Abstract
Objective
A variety of murine models of experimental prostatitis that mimic the phenotype of human chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) have been developed. However, there is still a lack of explicit diagnosis criteria about those animal model. Our study is to establish histopathological classification criteria, which will be conducive to evaluate the animal models.
Methods
We firstly established a rat model of experimental autoimmune prostatitis that is considered a valid model for CP/CPPS. For modelling, male Sprague–Dawley rats were immunized with autologous prostate tissue homogenate supernatant emulsified with complete Freund’s adjuvant by subcutaneous injection into abdominal flank and simultaneously immunized with pertussis–diphtheria–tetanus vaccine by intraperitoneal injection. Three immunizations were administered semimonthly. At the 45th day, animals were killed, and prostate tissues were examined for morphology.
Results
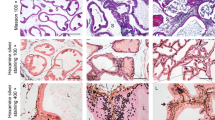
Histologically, the prostate tissues were characterized by lymphoproliferation, atrophy of acini, and chronic inflammatory cells infiltration in the stromal connective tissue around the acini or ducts. Finally, we built histopathological classification criteria incorporating inflammation locations (mesenchyme, glands, periglandular tissues), ranges (focal, multifocal, diffuse), and grades (grade I–IV). To verify the effectiveness and practicability of the histopathological classification criteria, we conducted the treatment study with one of the alpha blockers, tamsulosin.
Conclusion
The histopathological classification criteria of rat model of CP/CPPS will serve for further research of the pathogenesis and treatment strategies of the disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaeffer AJ (2006) Clinical practice. Chronic prostatitis and the chronic pelvic pain syndrome. N Engl J Med 355:1690–1698
Collins MM, Stafford RS, O’Leary MP, Barry MJ (1998) How common is prostatitis? A national survey of physician visits. J Urol 159:1224–1228
Pontari MA, Joyce GF, Wise M, McNaughton-Collins M (2007) Prostatitis. J Urol 177:2050–2057
Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr, Nickel JC (1999) NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA 282:236–237
Nickel JC, Nyberg LM, Hennenfent M (1999) Research guidelines for chronic prostatitis: consensus report from the first national institutes of health international prostatitis collaborative network. Urology 54:229–233
Marszalek M, Wehrberger C, Temml C, Ponholzer A, Berger I, Madersbacher S (2009) Chronic pelvic pain and lower urinary tract symptoms in both sexes: analysis of 2749 participants of an urban health screening project. Eur Urol 55:499–507
Habermacher GM, Chason JT, Schaeffer AJ (2006) Prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Annu Rev Med 57:195–206
Nickel JC, Downey J, Hunter D, Clark J (2001) Prevalence of prostatitis-like symptoms in a population based study using the national institutes of health chronic prostatitis symptom index. J Urol 165:842–845
Wagenlehner FM, van Till JW, Magri V, Perletti G, Houbiers JG, Weidner W et al (2013) National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) symptom evaluation in multinational cohorts of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Eur Urol 63:953–959
Walz J, Perrotte P, Hutterer G, Suardi N, Jeldres C, Benard F et al (2007) Impact of chronic prostatitis-like symptoms on the quality of life in a large group of men. BJU Int 100:1307–1311
Nickel JC (2009) Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain: the syndrome. J Urol 182:18–19
Pontari M (2009) Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain: the disease. J Urol 182:19–20
Tripp DA, Nickel JC, Ross S, Mullins C, Stechyson N (2009) Prevalence, symptom impact and predictors of chronic prostatitis-like symptoms in Canadian males aged 16–19 years. BJU Int 103:1080–1084
Shoskes DA, Nickel JC, Rackley RR, Pontari MA (2009) Clinical phenotyping in chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and interstitial cystitis: a management strategy for urologic chronic pelvic pain syndromes. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12:177–183
