Abstract
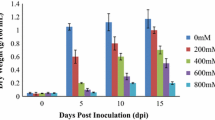
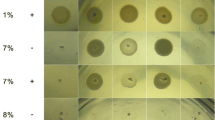
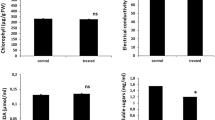
Dunaliella salina (Dunal) Teod, a unicellular eukaryotic green alga, is a highly salt-tolerant organism. To identify novel genes with potential roles in salinity tolerance, a salt stress-induced D. salina cDNA library was screened based on the expression in Haematococcus pluvialis, an alga also from Volvocales but one that is hypersensitive to salt. Five novel salt-tolerant clones were obtained from the library. Among them, Ds-26-16 and Ds-A3-3 contained the same open reading frame (ORF) and encoded a 6.1 kDa protein. Transgenic tobacco overexpressing Ds-26-16 and Ds-A3-3 exhibited increased leaf area, stem height, root length, total chlorophyll, and glucose content, but decreased proline content, peroxidase activity, and ascorbate content, and enhanced transcript level of Na+/H+ antiporter salt overly sensitive 1 gene (NtSOS1) expression, compared to those in the control plants under salt condition, indicating that Ds-26-16 enhanced the salt tolerance of tobacco plants. The transcript of Ds-26-16 in D. salina was upregulated in response to salt stress. The expression of Ds-26-16 in Escherichia coli showed that the ORF contained the functional region and changed the protein(s) expression profile. A mass spectrometry assay suggested that the most abundant and smallest protein that changed is possibly a DNA-binding protein or Cold shock-like protein. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that Ds-26-16 was located in the nuclei of onion epidermal cells or nucleoid of E. coli cells. In addition, the possible use of shoots regenerated from leaf discs to quantify the salt tolerance of the transgene at the initial stage of tobacco transformation was also discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkayal F, Albion RL, Tillett RL, Hathwaik LT, Lemos MS, Cushman JC (2010) Expressed sequence tag (EST) profiling in hyper saline shocked Dunaliella salina reveals high expression of protein synthetic apparatus components. Plant Sci 179:437–449
Blaudez D, Kohler A, Martin F, Sanders D, Chalot M (2003) Poplar metal tolerance protein 1 confers zinc tolerance and is an oligomeric vacuolar zinc transporter with an essential leucine zipper motif. Plant cell 15:2911–2928
Chatzissavvidis C, Veneti G, Papadakis I, Therios I (2008) Effect of NaCl and CaCl2 on the antioxidant mechanism of leaves and stems of the rootstock CAB-6P (Prunus cerasus L.) under in vitro conditions. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 95:37–45
Chen H, Jiang J (2009) Osmotic responses of Dunaliella to the changes of salinity. J Cell Physiol 219:251–258
Dame RT, Goosen N (2002) HU: promoting or counteracting DNA compaction? FEBS Lett 529:151–156
Domínguez-Bocanegra AR, Guerrero Legarreta I, Martinez Jeronimo F, Tomasini Campocosio A (2004) Influence of environmental and nutritional factors in the production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis. Bioresour Technol 92:209–214
Du J, Huang YP, Xi J, Cao MJ, Ni WS, Chen X, Zhu JK, Oliver DJ, Xiang CB (2008) Functional gene-mining for salt-tolerance genes with the power of Arabidopsis. Plant J 56:653–664
Eguchi K, Nagase H, Ozawa M, Endoh YS, Goto K, Hirata K, Miyamoto K, Yoshimura H (2004) Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 57:1733–1738
Fisher M, Gokhman I, Pick U, Zamir A (1996) A salt-resistant plasma membrane carbonic anhydrase is induced by salt in Dunaliella salina. J Biol Chem 271:17718–17723
Fisher M, Gokhman I, Pick U, Zamir A (1997) A structurally novel transferrin-like protein accumulates in the plasma membrane of the unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina grown in high salinities. J Biol Chem 272:1565–1570
Flowers TJ, Flowers SA, Greenway H (1986) Effects of sodium chloride on tobacco plants. Plant, Cell Environ 9:645–651
Galvan-Ampudia CS, Testerink C (2011) Salt stress signals shape the plant root. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:296–302
Gao C, Jiang B, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang C (2012) Overexpression of a heat shock protein (ThHSP18.3) from Tamarix hispida confers stress tolerance to yeast. Mol Biol Rep 39:4889–4897
Gong Q, Li P, Ma S, Indu Rupassara S, Bohnert HJ (2005) Salinity stress adaptation competence in the extremophile Thellungiella halophila in comparison with its relative Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 44:826–839
Gong WF, Lu LJ, Chen XW, Chen DF (2013) Effect of silencing lycB gene on the carotenoid synthesis in Haematococcus pluvialis. Hereditas (Beijing) 35:233–240 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gupta K, Agarwal PK, Reddy MK, Jha B (2010) SbDREB2A, an A-2 type DREB transcription factor from extreme halophyte Salicornia brachiata confers abiotic stress tolerance in Escherichia coli. Plant Cell Rep 29:1131–1137
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir- and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303:179–180
Imamoglu E, Vardar Sukan F, Conk Dalay M (2007) Effect of different culture media and light intensities on growth of Haematococcus pluvialis. Int J Nat Eng Sci 1:05–09
Jha B, Lal S, Tiwari V, Yadav SK, Agarwal PK (2012) The SbASR-1 gene cloned from an extreme halophyte Salicornia brachiata enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Mar Biotechnol 14:782–792
Kant S, Kant P, Raveh E, Barak S (2006) Evidence that differential gene expression between the halophyte, Thellungiella halophila, and Arabidopsis thaliana is responsible for higher levels of the compatible osmolyte proline and tight control of Na+ uptake in T. halophila. Plant, Cell Environ 29:1220–1234
