Abstract
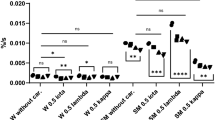
Emulsions have been used as a model food system for many studies on food behavior, including tribological studies. Several studies have examined the effect of fat content and emulsifier on emulsion friction behavior; however, other emulsion parameters such as ionic strength, pH, and homogenization pressure have received little attention in the literature. Additionally, emulsion friction measurements are generally compared to sensory data rather than physical property data. Thus, the objective of this study was to investigate the effect of various emulsion parameters on emulsion physical properties and rheological and friction behavior. Emulsion salt content, pH, and homogenization pressure all affected friction behavior, with specific effects dependent on the emulsifying protein. All emulsions showed reduced friction coefficient with increased fat content. Emulsion rheological behavior was not strongly impacted by changes in the emulsion parameters. Changing emulsion pH had the strongest effect on emulsion physical properties. The results of this study suggest that tribology may be used to develop a “fingerprint” for emulsions prepared using different parameters, allowing improved differentiation of these emulsions compared to traditional rheometry.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dresselhuis, D.M., de Hoog, E.H.A., Cohen Stuart, M.A., van Aken, G.A.: Application of oral tissue in tribological measurements in an emulsion perception context. Food Hydrocoll. 22, 323–335 (2008)
Bellamy, M., Godinot, N., Mischler, S., Martin, N., Hartmann, C.: Influence of emulsion composition on lubrication capacity and texture perception. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 44, 1939–1949 (2009)
Malone, M.E., Appelqvist, I.A.M., Norton, I.T.: Oral behaviour of food hydrocolloids and emulsions. Part 1. Lubrication and deposition considerations. 6th International Hydrocolloids Conference—part 2, vol. 17, pp. 763–773 (2003)
Dresselhuis, D., Klok, H., Stuart, M., de Vries, R., van Aken, G., de Hoog, E.: Tribology of o/w emulsions under mouth-like conditions: determinants of friction. Food Biophys. 2, 158–171 (2007)
Chojnicka-Paszun, A., de Jongh, H.H.J., de Kruif, C.G.: Sensory perception and lubrication properties of milk: influence of fat content. 7th NIZO Dairy Conference, vol. 26, pp. 15–22 (2012)
Terpstra, M.E.J., Jellema, R.H., Janssen, A.M., de Wijk, R.A., Prinz, J.F., van der Linden, E.: Prediction of texture perception of mayonnaises from rheological and novel instrumental measurements. J. Texture Stud. 40, 82–108 (2009)
Meyer, D., Vermulst, J., Tromp, R.H., De Hoog, E.H.A.: The effect of inulin on tribology and sensory profiles of skimmed milk. J. Texture Stud. 42, 387–393 (2011)
de Wijk, R.A., Prinz, J.F., Janssen, A.M.: Explaining perceived oral texture of starch-based custard desserts from standard and novel instrumental tests. Food Hydrocoll. 20, 24–34 (2006)
Butt, H.J., Graf, K., Kappl, M.: Friction, lubrication, and wear. Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces, pp. 223–245. Wiley, New Jersey (2004)
Bongaerts, J.H.H., Fourtouni, K., Stokes, J.R. Soft-tribology: lubrication in a compliant PDMS–PDMS contact. Tribology at the Interface: Proceedings of the 33rd Leeds-Lyon Symposium on Tribology (Leeds, 2006), vol. 40, pp. 1531–1542 (2007)
Selway, N., Stokes, J.R.: Insights into the dynamics of oral lubrication and mouthfeel using soft tribology: Differentiating semi-fluid foods with similar rheology. Food Res. Int. 54, 423–431 (2013)
de Vicente, J., Stokes, J.R., Spikes, H.A.: The frictional properties of Newtonian fluids in rolling–sliding soft-EHL contact. Tribol. Lett. 20, 273–286 (2005)
Stokes, J.R., Macakova, L., Chojnicka-Paszun, A., de Kruif, C.G., de Jongh, H.H.J.: Lubrication, adsorption, and rheology of aqueous polysaccharide solutions. Langmuir 27, 3474–3484 (2011)