Sonmez NC, Kiremit MC, Guney S, Arisan S, Akca O, Dalkilic A (2011) Sexual dysfunction in type III chronic prostatitis (CP) and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) observed in Turkish patients. Int Urol Nephrol 43:309–314
Ismail M, Mackenzie K, Hashim H (2013) Contemporary treatment options for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Drugs Today (Barc) 49:457–462
Anothaisintawee T, Attia J, Nickel JC, Thammakraisorn S, Numthavaj P, McEvoy M et al (2011) Management of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. JAMA 305:78–86
Tang P, Xie KJ, Wang B, Deng XR, Ou RB (2010) Antibacterial therapy improves the effectiveness of prostate cancer detection using prostate-specific antigen in patients with asymptomatic prostatitis. Int Urol Nephrol 42:13–18
Tomaskovic I, Ruzic B, Trnski D, Kraus O (2009) Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males may be an autoimmune disease, potentially responsive to corticosteroid therapy. Med Hypotheses 72:261–262
Ku JH, Kim SW, Paick JS (2005) Epidemiologic risk factors for chronic prostatitis. Int J Androl 28:317–327
Pontari MA, McNaughton-Collins M, O’Leary MP, Calhoun EA, Jang T, Kusek JW et al (2005) A case–control study of risk factors in men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome. BJU Int 96:559–565
Krieger JN, Ross SO, Riley DE (2002) Chronic prostatitis: epidemiology and role of infection. Urology 60:8–13
Vykhovanets EV, Resnick MI, MacLennan GT, Gupta S (2007) Experimental rodent models of prostatitis: limitations and potential. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 10:15–29
Rivero VE, Motrich RD, Maccioni M, Riera CM (2007) Autoimmune etiology in chronic prostatitis syndrome: an advance in the understanding of this pathology. Crit Rev Immunol 27:33–46
Altuntas CZ, Daneshgari F, Veizi E, Izgi K, Bicer F, Ozer A et al (2013) A novel murine model of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) induced by immunization with a spermine binding protein (p25) peptide. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 304:R415–R422
Galmarini M, Riera CM, Pesoa S, Vullo C, Vottero-Cima E (1981) Induction of humoral autoimmune response to rat male accessory glands. Medicina (B Aires) 41:349–353
Maccioni M, Rivero V, Riera CM (1996) Autoantibodies against rat prostate antigens. Association of specific IGG2b and IGG2c with the DTH response. J Autoimmun 9:485–491
Keetch DW, Humphrey P, Ratliff TL (1994) Development of a mouse model for nonbacterial prostatitis. J Urol 152:247–250
Rivero V, Carnaud C, Riera CM (2002) Prostatein or steroid binding protein (PSBP) induces experimental autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) in NOD mice. Clin Immunol 105:176–184
Penna G, Amuchastegui S, Cossetti C, Aquilano F, Mariani R, Giarratana N et al (2007) Spontaneous and prostatic steroid binding protein peptide-induced autoimmune prostatitis in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J Immunol 179:1559–1567
Maccioni M, Rivero VE, Riera CM (1998) Prostatein (or rat prostatic steroid binding protein) is a major autoantigen in experimental autoimmune prostatitis. Clin Exp Immunol 112:159–165
Liu KJ, Chatta GS, Twardzik DR, Vedvick TS, True LD, Spies AG et al (1997) Identification of rat prostatic steroid-binding protein as a target antigen of experimental autoimmune prostatitis: implications for prostate cancer therapy. J Immunol 159:472–480
Pontari MA (2013) Etiology of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: psychoimmunoneurendocrine dysfunction (PINE syndrome) or just a really bad infection? World J Urol 31:725–732
Nickel JC, Alexander RB, Schaeffer AJ, Landis JR, Knauss JS, Propert KJ et al (2003) Leukocytes and bacteria in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome compared to asymptomatic controls. J Urol 170:818–822
Keith IM, Jin J, Neal D Jr, Teunissen BD, Moon TD (2001) Cell relationship in a Wistar rat model of spontaneous prostatitis. J Urol 166:323–328
Naslund MJ, Strandberg JD, Coffey DS (1988) The role of androgens and estrogens in the pathogenesis of experimental nonbacterial prostatitis. J Urol 140:1049–1053
Seo SI, Lee SJ, Kim JC, Choi YJ, Sw SW, Hwang TK et al (2003) Effects of androgen deprivation on chronic bacterial prostatitis in a rat model. Int J Urol 10:485–491
