Abstract
Purpose
In bladder cancer (BCa) patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy (RCPx), concomitant prostate cancer (PCa) is a common finding. Up to now there is no clear evidence to suggest that concomitant PCa is a predictor of outcome in these patients. Aim of this study was to assess incidence and clinicopathologic characteristics of concomitant PCa in RCPx specimen and correlate it to survival parameters from a single-centre material over two decades.
Methods
All men who had undergone RCPx for BCa at our institution between 1994 and 2013 were included in this study. Clinicopathologic parameters for BCa and PCa were evaluated and correlated with outcome parameters. Survival analysis was performed for the subgroup of nonmetastatic organ-confined BCa to evaluate the role of concomitant Gleason Score (GS) ≥7 PCa.
Results
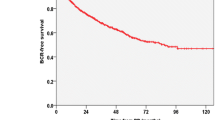
Of 945 men who had undergone RCPx for BCa, concomitant PCa was present in 237 patients (25.1 %). There was a significant increase in PCa incidence from 18.9 to 32.3 % between 1994 and 2013 (p = 0.009). Concomitant PCa represented a more aggressive phenotype at the end of the study (p = 0.037). In nonmetastatic organ-confined BCa, concomitant GS ≥7 PCa (HR 3.09; p = 0.0001) and age > 68 (HR 1.80; p = 0.0004) were independent negative predictors for overall survival.
Conclusions
Concomitant PCa in RCPx specimen of BCa patients is a common finding. The incidence of concomitant PCa has significantly increased within 2 decades, presenting a more aggressive phenotype. Age and in particular concomitant GS ≥7 PCa are independent prognosticators for poor survival in patients with nonmetastatic organ-confined BCa.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCa:
-
Bladder cancer
- GS:
-
Gleason Score
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- ICR:
-
Interquartile range
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PCa:
-
Prostate cancer
- RCPx:
-
Radical cystoprostatectomy
References
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC et al (2014) EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur Urol 65:778–792
Daminao R, Di Lorenzo G, Cantiello F et al (2007) Clinicopathologic features of prostate adenocarcinoma incidentally discovered at time of radical cystectomy: an evidence-based analysis. Eur Urol 52:648–657
Thomas C, Wiesner C, Melchior S et al (2008) Indications for preoperative prostate biopsy in patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy for bladder cancer. J Urol 180:1938–1941
Gakis G, Schilling D, Bedke J et al (2009) Incidental prostate cancer at radical cystoprostatectomy: implications for apex-sparing surgery. BJU Int 105:468–471
Wetterauer C, Weibel M, Gsponer JR et al (2014) Incidental prostate cancer prevalence at radical cystoprostatectomy, importance of histopathological work-up. Virchows Arch 465:629–636
Barbisan F, Mazzucchelli R, Scarpelli M et al (2008) Urothelial and incidental prostate carcinoma in prostates from cystoprostatectomies for bladder cancer: is there a relationship between urothelial and prostate cancer? BJU Int 103:158–1063
Pepe P, Fraggetta F, Galia A et al (2014) Preoperative findings, pathological stage PSA recurrence in men with prostate cancer incidentally detected at radical cystectomy: our experience in 242 cases. Int Urol Nephrol 46:1325–1328
Alsinnawi M, Loftus B, Flynn R et al (2012) The incidence and relevance of prostate cancer in radial cystoprostatectomy specimens. Int Urol Nephrol 44:1705–1710
Kurahashi T, Miyake H, Furukawa J et al (2010) Characterization of prostate cancer incidentally detected in radical cystoprostatectomy specimens from Japanese men with bladder cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 42:73–79
Pignot G, Salomon L, Neuzillet Y et al (2014) Clinicopathological characteristics of incidental prostate cancer discovered from radical cystoprostatectomy specimen: a multicenter French study. Ann Sug Oncol 21:684–690
Bruins HM, Djaladat H, Ahmadi H et al (2013) Incidental prostate cancer in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma: comprehensive analysis of 1476 radical cystoprostatectomy specimen. J Urol 109:1704–1709
Buse S, Höfner T, Müller SC et al (2013) Characterization and risk stratification of prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy. Int J Urol 20:866–871
Fritsche HM, Aziz A, Eder F et al (2012) Potentially clinically relevant prostate cancer is found frequently after complete than after partial histopathological processing of radical cystoprostatectomy specimen. Virchws Arch 461:655–661
Greenberg DC, Wright KA, Lophathanon A et al (2013) Changing presentation of prostate cancer in a UK population–10 year trends in prostate cancer risk profiles in the East of England. Br J Cancer 109:2115–2120
Mistry M, Parkin DM, Ahmad AS et al (2011) Cancer incidence in the United Kindom:projections to the year 2030. Br J Cancer 105:1795–1803
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC, Amn MB et al (2005) The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference of gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 29:1228
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19:666–675
Gakis G, Stenz A, Renninger M (2013) Evolution of the concept of androgen-sensitive bladder cancer. Scand J Urol 47:173–178
Miyamoto H, Yang Z, Chen YT et al (2007) Promotion of bladder cancer development and progression by androgen receptor signals. J Natl Cancer Inst 99:558–568
Jing Y, Cui D, Guo W et al (2014) Activated androgen receptor promotes bladder cancer metastasis via Slug mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett 348:135–145
Izumi K, Taguri M, Miyamoto H et al (2014) Androgen deprivation therapy prevents bladder cancer recurrence. Oncotarget 30:12665–12674
Giovannucci E, Liu Y, Platz EA et al (2007) Risk factors for prostate cancer incidence and progression in the health professionals follow-up study. Int J Cancer 121:1571–1578
Häggström C, Stocks T, Ulmert D et al (2012) Prospective study on metabolic factors and risk of prostate cancer. Cancer 118:6199–6206
Häggström C, Stocks T, Nagel G et al (2014) Prostate cancer, prostate cancer death, and death from other causes, among men with metabolic aberrations. Epidemiology 25:823–828
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the doctoral thesis of Alexander Giesswein. We thank Lara Ermer, Katharina Sprigade and Annika Miller for their support in data acquisition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Christoph Wiesner and Joachim W. Thüroff have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, C., Giesswein, A., Hainz, M. et al. Concomitant Gleason Score ≥7 prostate cancer is an independent prognosticator for poor survival in nonmetastatic bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 1789–1796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1110-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1110-1