Chojnicka, A., Sala, G., de Kruif, C.G., van de Velde, F.: The interactions between oil droplets and gel matrix affect the lubrication properties of sheared emulsion-filled gels. Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1038–1046 (2009)
Bongaerts, J., Rossetti, D., Stokes, J.: The lubricating properties of human whole saliva. Tribol. Lett. 27, 277–287 (2007)
de Vicente, J., Stokes, J.R., Spikes, H.A.: Rolling and sliding friction in compliant, lubricated contact. J. Eng. Tribol. 220, 55–63 (2006)
de Hoog, E.H.A., Prinz, J.F., Huntjens, L., Dresselhuis, D.M., Van Aken, G.A.: Lubrication of oral surfaces by food emulsions: the importance of surface characteristics. J. Food Sci. 71, E337–E341 (2006)
Lui, S., Luo, J., Li, G., Zhang, C., Lu, X.: Effect of surface physicochemical properties on the lubricating properties of water film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 7137–7142 (2008)
Heyer, P., Lauger, J.: A flexible platform for tribological measurements on a rheometer. Ann. Trans. Nordic Rheol. Soc. 17:np (2009)
Çakır, E., Foegeding, E.A.: Combining protein micro-phase separation and protein–polysaccharide segregative phase separation to produce gel structures. Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1538–1546 (2011)
de Vicente, J., Stokes, J.R., Spikes, H.A.: Lubrication properties of non-adsorbing polymer solutions in soft elastohydrodynamic (EHD) contacts. Tribol. Int. 38, 515–526 (2005)
de Vicente, J., Stokes, J.R., Spikes, H.A.: Soft lubrication of model hydrocolloids. Part Spec. Issue WCFS Food Summit 20, 483–491 (2006)
Joyner, H.S., Pernell, C.R., Daubert, C.R.: Impact of parameter settings on normal force and gap height during tribological measurements. J. Food Eng. 137, 51–63 (2014)
Kulmyrzaev, A., Chanamai, R., McClements, D.J.: Influence of pH and CaCl2 on the stability of dilute whey protein stabilized emulsions. Food Res. Int. 33, 15–20 (2000)
Demetriades, K., Coupland, J.N., McClements, D.J.: Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. J. Food Sci. 62, 342–347 (1997)
Zhang, Z., Dalgleish, D.G., Goff, H.D.: Effect of pH and ionic strength on competitive protein adsorption to air/water interfaces in aqueous foams made with mixed milk proteins. Colloids Surf. B 34, 113–121 (2004)
Hunt, J.A., Dalgleish, D.G.: Heat stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing milk proteins: effect of ionic strength and pH. J. Food Sci. 60, 1120–1123 (1995)
Dickinson, E.: Properties of emulsions stabilized with milk proteins: overview of some recent developments. J. Dairy Sci. 80, 2607–2619 (1997)
Singh, H.: Protein interactions and functionality of milk protein products. In: Corredig, M. (ed.) Dairy-Derived Ingredients-Food and Nutraceutical Uses, p. 690. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2009)
Wohlfarth, C.: Surface tension of water. Supplement to IV/16, pp. 16–21. Springer, New York (2008)
Esteban, B., Riba, J.-B., Baquero, G., Puig, R., Rius, A.: Characterization of the surface tension of vegetable oils to be used as fuel in diesel engines. Fuel 102, 231–238 (2012)
Bos, M.A., van Vliet, T.: Interfacial rheological properties of adsorbed protein layers and surfactants: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 91, 437–471 (2001)
Arakawa, T., Timasheff, S.N.: Mechanism of protein salting in and salting out by divalent cation salts: balance between hydration and salt binding. Biochemistry 23, 5912–5923 (1984)
Walstra, P.: Physical Chemistry of Foods. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, NY (2003)
Carr, A.J., Munro, P.A., Campanella, O.H.: Effect of added monovalent or divalent cations on the rheology of sodium caseinate solutions. Int. Dairy J. 12, 487–492 (2002)