Robinette CL (1988) Sex-hormone-induced inflammation and fibromuscular proliferation in the rat lateral prostate. Prostate 12:271–286
Yatkin E, Bernoulli J, Talvitie EM, Santti R (2009) Inflammation and epithelial alterations in rat prostate: impact of the androgen to oestrogen ratio. Int J Androl 32:399–410
Bernoulli J, Yatkin E, Konkol Y, Talvitie EM, Santti R, Streng T (2008) Prostatic inflammation and obstructive voiding in the adult Noble rat: impact of the testosterone to estradiol ratio in serum. Prostate 68:1296–1306
Matsumoto S, Kawai Y, Oka M, Oyama T, Hashizume K, Wada N et al (2013) Bladder function in 17β-estradiol-induced nonbacterial prostatitis model in Wistar rat. Int Urol Nephrol 45:749–754
Qi X, Han L, Liu X, Zhi J, Zhao B, Chen D et al (2012) Prostate extract with aluminum hydroxide injection as a novel animal model for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology 80(1389):e1389–e1389
Chung SD, Lin HC (2013) Association between chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and anxiety disorder: a population-based study. PLoS ONE 8:e64630
Anderson RU, Orenberg EK, Morey A, Chavez N, Chan CA (2009) Stress induced hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis responses and disturbances in psychological profiles in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol 182:2319–2324
Gatenbeck L, Aronsson A, Dahlgren S, Johansson B, Stromberg L (1987) Stress stimuli-induced histopathological changes in the prostate: an experimental study in the rat. Prostate 11:69–76
Takechi S, Yokoyama M, Tanji N, Nishio S, Araki N (1999) Nonbacterial prostatitis caused by partial urethral obstruction in the rat. Urol Res 27:346–350
Sharma OP, Adlercreutz H, Strandberg JD, Zirkin BR, Coffey DS, Ewing LL (1992) Soy of dietary source plays a preventive role against the pathogenesis of prostatitis in rats. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 43:557–564
Kwon SM, Kim SI, Chun DC, Cho NH, Chung BC, Park BW et al (2001) Development of rat prostatitis model by oral administration of isoflavone and its characteristics. Yonsei Med J 42:395–404
Motrich RD, Maccioni M, Riera CM, Rivero VE (2007) Autoimmune prostatitis: state of the art. Scand J Immunol 66:217–227
Zhang ZY, Schluesener HJ (2012) HDAC inhibitor MS-275 attenuates the inflammatory reaction in rat experimental autoimmune prostatitis. Prostate 72:90–99
Penna G, Fibbi B, Maggi M, Adorini L (2009) Prostate autoimmunity: from experimental models to clinical counterparts. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 5:577–586
Motrich RD, Maccioni M, Ponce AA, Gatti GA, Oberti JP, Rivero VE (2006) Pathogenic consequences in semen quality of an autoimmune response against the prostate gland: from animal models to human disease. J Immunol 177:957–967
Ludwig M, Steltz C, Huwe P, Schaffer R, Altmannsberger M, Weidner W (2001) Immunocytological analysis of leukocyte subpopulations in urine specimens before and after prostatic massage. Eur Urol 39:277–282
Kouiavskaia DV, Southwood S, Berard CA, Klyushnenkova EN, Alexander RB (2009) T-cell recognition of prostatic peptides in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol 182:2483–2489
Dunphy EJ, Eickhoff JC, Muller CH, Berger RE, McNeel DG (2004) Identification of antigen-specific IgG in sera from patients with chronic prostatitis. J Clin Immunol 24:492–502
Hou Y, DeVoss J, Dao V, Kwek S, Simko JP, McNeel DG et al (2009) An aberrant prostate antigen-specific immune response causes prostatitis in mice and is associated with chronic prostatitis in humans. J Clin Invest 119:2031–2041
Ponniah S, Arah I, Alexander RB (2000) PSA is a candidate self-antigen in autoimmune chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Prostate 44:49–54
Rivero VE, Iribarren P, Riera CM (1995) Mast cells in accessory glands of experimentally induced prostatitis in male Wistar rats. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 74:236–242
Depiante-Depaoli M, Pacheco-Rupil B, Britos S, Casas A (1984) Experimental autoimmune damage to rat male accessory glands. I. Transfer of autoimmune response by spleen cells. Am J Reprod Immunol 5:9–14