Kanwischer M, Porfirova S, Bergmüller E, Dörmann P (2005) Alterations in tocopherol cyclase activity in transgenic and mutant plants of Arabidopsis affect tocophero content, tocopherol composition, and oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 137:713–723
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu J, Kim K, Agarwal M, Fu X, Huang A, Zhu JK (2006) The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 interacts with RCD1 and functions in oxidative stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18816–18821
Katz A, Pick U (2001) Plasma membrane electron transport coupled to Na+ extrusion in the halotolerant alga Dunaliella. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:423–431
Krishnaswamy S, Verma S, Rahman MH, Kav NN (2011) Functional characterization of four APETALA2-family genes (RAP2.6, RAP2.6L, DREB19 and DREB26) in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 75:107–127
Kumar R, Mustafiz A, Sahoo KK, Sharma V, Samanta S, Sopory SK, Pareek A, Singla-Pareek SL (2012) Functional screening of cDNA library from a salt tolerant rice genotype Pokkali identifies mannose-1-phosphate guanyl transferase gene (OsMPG1) as a key member of salinity stress response. Plant Mol Biol 79:555–568
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol 148:350–382
Liu J, Zhu JK (1997) Proline accumulation and salt-stress-induced gene expression in a salt-hypersensitive mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 114:591–596
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real-Time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Oren A (2005) A hundred years of Dunaliella research: 1905–2005. Saline Syst 1:1–14
Sadka A, Himmelhoch S, Zamir A (1991) A 150-kilodalton cell surface protein is induced by salt in the halotolerant green alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol 95:822–831
Song NH, Ahn YJ (2011) DcHsp17.7, a small heat shock protein in carrot, is tissue-specifically expressed under salt stress and confers tolerance to salinity. N Biotechnol 28:698–704
Stübs D, Fuchs TM, Schneider B, Bosserhoff A, Gross R (2005) Identification and regulation of cold-induciblefactors of Bordetell bronchiseptica. Microbiology 151:1895–1909
Teng CY, Liang CW, Qin S, Zeng CK (2005) Study on sensitivities of Haematococcus pluvialis to ten selective reagents for genetic engineering. Oceanol Limnol Sin 36:302–306 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Timmins M, Thomas-Hall SR, Darling A, Zhang E, Hankamer B, Marx UC, Schenk PM (2009) Phylogenetic and molecular analysis of hydrogen-producing green algae. J Exp Bot 60:1691–1702
Wang H, Benham CJ (2008) Superhelical destabilization in regulatory regions of stress response genes. PLoS Comput Biol 4:62–76
Wang H, Chen X, Xing X, Hao X, Chen D (2010) Transgenic tobacco plants expressing atzA exhibit resistance and strong ability to degrade atrazine. Plant Cell Rep 29:1391–1399
Wang H, Chen X, Hao X, Chen D (2011) High throughput screening atrazine chlorohydrolase mutants with enhanced activity through Haematococcus pluvialis expression system. Chin J Biotechnol 27:620–628 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Williams RM, Rimsky S (1997) Molecular aspects of the E. coli nucleoid protein, H-NS: a central controller of gene regulatory networks. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156:175–185
Yadav S, Irfan M, Ahmad A, Hayat S (2011) Causes of salinity and plant manifestations to salt stress: a review. J Environ Biol 32:667–685
Yamada A, Tsutsumi K, Tanimoto S, Ozeki Y (2003) Plant RelA/SpoT homolog confers salt tolerance in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Cell Physiol 44:3–9
Yang CW, Deng W, Tang N, Wang XM, Yan F, Lin DB, Li ZG (2013) Overexpression of ZmAFB2, the maize homologue of AFB2 gene, enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 112:171–179
Yarra R, He SJ, Abbagani S, Ma B, Bulle B, Zhang WK (2012) Overexpression of a wheat Na+/H+ antiporter gene (TaNHX2) enhances tolerance to salt stress in transgenic tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 111:49–57
Yuan H, Meng X, Gao Q, Qu W, Xu T, Xu Z, Song R (2011) The characterization of two peroxiredoxin genes in Dunaliella viridis provides insights into antioxidative response to salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 30:1503–1512
Yue Y, Zhang M, Zhang J, Duan L, Li Z (2011) Arabidopsis LOS5/ABA3 overexpression in transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc) results in enhanced drought tolerance. Plant Sci 181:405–411
Zhao LN, Gong WF, Chen XW, Chen DF (2013) Characterization of genes and enzymes in Dunaliella salina involved in glycerol metabolism in response to salt changes. Phycol Res 61:37–45
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Peter Dörmann at University of Bonn for critically reading this manuscript. This work was supported by the Key Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (Grant No. 12YFJZJC01700), the grant of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31070717) and the 111 Project (No. B08011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Wf., Zhao, Ln., Hu, B. et al. Identifying novel salt-tolerant genes from Dunaliella salina using a Haematococcus pluvialis expression system. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 117, 113–124 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0425-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0425-4