Abstract
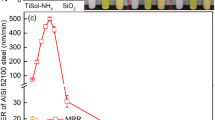
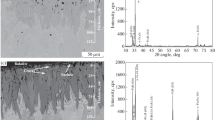
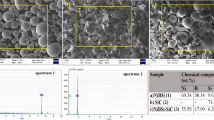
AISI 1045 steel has been widely used as the substrate for thin film deposition. In some cases, an ultra-smooth surface of AISI 1045 steel is needed and is even indispensible for the satisfactory deposition of thin film. In this paper, chemical mechanical polishing technique was employed to prepare the ultra-smooth surface of AISI 1045 steel. The effects of pH and H2O2 on the polishing performance of AISI 1045 steel were investigated. It is revealed that, with the increase of pH, the material removal rate (MRR) and the static etching rate (SER) of AISI 1045 steel gradually decrease due to the formation of passive iron oxides on the top surface, and thus the surface quality gradually improves. At pH 4.00, with the addition of H2O2, the SER of AISI 1045 steel is further suppressed; while the MRR of AISI 1045 steel first dramatically increases due to the formation of porous iron oxides with relatively low mechanical strength on the surface when the H2O2 concentration increases from 0 to 0.01 wt%, and then decreases since the porous iron oxides gradually grow compact when the H2O2 concentration further increases. The increase of the compactness of the iron oxides might be attributed to the crystallization of γ-FeOOH into α-FeOOH and even into α-Fe2O3 and the resulting polymerization of the amorphous iron oxides.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Contreras, G., Fajardo, C., Berríos, J., Pertuz, A., Chitty, J., Hintermann, H., Puchi, E.: Fatigue properties of an AISI 1045 steel coated with an electroless Ni–P deposit. Thin Solid Films 355, 480–486 (1999)
Su, Y., Yao, S., Wei, C., Kao, W., Wu, C.: Influence of single- and multilayer TiN films on the axial tension and fatigue performance of AISI 1045 steel. Thin Solid Films 338(1), 177–184 (1999)
Ahn, S., Yoo, J., Choi, Y., Kim, J., Han, J.: Corrosion behavior of PVD-grown WC–(Ti1−xAlx)N films in a 3.5 % NaCl solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 162(2), 212–221 (2003)
Qingliang, W., Yanmin, S., Lei, Z.: Tribological properties of diamond-like carbon films deposited by PECVD. Chi. J. Mater. Res. 25(1), 73–78 (2011). (in Chinese)
Wang, Y.-R., Wang, Y.-Q., Hui, Z.-P., Song, J.-I.: Mechanical properties of AISI 1045 ceramic coated materials by nano indentation and crack opening displacement method. J. Central South Univ. 19(11), 3023–3027 (2012)
Aperador, W., Caicedo, J.C., España, C., Cabrera, G., Amaya, C.: Bilayer period effect on corrosion–erosion resistance for [TiN/AlTiN]n multilayered growth on AISI 1045 steel. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71(12), 1754–1759 (2010)
Li-na, Z., Cheng-biao, W., Hai-dou, W., Bin-shi, X., Da-ming, Z., Jia-jun, L., Guo-lu, L.: Tribological properties of WS2 composite film prepared by a two-step method. Vacuum 85(1), 16–21 (2010)
Caicedo, J.C., Cabrera, G., Caicedo, H.H., Amaya, C., Aperador, W.: Nature in corrosion–erosion surface for [TiN/TiAlN]n nanometric multilayers growth on AISI 1045 steel. Thin Solid Films 520(13), 4350–4361 (2012)
Peng, D.-X.: Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using aluminum nanoparticles abrasive slurry. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 66(1), 124–130 (2014)
Hu, X., Song, Z., Liu, W., Qin, F., Zhang, Z., Wang, H.: Chemical mechanical polishing of stainless steel foil as flexible substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(15), 5798–5802 (2012)
Lee, S.-J., Chen, Y.-H., Hu, S.-C., Lin, Y.-C., Chang, J.-W., Poon, T.-L., Ke, W.-C.: Improved performance of amorphous Si thin-film solar cells on 430 stainless steel substrate by an electrochemical mechanical polishing process. J. Alloys Compd. 558, 95–98 (2013)
Li, Y.: Microelectronic applications of chemical mechanical planarization. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Zhao, D., Lu, X.: Chemical mechanical polishing: theory and experiment. Friction 1(4), 306–326 (2013)
Zhang, W., Lei, H.: Abrasive-free polishing of hard disk substrate with H2O2-C4H10O2-Na2S2O5 slurry. Friction 1(4), 359–366 (2013)
He, X., Chen, Y., Zhao, H., Sun, H., Lu, X., Liang, H.: Y2O3 nanosheets as slurry abrasives for chemical–mechanical planarization of copper. Friction 1(4), 327–332 (2013)
Ahn, Y., Yoon, J.-Y., Baek, C.-W., Kim, Y.-K.: Chemical mechanical polishing by colloidal silica-based slurry for micro-scratch reduction. Wear 257(7–8), 785–789 (2004)
