci Technol 60(8):2041–2053
Champely S, Doledec S (1997) How to separate long-term trends from periodic variation in water quality monitoring. Water Res 31(11):2849–2857
Chen SY (1998) Engineering fuzzy set theory and application. Natl Def Ind Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chinese Environmental Protection Agency (2002) National surface water environmental quality standards of China (GB3838-2002). China Standards Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Haggarty RA, Miller CA, Scott EM (2012) Functional clustering of water quality data in Scotland. Environmetrics 23(8):685–695
Henderson B (2006) Exploring between site differences in water quality trends: a functional data analysis approach. Environmetrics 17(1):65–80
Li JZ, Tan SM, Wei ZZ et al (2014) A new method of change point detection using variable fuzzy sets under environmental change. Water Resour Manag 28:5125–5138
Local chronicles committee of Jiangsu province (2005) Water conservancy of Jiangsu province. Jiangsu Phoenix House, Nanjing (in Chinese)
Lu RS, Lo SL, Hu JY (1999) Analysis of reservoir water quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 13(5):327–336
Lu XW, Li LY, Lei K et al (2010) Water quality assessment of Wei River, China using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Environ Earth Sci 60(8):1693–1699
Ocampo-Duque W, Osorio C, Piamba C et al (2013) Water quality analysis in rivers with non-parametric probability distributions and fuzzy inference systems: Application to the Cauca River, Colombia. Environ Int 52:17–28
Office of the South-to-North water Diversion Project Commission of the State Council (2001) General Layout of South-to-North Water Diversion. http://www.nsbd.gov.cn/zx/english/erp.htm
Ramsay JO, Silverman BW (2002) Applied functional data analysis: methods and case studies. Springer, New York
Sasikumar K, Mujumdar PP (2000) Application of fuzzy probability in water quality management of a river system. Int J Syst Sci 31(5):575–591
Srdjevic B, Medeiros YDP (2008) Fuzzy AHP assessment of water management plans. Water Resour Manag 22(7):877–894
Srebotnjak T, Carr G, de Sherbinin A et al (2012) A global Water Quality Index and hot-deck imputation of missing data. Ecol Indic 17:108–119
Terrado M, Borrell E, de Campos S (2010) Surface-water-quality indices for the analysis of data generated by automated sampling networks. Trac-Trends Anal Chem 29(1):40–52
Ullah S, Finch CF (2013) Applications of functional data analysis: a systematic review. BMC Med Res Methodol 13:43
Wan XY, Zhong PA, Emmanuel K (2014) Variable sets and fuzzy rating interval for water allocation options assessment. Water Resour Manag 28:2833–2849
Wang XJ, Zhao RH, Hao YW (2011) Flood control operations based on the theory of variable fuzzy sets. Water Resour Manag 25:777–792
Wang XJ, Zou ZH, Zou H (2013) Water quality evaluation of Haihe River with fuzzy similarity measure methods. J Environ Sci-China 25(10):2041–2046
Wang YK, Sheng D, Wang D et al (2014) Variable fuzzy set theory to assess water quality of the Meiliang Bay in Taihu lake basin. Water Resour Manag 28:867–880
Yan F, Liu L (2014) Water quality assessment of the Li Canal using a functional fuzzy synthetic evaluation model, Environmental science. Processes Impacts 16(7):1764–1771
Zhang HX (2009) The analysis of the reasonable structure of water conservancy investment of capital construction in China by AHP method. Water Resour Manag 23(1):1–18
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the contract Nos. 51279060 and 41301531.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, F., Liu, L., Zhang, Y. et al. The Research of Dynamic Variable Fuzzy Set Assessment Model in Water Quality Evaluation. Water Resour Manage 30, 63–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1146-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1146-0