Dickinson, E., Semenova, M.G., Antipova, A.S.: Salt stability of casein emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 12, 227–235 (1998)
Mizuno, R., Lucey, J.A.: Effects of emulsifying salts on the turbidity and calcium-phosphate–protein interactions in casein micelles. J. Dairy Sci. 88, 3070–3078 (2005)
Dickinson, E., Davies, E.: Influence of ionic calcium on stability of sodium caseinate emulsions. Colloids Surf. B 12, 203–212 (1999)
Keowmaneechai, E., McClements, D.J.: Effect of CaCl2 and KCl on physiochemical properties of model nutritional beverages based on whey protein stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. J. Food Sci. 67, 665–671 (2002)
Kulmyrzaev, A., Sivestre, M.P.C., McClements, D.J.: Rheology and stability of whey protein stabilized emulsions with high CaCl2 concentrations. Food Res. Int. 33, 21–25 (2000)
Radford, S.J., Dickinson, E., Golding, M.: Stability and rheology of emulsions containing sodium caseinate: combined effects of ionic calcium and alcohol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 274, 673–686 (2004)
Lucey, J.A., Singh, H.: Formation and physical properties of acid milk gels: a review. Food Res. Int. 30, 529–542 (1997)
Lucey, J.A., Munro, P.A., Singh, H.: Effects of heat treatment and whey protein addition on the rheological properties and structure of acid skim milk gels. Int. Dairy J. 9, 275–279 (1999)
Lucey, J.A.: Cultured dairy products: an overview of their gelation and texture properties. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 57, 77–84 (2004)
Vingerhoeds, M.H., Blijdenstein, T.B.J., Zoet, F.D., van Aken, G.A.: Emulsion flocculation induced by saliva and mucin. Food Hydrocolloids 19, 915–922 (2005)
Stokes, J.R.: ‘Oral’ Tribology. In: Chen, J., Engelen, L. (eds.) Food Oral Processing: Fundamentals of Eating and Sensory Perception, pp. 265–287. Wiley, New Jersey (2012)
de Wijk, R.A., Prinz, J.F.: The role of friction in perceived oral texture. Food Qual. Prefer. 16, 121–129 (2005)
Giasson, S., Israelachvili, J., Yoshizawa, H.: Thin film morphology and tribology study of mayonnaise. J. Food Sci. 62, 640–652 (1997)
Dresselhuis, D.M., de Hoog, E.H.A., Cohen Stuart, M.A., Vingerhoeds, M.H., van Aken, G.A.: The occurrence of in-mouth coalescence of emulsion droplets in relation to perception of fat. Food Hydrocoll. 22, 1170–1183 (2008)
Krzeminski, A., Wohlhüter, S., Heyer, P., Utz, J., Hinrichs, J.: Measurement of lubricating properties in a tribosystem with different surface roughness. 7th NIZO Dairy Conf. 26, 23–30 (2012)
Myant, C., Spikes, H.A., Stokes, J.R.: Influence of load and elastic properties on the rolling and sliding friction of lubricated compliant contacts. Tribol. Int. 43, 55–63 (2010)
Ranc, H., Servais, C., Chauvy, P., Debaud, S., Mischler, S.: Effect of surface structure on frictional behaviour of a tongue/palate tribological system 39, 1518–1526 (2006)
de Wijk, R.A., Prinz, J.F.: Mechanisms underlying the role of friction in oral texture. J. Texture Stud. 37, 413–427 (2006)
Myant, C., Fowell, M., Spikes, H.A., Stokes, J.R.: An investigation of lubricant film thickness in sliding compliant contacts. Tribol. Trans. 53, 684–694 (2010)
van Aken, G.A., Vingerhoeds, M.H., de Hoog, E.H.A.: Colloidal behavior of food emulsions under oral conditions. In: Dickinson, E. (ed.) Food Colloids: Interactions, Microstructure, and Processing, pp. 497. Royal Society of Chemistry, London (2005)
Acknowledgments
Funding for this work was provided by Dairy Management, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joyner, H.S., Pernell, C.W. & Daubert, C.R. Impact of Oil-in-Water Emulsion Composition and Preparation Method on Emulsion Physical Properties and Friction Behaviors. Tribol Lett 56, 143–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0393-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0393-1