Xiangfeng, C., Xiujin, L., Yongping, D., Wangbing, Z., Linshan, B.: Investigation of CMP of Ni in the preparation process of micro-electro-mechanical system devices. Rare Metal Mater Eng 41(4), 585–588 (2012)
Lei, H., Luo, J.: CMP of hard disk substrate using a colloidal SiO2 slurry: preliminary experimental investigation. Wear 257(5–6), 461–470 (2004)
Peethala, B.C., Amanapu, H.P., Lagudu, U.R.K., Babu, S.V.: Cobalt polishing with reduced galvanic corrosion at copper/cobalt interface using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizer in colloidal silica-based slurries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159(6), H582–H588 (2012)
Jindal, A., Babu, S.: Effect of pH on CMP of copper and tantalum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151(10), G709–G716 (2004)
Nishizawa, H., Nojo, H., Isobe, A.: Fundamental study of chemical–mechanical polishing slurry of cobalt barrier metal for the next-generation interconnect process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49(5), 05FC03-01-05FC03-02 (2010)
Teugels, L., Eynde, M.V.D., Delande, T., Leunissen, P.: Chemical mechanical polishing of nickel for damascene applications. In: Clarkson University 17th International Symposium on Chemical Mechanical Planarization, Lake Placid, NY, USA 2012
Li, J., Chai, Z., Liu, Y., Lu, X.: Tribo-chemical behavior of copper in chemical mechanical planarization. Tribol. Lett. 50(2), 177–184 (2013)
Du, T., Vijayakumar, A., Sundaram, K.B., Desai, V.: Chemical mechanical polishing of nickel for applications in MEMS devices. Microelectron. Eng. 75(2), 234–241 (2004)
Beverskog, B., Puigdomenech, I.: Revised Pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25–300 °C. Corros. Sci. 38(12), 2121–2135 (1996)
Vesel, A., Mozetič, M., Zalar, A.: Oxidation of AISI 304L stainless steel surface with atomic oxygen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 200(1), 94–103 (2002)
Deshpande, S., Kuiry, S.C., Klimov, M., Seal, S.: Elucidating Cu-glycine and BTA complexations in Cu-CMP using SIMS and XPS. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 8(4), G98–G101 (2005)
Yulan, R., Jingmin, Y., Yinghua, L., Yingli, W.: Inhibition behavior and mechanism of molybdate compound inhibitor for carbon steel in sea water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(4), 23–25 (2007). (in Chinese)
Wilson, D., Langell, M.A.: XPS analysis of oleylamine/oleic acid capped Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a function of temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 303, 6–13 (2014)
Graat, P.C.J., Somers, M.A.J.: Simultaneous determination of composition and thickness of thin iron-oxide films from XPS Fe 2p spectra. Appl. Surf. Sci. 100–101, 36–40 (1996)
Jie, D., Junhua, D., Enhou, H., Chunming, L., Wei, K.: Rusting evolvement of mild steel under wet/dry cyclic condition with pH 4.00 NaHSO3 solution. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. 21(1), 1–4 (2009). (in Chinese)
Joong Kim, K., Moon, D.W., Lee, S.K., Jung, K.-H.: Formation of a highly oriented FeO thin film by phase transition of Fe3O4 and Fe nanocrystallines. Thin Solid Films 360(1–2), 118–121 (2000)
Gao, X., Wu, X., Zhang, Z., Guan, H., Han, E.-H.: Characterization of oxide films grown on 316L stainless steel exposed to H2O2-containing supercritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 42(1), 157–163 (2007)
Choi, S., Tripathi, S., Dornfeld, D.A., Doyle, F.M.: Copper CMP modeling: millisecond scale adsorption kinetics of BTA in glycine-containing solutions at pH 4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(12), H1153–H1159 (2010)
Junhua, D., Wei, K.: The accelerated test of simulated atmospheric corrosion and the rust evolution of low carbon steel. Electrochemistry 15(2), 170–178 (2009). (in Chinese)
Chao, Y., Huixia, Z., Weimin, G., Yubin, F.: Effects of H2O2 addition on corrosion behavior of high-strength low-alloy steel in seawater. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Protect. 33(003), 205–210 (2013). (in Chinese)
Xiaofang, Y., Wenlong, Z.: Analysis on the corrosion rust of weathering steel and carbon steel exposed to atmosphere for two years. Corros. Prot. 23(3), 97–98 (2002). (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support of NSFC of China (51321092 and 51275263) and the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. 2014CB046404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., He, Y. & Luo, J. Effects of pH and Oxidizer on Chemical Mechanical Polishing of AISI 1045 Steel. Tribol Lett 56, 327–335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0412-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0412-2