Abstract
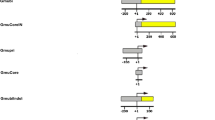
The influence of the CaMV 35S promoter/enhancer on expression profiles of four Arabidopsis thaliana pollen- and/or embryo-specific promoters, APRS, ESL, MXL, and DLL, was tested in transgenic tobacco plants. Individual promoters were fused to the gus reporter gene and cloned in head-to-head orientation with the CaMV 35S:hpt expression unit within the same T-DNA. With the exception of the TATA-less promoter DLL, all other combinations generated interactions between the promoter under investigation and 35S promoter/enhancer resulting in ectopic β-glucuronidase (GUS) expression in vegetative organs and tissues, the most susceptible being the stem, followed by callus, leaf, and root. To eliminate this crosstalk, DNA spacers of length 1, 2 and 5 kb were cloned between the interacting sequences. Ectopic GUS staining was dependent on the affected promoter as well as the distance between the 5′-end of the CaMV 35S promoter and the reporter gene translation start site. When this distance was less than 1 kb strong ectopic GUS staining was observed in all vegetative tissues, similar to the CaMV35S:gus expression profile in transgenic tobacco plants. Insertion of spacer DNA sequences of increasing length resulted in gradual reduction of ectopic GUS staining in tested plants. Of the tissues and organs related to plant reproduction, only anthers and seed coats in the early stages of seed development showed ectopic GUS staining. Developing pollen and embryos showed a pattern of GUS activity consistent with the predicted role of a developmental stage-specific promoter in transgenic tobacco plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anish R, Hossain MB, Jacobson RH, Takada S (2009) Characterization of transcription from TATA-less promoters: identification of a new core promoter element XCPE2 and analysis of factor requirements. PLoS ONE 4(4):e5103. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005103
Babitha KC, Ramu SV, Pruthvi V, Mahesh P, Nataraja KN, Udayakumar M (2013) Co-expression of AtbHLH17 and AtWRKY28 confers resistance to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis. Transgenic Res 22:327–341
Bakhsh A, Rao AQ, Shamim Z, Husnain T (2011) A minireview: Rubisco small subunit as a strong, green tissue-specific promoter. Arch Biol Sci 63:299–307
Berrocal-Lobo M, Molina A, Solano R (2002) Constitutive expression of ethylene-response-factor1 in Arabidopsis confers resistance to several necrotrophic fungi. Plant J 29:23–32
Bevan M (1984) Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8711–8721
Bondarenko VA, Liu YV, Jiang YI, Studitsky VM (2003) Communication over a large distance: enhancers and insulators. Biochem Cell Biol 81:241–251
Bowling SA, Clarke JD, Liu YD, Klessig DF, Dong XN (1997) The cpr5 mutant of Arabidopsis expresses both NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent resistance. Plant Cell 9:1573–1584
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Butler JEF, Kadonaga JT (2001) Enhancer–promoter specificity mediated by DPE or TATA core promoter motifs. Genes Dev 15:2515–2519
Cai HNN, Zhang ZG, Adams JR, Shen P (2001) Genomic context modulates insulator activity through promoter competition. Development 128:4339–4347
Casson S, Spencer M, Walker K, Lindsey K (2005) Laser capture microdissection for the analysis of gene expression during embryogenesis of Arabidopsis. Plant J 42:111–123
Dalal M, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2010) Isolation and functional characterization of Lycopene beta-cyclase (CYC-B) promoter from Solanum habrochaites. BMC Plant Biol 10:61
Drea SC, Lao NT, Wolfe KH, Kavanagh TA (2006) Gene duplication, exon gain and neofunctionalization of OEP16-related genes in land plants. Plant J 46:723–735
Grace ML, Chandrasekharan MB, Hall TC, Crowe AJ (2004) Sequence and spacing of TATA box elements are critical for accurate initiation from the beta-phaseolin promoter. J Biol Chem 279:8102–8110
