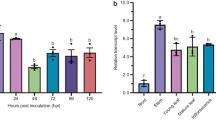
Abstract
Black root rot, caused by Thielaviopsis basicola, is an important disease in several crops including cotton. We studied the response of Arabidopsis NPR1 (AtNPR1)-expressing cotton lines, previously shown to be highly resistant to a diverse set of pathogens, to a challenge from T. basicola. In four different experiments, we found significant degree of tolerance in the transgenic lines to black root rot. Although transformants showed the typical root discoloration symptoms similar to the wild-type control plants following infection, their roots tended to recover faster and resumed normal growth. Better performance of transgenic plants is reflected by the fact that they have significantly higher shoot and root mass, longer shoot length, and greater number of boll-set. Transcriptional analysis of the defense response showed that the roots of AtNPR1-overexpressing transgenic plants exhibited stronger and faster induction of most of these defense-related genes, particularly PR1, thaumatin, glucanase, LOX1, and chitinase. The results obtained in this investigation provide further support for a broad-spectrum nature of the resistance conferred by overexpression of AtNPR1 gene in cotton.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen SJ (2001) Black root rot. In: Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (eds) Compendium of cotton diseases. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, pp 16–17
Brogue K, Chet I, Holliday M, Cressman R, Biddle P, Knowlton S, Mauvais CJ, Broglie R (1991) Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science 254:1194–1197
Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong X (1994) Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 6:1583–1592
Cao H, Li X, Dong X (1998) Generation of broad-spectrum disease resistance by overexpression of an essential regulatory gene in systemic acquired resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6531–6536
Chern MS, Fitzgerald HA, Yadav RC, Canlas PE, Dong X, Ronald PC (2001) Evidence for a disease-resistance pathway in rice similar to the NPR1-mediated signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J 27:101–113
Dana MM, Pintor-Toro JA, Cubero B (2006) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing chitinases of fungal origin show enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stress agents. Plant Physiol 142:722–730
Djonović S, Pozo MJ, Dangott LJ, Howell CR, Kenerley CM (2006) Sm1, a proteinaceous elicitor secreted by the biocontrol fungus Trichoderma virens induces plant defense responses and systemic resistance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:838–853
Dowd C, Wilson IW, McFadden H (2004) Gene expression profile changes in cotton root and hypocotyl tissues in response to infection with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:654–667
Emani C, Garcia JM, Lopata-Finch E, Pozo MJ, Uribe P, Kim DJ, Sunilkumar G, Cook DR, Kenerley CM, Rathore KS (2003) Enhanced fungal resistance in transgenic cotton expressing an endochitinase gene from Trichoderma virens. Plant Biotechnol J 1:321–336
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993) Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261:754–756
Hillocks RJ (1992) Cotton diseases. C.A.B International, Wallingford
Jalloul A, Montillet JL, Assigbetsé K, Agnel JP, Delannoy E, Triantaphylidès C, Daniel JF, Marmey P, Geiger JP, Nicole M (2002) Lipid peroxidation in cotton: Xanthomonas interactions and the role of lipoxygenases during the hypersensitive reaction. Plant J 32:1–12
Jha S, Chattoo BB (2010) Expression of a plant defensin in rice confers resistance to fungal phytopathogens. Transg Res 19:373–384
King CJ, Presley JT (1942) A root rot of cotton caused by Thielaviopsis basicola. Phytopathology 32:752–761
Kumar V, Parkhi V, Kenerley CM, Rathore KS (2009) Defense-related gene expression and enzyme activities in transgenic cotton plants expressing an endochitinase gene from Trichoderma virens in response to interaction with Rhizoctonia solani. Planta 230:277–291
Kumar V, Parkhi V, Joshi SG, Christensen S, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS, Kolomiets M, Rathore KS (2012) A novel, conditional, lesion mimic phenotype in cotton cotyledons due to the expression of an endochitinase gene from Trichoderma virens. Plant Sci 183:86–95
Linderman RG, Toussoum TA (1967) Behavior of chlamydospores and endoconidia of Thielaviopsis basicola in nonsterilized soil. Phytopathology 57(729):731
Lorito M, Woo SL, Garcia I, Colucci G, Harman GE, Pintor-Toro JA, Filippone E, Muccifora S, Lawrence CB, Zoina A, Tuzun S, Scala F (1998) Genes from mycoparasitic fungi as a source for improving plant resistance to fungal pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7860–7865
