Abstract
Purpose
To identify preoperative factors correlated with postoperative early renal function in patients who had undergone radical cystectomy (RC) and intestinal urinary diversion.
Methods
We retrospectively identified 201 consecutive bladder cancer patients without distant metastasis who had undergone RC at our institution between 2003 and 2012. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the modified Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology equation before RC and 3 months following RC. Univariate and stepwise multiple linear regression analyses were applied to estimate postoperative renal function and to identify significant preoperative predictors of postoperative renal function.
Results
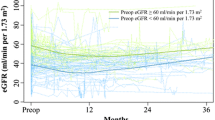
Patients who had undergone intestinal urinary diversion and were available for the collection of follow-up data (n = 164) were eligible for the present study. Median preoperative and postoperative eGFRs were 69.7 (interquartile range [IQR] 56.3–78.0) and 70.7 (IQR 57.3–78.1), respectively. In univariate analyses, age, preoperative proteinuria, thickness of abdominal subcutaneous fat tissue (TSF), preoperative serum creatinine level, preoperative eGFR, and urinary diversion type were significantly associated with postoperative eGFR. In a stepwise multiple linear regression analysis, preoperative eGFR, age, and TSF were significant factors for predicting postoperative eGFR (p < 0.001, p = 0.02, and p = 0.046, respectively). The estimated postoperative eGFRs correlated well with the actual postoperative eGFRs (r = 0.65, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Preoperative eGFR, age, and TSF were independent preoperative factors for determining postoperative renal function in patients who had undergone RC and intestinal urinary diversion. These results may be used for patient counseling before surgery, including the planning of perioperative chemotherapy administration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark PE, Agarwal N, Biagioli MC, Eisenberger MA, Greenberg RE, Herr HW et al (2013) Bladder cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 11:446–475
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19:666–675
Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration (2005) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur Urol 48:202–205
Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration (2005) Adjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration. Eur Urol 48:189–199
Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM et al (2003) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 349:859–866
Griffiths G, Hall R, Sylvester R, Raghavan D et al (2011) International phase III trial assessing neoadjuvant cisplatin, methotrexate, and vinblastine chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: long-term results of the BA06 30894 trial. J Clin Oncol 29:2171–2177
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC et al (2014) EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur Urol 65:778–792
David KA, Milowsky MI, Ritchey J et al (2007) Low incidence of perioperative chemotherapy for stage III bladder cancer 1998–2003: a report from the National Cancer Data Base. J Urol 178:451–454
Zaid HB, Patel SG, Stimson CJ et al (2014) Trends in the utilization of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: results from the National Cancer Database. Urology 83:75–80
Rehman S, Crane A, Din R et al (2013) Understanding avoidance, refusal, and abandonment of chemotherapy before and after cystectomy for bladder cancer. Urology 82:1370–1375
Canter D, Viterbo R, Kutikov A et al (2011) Baseline renal function status limits patient eligibility to receive perioperative chemotherapy for invasive bladder cancer and is minimally affected by radical cystectomy. Urology 77:160–165
Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Kim SP et al (2014) Eligibility for neoadjuvant/adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy among radical cystectomy patients. BJU Int 113:17–21
Horio M, Imai E, Yasuda Y et al (2010) Modification of the CKD epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation for Japanese: accuracy and use for population estimates. Am J Kidney Dis 56:32–38
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH et al (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
Fujii T, Tsutsumi S, Matsumoto A et al (2010) Thickness of subcutaneous fat as a strong risk factor for wound infections in elective colorectal surgery: impact of prediction using preoperative CT. Dig Surg 27:331–335
Foster MC, Hwang SJ, Larson MG et al (2008) Overweight, obesity, and the development of stage 3 CKD: the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Kidney Dis 52:39–48
Elsayed EF, Sarnak MJ, Tighiouart H et al (2008) Waist-to-hip ratio, body mass index, and subsequent kidney disease and death. Am J Kidney Dis 52:29–38
Oh H, Quan SA, Jeong JY et al (2013) Waist circumference, not body mass index, is associated with renal function decline in korean population: Hallym Aging Study. PLoS ONE 8:e59071
Bavbek N, Isik B, Kargili A et al (2008) Association of obesity with inflammation in occult chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol 21:761–767
Carey VJ, Walters EE, Colditz GA et al (1997) Body fat distribution and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. The Nurses’ Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 145:614–619
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R (2004) Waist circumference and not body mass index explains obesity-related health risk. Am J Clin Nutr 79:379–384
Tanaka S, Horimai C, Katsukawa F (2003) Ethnic differences in abdominal visceral fat accumulation between Japanese, African-Americans, and Caucasians: a meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol 40:S302–S304
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest with any institution or product.
Informed consent
The institutional review board approved this retrospective study and issued a waiver of informed consent. IRB approved protocol number is 1621.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gondo, T., Ohno, Y., Nakashima, J. et al. Preoperative determinant of early postoperative renal function following radical cystectomy and intestinal urinary diversion. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 233–238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1462-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1462-1