Gudynaite-Savitch L, Johnson DA, Miki BLA (2009) Strategies to mitigate transgene–promoter interactions. Plant Biotechnol J 7:472–485
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994
Hily JM, Singer SD, Yang YZ, Liu ZR (2009) A transformation booster sequence (TBS) from Petunia hybrida functions as an enhancer-blocking insulator in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 28:1095–1104
Hirner B, Fischer WN, Rentsch D, Kwart M, Frommer WB (1998) Developmental control of H +/amino acid permease gene expression during seed development of Arabidopsis. Plant J 14:535–544
Höfgen R, Willmitzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9877
Hogga I, Karch F (2002) Transcription through the iab-7 cis-regulatory domain of the bithorax complex interferes with maintenance of Polycomb-mediated silencing. Development 129:4915–4922
Honys D, Twell D (2004) Transcriptome analysis of haploid male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 5:11
Honys D, Oh SA, Renak D, Donders M, Solcova B, Johnson JA, Boudova R, Twell D (2006) Identification of microspore-active promoters that allow targeted manipulation of gene expression at early stages of microgametogenesis in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 6:31
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general-method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Hraska M, Rakousky S, Curn V (2008) Tracking of the CaMV-35S promoter performance in GFP transgenic tobacco, with a special emphasis on flowers and reproductive organs, confirmed its predominant activity in vascular tissues. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 94:239–251
Jagannath A, Bandyopadhyay P, Arumugam N, Gupta V, Burma PK, Pental D (2001) The use of a spacer DNA fragment insulates the tissue-specific expression of a cytotoxic gene (barnase) and allows high-frequency generation of transgenic male sterile lines in Brassica juncea L. Mol Breed 8:11–23
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions—beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher-plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jopcik M, Bauer M, Moravcikova J, Boszoradova E, Matusikova I, Libantova J (2013) Plant tissue-specific promoters can drive gene expression in Escherichia coli. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 113:387–396
Koltunow AM, Truettner J, Cox KH, Wallroth M, Goldberg RB (1990) Different temporal and spatial gene-expression patterns occur during anther development. Plant Cell 2:1201–1224
Kumar V, Joshi SG, Bell AA, Rathore KS (2013) Enhanced resistance against Thielaviopsis basicola in transgenic cotton plants expressing Arabidopsis NPR1 gene. Transgenic Res 22:359–368
Larkin JC, Oppenheimer DG, Pollock S, Marks MD (1993) Arabidopsis GLABROUS1 gene requires downstream sequences for function. Plant Cell 5:1739–1748
Ling JH, Baibakov B, Pi WH, Emerson BM, Tuan D (2005) The HS2 enhancer of the beta-globin locus control region initiates synthesis of non-coding, polyadenylated RNAs independent of a cis-linked globin promoter. J Mol Biol 350:883–896
Merkouropoulos G, Shirsat AH (2012) Histochemical map of the ectopic expression of the Arabidopsis atExt1 extension gene in transgenic tobacco. Genet Mol Res 11:1830–1840
Moravcikova J, Libantova J, Matusikova I, Libiakova G, Nap JP, Mlynarova L (2003) Genetic transformation of Slovak cultivar of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): efficiency and the behaviour of the transgene. Biologia 58:1075–1080
Moravcikova J, Libantova J, Heldak J, Salaj J, Bauer M, Matusikova I, Galova Z, Mlynarova L (2007) Stress-induced expression of cucumber chitinase and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia beta-1,3-glucanase genes in transgenic potato plants. Acta Physiol Plant 29:133–141
Odell JT, Hoopes JL, Vermerris W (1994) Seed-specific gene activation mediated by the Cre/lox site-specific recombination system. Plant Physiol 106:447–458
Ouwerkerk PBF, de Kam RJ, Hodge JHC, Meijer AH (2001) Glucocorticoid-inducible gene expression in rice. Planta 213:370–378