Depiante-Depaoli M, Pacheco-Rupil B (1985) Experimental autoimmunity to rat male accessory glands (MAG): circulating antibodies, immunoglobulins bound to target glands, and immunoglobulins-secreting cells. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol 7:32–38
Casas-Ingaramo A, Depiante-Depaoli M, Pacheco-Rupil B (1991) Activation of cytotoxic cells by syngeneic prostate antigens in experimental autoimmune vesiculo-prostatitis. Autoimmunity 9:151–157
Penna G, Amuchastegui S, Cossetti C, Aquilano F, Mariani R, Sanvito F et al (2006) Treatment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis in nonobese diabetic mice by the vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol. J Immunol 177:8504–8511
Jackson CM, Flies DB, Mosse CA, Parwani A, Hipkiss EL, Drake CG (2013) Strain-specific induction of experimental autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) in mice. Prostate 73:651–656
Breser ML, Motrich RD, Sanchez LR, Mackern-Oberti JP, Rivero VE (2013) Expression of CXCR3 on specific T cells is essential for homing to the prostate gland in an experimental model of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Immunol 190:3121–3133
Klyushnenkova EN, Kouiavskaia DV, Kodak JA, Vandenbark AA, Alexander RB (2007) Identification of HLA-DRB1*1501-restricted T-cell epitopes from human prostatic acid phosphatase. Prostate 67:1019–1028
Fong L, Ruegg CL, Brockstedt D, Engleman EG, Laus R (1997) Induction of tissue-specific autoimmune prostatitis with prostatic acid phosphatase immunization: implications for immunotherapy of prostate cancer. J Immunol 159:3113–3117
Motrich RD, van Etten E, Baeke F, Riera CM, Mathieu C, Rivero VE (2010) Crucial role of interferon-gamma in experimental autoimmune prostatitis. J Urol 183:1213–1220
Zhang ZY, Zug C, Schluesener HJ (2011) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator FTY720 suppresses rat experimental autoimmune prostatitis. Scand J Immunol 73:546–553
Cunha GR, Donjacour AA, Cooke PS, Mee S, Bigsby RM, Higgins SJ et al (1987) The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocr Rev 8:338–362
Pontari MA, Ruggieri MR (2008) Mechanisms in prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol 179:S61–S67
Byun JS, Yoon TK, Rhee HW, Kim JH, Shin JS, Kim HS et al (2012) Chronic pelvic pain syndrome and semen quality of Korean men in their fourth decade. J Androl 33:876–885
Meng J, Mostaghel EA, Vakar-Lopez F, Montgomery B, True L, Nelson PS (2011) Testosterone regulates tight junction proteins and influences prostatic autoimmune responses. Horm Cancer 2:145–156
Sugimoto M, Oka M, Tsunemori H, Yamashita M, Kakehi Y (2011) Effect of a phytotherapeutic agent, Eviprostat®, on prostatic and urinary cytokines/chemokines in a rat model of nonbacterial prostatitis. Prostate 71:438–444
Shibuya S, Xia Z, Sugimoto M, Ueda N, Haba R, Kakehi Y (2014) The phytotherapeutic agent, eviprostat, suppresses stromal proliferation and inflammation even after establishment of nonbacterial prostatitis in the rat prostate. Urology 83:528–534
Tsunemori H, Sugimoto M, Xia Z, Taoka R, Oka M, Kakehi Y (2011) Effect of the phytotherapeutic agent eviprostat on inflammatory changes and cytokine production in a rat model of nonbacterial prostatitis. Urology 77(1507):e1515–e1520
Wilson MJ, Woodson M, Wiehr C, Reddy A, Sinha AA (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of estradiol-induced nonbacterial prostatitis in the lateral prostate lobe of the Wistar rat. Exp Mol Pathol 77:7–17
Nickel JC, True LD, Krieger JN, Berger RE, Boag AH, Young ID (2001) Consensus development of a histopathological classification system for chronic prostatic inflammation. BJU Int 87:797–805
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270195), and the Key Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (SHD09411950400). We thank Shanghai Showbio, Biotech Co., Ltd. and Dr Yan-Qin Hu (Shanghai Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Shanghai, China) for their expert technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xianjin Wang and Shan Zhong have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhong, S., Xu, T. et al. Histopathological classification criteria of rat model of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 307–316 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0868-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0868-x