Makandar R, Essig JS, Schapaugh MA, Trick HN, Shah J (2006) Genetically engineered resistance to Fusarium head blight in wheat by expression of Arabidopsis NPR1. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:123–129
Malnoy M, Jin Q, Borejsza-Wysocka EE, He SY, Aldwinckle HS (2007) Overexpression of the Apple MpNPR1 eene confers increased disease resistance in Malus × domestica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:1568–1580
Meur G, Budatha M, Srinivasan T, Rajesh Kumar KR, Dutta Gupta A, Kirti PB (2008) Constitutive expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 confers enhanced resistance to the early instars of Spodoptera litura in transgenic tobacco. Physiol Plant 133:765–775
Palmateer AJ, Lawrence KS, van Santen E, Morgan-Jones G (2004) Interaction of Rotylenchulus reniformis with seedling disease pathogens of cotton. J Nematol 36:160–166
Parkhi V, Kumar V, Campbell LAM, Bell AA, Rathore KS (2010a) Expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 in transgenic cotton confers resistance to non-defoliating isolates of Verticillium dahliae but not the defoliating isolates. J Phytopathol 158:822–825
Parkhi V, Kumar V, Campbell LM, Bell AA, Shah J, Rathore KS (2010b) Resistance against various fungal pathogens and reniform nematode in transgenic cotton plants expressing Arabidopsis NPR1. Trans Res 19:959–975
Pieterse CM, Van Loon LC (2004) NPR1: the spider in the web of induced resistance signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:456–464
Rivero M, Furman N, Mencacci N, Picca P, Toum L, Lentz E, Bravo-Almonacid F, Mentaberry A (2012) Stacking of antimicrobial genes in potato transgenic plants confers increased resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. J Biotechnol 157:334–343
Rothrock CS (1992) Influence of soil temperature water and texture on Thielaviopsis basicola and black root rot of cotton. Phytopathology 82:1201–1206
Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner HY, Hunt MD (1996) Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 8:1809–1819
Salmeron JM, Vernooij B (1998) Transgenic approaches to microbial disease resistance in crop plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:347–352
Shah J, Tsui F, Klessig DF (1997) Characterization of a salicylic acid-insensitive mutant (sai1) of Arabidopsis thaliana, identified in a selective screen utilizing the SA-inducible expression of the tms2 gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:69–78
Sunilkumar G, Rathore KS (2001) Transgenic cotton: factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and regeneration. Mol Breed 8:37–52
Verma SS, Yajima WR, Rahman MH, Shah S, Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK, Kav NN (2012) A cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide from Pinus monticola (PmAMP1) confers resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in canola (Brassica napus). Plant Mol Biol 79(1–2):61–74
Walker NR, Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (1998) Interaction between Meloidogyne incognita and Thielaviopsis basicola on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). J Nematol 30:415–422
Walker NR, Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (1999) Effect of temperature on and histopathology of the interaction between Meloidogyne incognita and Thielaviopsis basicola on cotton. Phytopathology 89:613–617
Walker NR, Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (2000) Influence of Meloidogyne incognita and Thielaviopsis basicola populations on early-season disease development and cotton growth. Plant Dis 84:449–453
Wally O, Jayaraj J, Punja ZK (2009) Broad-spectrum disease resistance to necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens in transgenic carrots (Daucus carota L.) expressing an Arabidopsis NPR1 gene. Planta 231:131–141
Wang H, Davis RM (1997) Susceptibility of selected cotton cultivars to seedling disease pathogens and benefits of chemical seed treatments. Plant Dis 81:1085–1088
Zhang Y, Shi J, Liu JY, Zhang JD, Guo XQ (2010) Identification of a novel NPR1-like gene from Nicotiana glutinosa and its role in resistance to fungal, bacterial and viral pathogens. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 12:23–34
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. LeAnne M. Campbell for the production of the transformants and Dr. Vilas Parkhi for the original characterization of the transgenic lines used in this study. This research was supported by funds from Cotton Inc., Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board—Advanced Research Program (#000517-0005-2006), and Texas AgriLife Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Joshi, S.G., Bell, A.A. et al. Enhanced resistance against Thielaviopsis basicola in transgenic cotton plants expressing Arabidopsis NPR1 gene. Transgenic Res 22, 359–368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-012-9652-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-012-9652-9