Peremarti A, Twyman RM, Gomez-Galera S, Naqvi S, Farre G, Sabalza M, Miralpeix B, Dashevskaya S, Yuan DW, Ramessar K, Christou P, Zhu CF, Bassie L, Capell T (2010) Promoter diversity in multigene transformation. Plant Mol Biol 73:363–378
Roberts CS, Rajagopal S, Smith LA, Nguyen TA, Yang W, Nugroho S, Ravi KS, Vijayachandra K, Harcourt KL, Dransfield L, Desamero N, Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P, Mayer JE, Keese P, Kilian K, Jefferson RA (2002) A comprehensive set of modular vectors for advanced manipulations and efficient transformation of plants by both Agrobacterium and direct DNA uptake methods. CAMBIA, Canberra, Australia. http://www.cambia.org
Sakebe NJ, Savic D, Nobrega MA (2012) Transcriptional enhancers in development and disease. Genome Biol 13:238
Savidge B, Rounsley SD, Yanofsky MF (1995) Temporal relationship between the transcription of 2 Arabidopsis MADS box genes and the floral organ identity genes. Plant Cell 7:721–733
Singer SD, Hily JM, Liu ZR (2010) A 1-kb bacteriophage Lambda fragment functions as an insulator to effectively block enhancer–promoter interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:69–76
Singer SD, Cox KD, Liu ZR (2011) Enhancer–promoter interference and its prevention in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 30:723–731
Smith PA, Corces VG (1995) The suppressor of hairy-wing protein regulates the tissue-specific expression of the drosophila GYPSY retrotransposon. Genetics 139:215–228
Smith DL, Fedoroff NV (1995) LRP1, a gene expressed in lateral and adventitious root primordia of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 7:735–745
Stangeland B, Salehian Z (2002) An improved clearing method for GUS assay in Arabidopsis endosperm and seeds. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:321
Vaculkova E, Moravcikova J, Matusikova I, Bauer M, Libantova J (2007) A modified low copy number binary vector pUN for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Biol Plant 51:538–540
vander Geest AHM, Hall TC (1997) The beta-phaseolin 5′ matrix attachment region acts as an enhancer facilitator. Plant Mol Biol 33:553–557
Wilkinson JE, Twell D, Lindsey K (1997) Activities of CaMV 35S and nos promoters in pollen: implications for field release of transgenic plants. J Exp Bot 48:265–275
Wisniewski M, Bassett C, Macarisin D, Norelli J, Artlip T, Korban S (2009) Transcriptomic and proteomic response of fruit trees to abiotic stress. In: Hanke MV, Dunemann F, Flachowsky H (eds) I international symposium on biotechnology of fruit species: Biotechfruit 2008, pp 681–687
Xiao YL, Redman JC, Monaghan EL, Zhuang J, Underwood BA, Moskal WA, Wang W, Wu HC, Town CD (2010) High throughput generation of promoter reporter (GFP) transgenic lines of low expressing genes in Arabidopsis and analysis of their expression patterns. Plant Methods 6:18 http://www.plantmethods.com/content/6/1/18
Yoo SY, Bomblies K, Yoo SK, Yang JW, Choi MS, Lee JS, Weigel D, Ahn JH (2005) The 35S promoter used in a selectable marker gene of a plant transformation vector affects the expression of the transgene. Planta 221:523–530
Zheng XL, Deng W, Luo KM, Duan H, Chen YQ, McAvoy R, Song SQ, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) The cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter sequence alters the level and patterns of activity of adjacent tissue- and organ-specific gene promoters. Plant Cell Rep 26:1195–1203
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Slovak Grant Agency VEGA Project No. 2/0090/14. The authors also thank Dr. Jan Miernyk and Miroslav Bauer for helpful comments and corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jopcik, M., Moravcikova, J., Matusikova, I. et al. Spacer length-dependent protection of specific activity of pollen and/or embryo promoters from influence of CaMV 35S promoter/enhancer in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 118, 507–518 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0503-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0503-7