Abstract
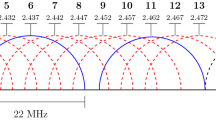
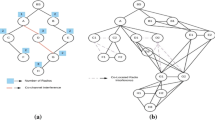
In this paper, linear optimization is used to model the interference aware joint channel assignment problem in Wireless Mesh Networks. The model selects the channels for the interfering links such that interference is minimized, overall throughput of the network is maximized, and network capacity is fairly distributed among the interfering links. The interference is minimized by classifying the interfering links into four different classes depending upon the geometric location of the sender and receiver of a link (i.e., Sender Connected, Asymmetric Incomplete State, Symmetric Incomplete State, and Far Hidden interfering links). Further, the classes of interfering links are assigned with distinct channels through optimized spectral re-usability of joint channels available in 2.4 GHz ISM band. As a result, it increases the simultaneous transmissions among the interfering links which in turn increases the aggregate throughput of the network while ensuring that capacity is fairly distributed among the interfering links. Numerical results indicated that joint channel assignment model has achieved better performance than non-overlapping channel assignment models. Hence, this validates the model, which can serve as a benchmark in the design and deployment of wireless mesh networks.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Wang, X., & Wang, W. (2005). Wireless mesh networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 47(4), 445–487. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2004.12.001.
Peng, Y., Yu, Y., Guo, L., Jiang, D., & Gai, Q. (2013). An efficient joint channel assignment and QoS routing protocol for IEEE 802.11 multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 36(2), 843–857. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2012.11.003.
Jiang, D., Xu, Z., Li, W., & Chen, Z. (2015). Network coding-based energy-efficient multicast routing algorithm for multi-hop wireless networks. Journal of Systems and Software, 104, 152–165. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2015.03.006.
Kim, J., & Lee, J. (2012). Cluster-based mobility supporting WMN for IoT networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Green Computing and Communications, (pp. 700–703). Besanon, France, 2012. doi:10.1109/GreenCom.2012.114.
Zhang, D., Yang, L., Chen, M., Zhao, S., Guo, M., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Real-time locating systems using active RFID for Internet of Things. IEEE Systems Journal, PP(99), 1–10, doi:10.1109/JSYST.2014.2346625.
Benyamina, D., Hafid, A., & Gendreau, M. (2012). Wireless mesh networks design—A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 14(2), 299–310. doi:10.1109/Surv.2011.042711.00007.
Kumar, N., Kumar, M., & Patel, R. B. (2011). Capacity and interference aware link scheduling with channel assignment in wireless mesh networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(1), 30–38. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2010.10.001.
Avokh, A., & Mirjalily, G. (2014). Interference-aware multicast and broadcast routing in wireless mesh networks using both rate and channel diversity. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 40(2), 624–640. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.05.008.
Ashraf, U., Abdellatif, S., & Juanole, G. (2012). Interference-Aware Bandwidth Reservation in multi-radio multi-channel mesh networks. Computer Communications, 35(17), 2138–2149. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2012.07.007.
Ashraf, U., Abdellatif, S., & Juanole, G. (2013). Route selection in IEEE 802.11 wireless mesh networks. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 1777–1795. doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9493-5.
Avallone, S. (2012). An energy efficient channel assignment and routing algorithm for multi-radio wireless mesh networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(6), 1043–1057. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2012.01.007.
Bin Ngadi, M. A., Ali, S., Abdullah, A. H., & Khokhar, R. H. (2012). A taxonomy of cross layer routing metrics for wireless mesh networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2012, 177. doi:10.1186/1687-1499-2012-177.
Gupta, P., & Kumar, P. R. (2000). The capacity of wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 46(2), 388–404. doi:10.1109/18.825799.
Tang, J., Xue, G., & Zhang, W. (2005). Interference-aware topology control and QoS routing in multi-channel wireless mesh networks. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad hoc Networking and Computing, (pp. 68–77). Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA, 2005. doi:10.1145/1062689.1062700.
Skalli, H., Ghosh, S., Das, S. K., Lenzini, L., & Conti, M. (2007). Channel assignment strategies for multiradio wireless mesh networks: Issues and solutions. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45(11), 86–93. doi:10.1109/Mcom.2007.4378326.
Ali, S., Naveed, A., Bin Ngadi, M. A., & Chaudhry, J. A. (2014). Interference nomenclature in wireless mesh networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 75(4), 1983–2003. doi:10.1007/s11277-013-1449-5.
Qiu, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, F., Han, M. K., & Mahajan, R. (2007). A general model of wireless interference. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, (pp. 171–182). Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2007. doi:10.1145/1287853.1287874.
Iyer, A., Rosenberg, C., & Karnik, A. (2009). What is the right model for wireless channel interference? IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(5), 2662–2671. doi:10.1109/twc.2009.080720.
Garetto, M., Shi, J., & Knightly, E. W. (2005). Modeling media access in embedded two-flow topologies of multi-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, (pp. 200–214). Cologne, Germany, 2005. doi:10.1145/1080829.1080851.
Garetto, M., Salonidis, T., & Knightly, E. W. (2008). Modeling per-flow throughput and capturing starvation in CSMA multi-hop wireless networks. IEEE-ACM Transactions on Networking, 16(4), 864–877. doi:10.1109/Tnet.2007.902687.
Alotaibi, E., Ramamurthi, V., Batayneh, M., & Mukherjee, B. (2010). Interference-aware routing for multi-hop wireless mesh networks. Computer Communications, 33(16), 1961–1971. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2010.06.025.
Naveed, A., & Kanhere, S. S. (2009). Cluster-based channel assignment in multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks. In IEEE 34th Conference on Local Computer Networks, (pp. 53–60). Zurich, Switzerland, 2009. doi:10.1109/LCN.2009.5355164.
Mishra, A., Shrivastava, V., Banerjee, S., & Arbaugh, W. (2006). Partially overlapped channels not considered harmful. ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, 34(1), 63. doi:10.1145/1140103.1140286.
Duarte, P. B. F., Fadlullah, Z. M., Vasilakos, A. V., & Kato, N. (2012). On the partially overlapped channel assignment on wireless mesh network backbone: A game theoretic approach. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30(1), 119–127. doi:10.1109/Jsac.2012.120111.
Raniwala, A., & Tzi-cker, C. (2005). Architecture and algorithms for an IEEE 802.11-based multi-channel wireless mesh network. In 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, (Vol. 3, pp. 2223–2234), Miami, FL, USA, 2005.
Nguyen, L. T., Beuran, R., & Shinoda, Y. (2007). Performance analysis of IEEE 802.11 in multi-hop wireless networks. In Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks, (Vol. 4864, pp. 326–337). Springer, Berlin, 2007.
Zotkiewicz, M., & Pioro, M. (2014). Exact approach to reliability of wireless mesh networks with directional antennas. Telecommunication Systems, 56(1), 201–211. doi:10.1007/s11235-013-9829-4.
Shi, J., Salonidis, T., & Knightly, E. W. (2006). Starvation mitigation through multi-channel coordination in CSMA multi-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad hoc Networking and Computing, (pp. 214–225). Florence, Italy, 2006. doi:10.1145/1132905.1132929.
Subramanian, A. P., Gupta, H., Das, S. R., & Cao, J. (2008). Minimum interference channel assignment in multiradio wireless mesh networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(12), 1459–1473. doi:10.1109/Tmc.2008.70.
Ding, Y., & Xiao, L. (2011). Channel allocation in multi-channel wireless mesh networks. Computer Communications, 34(7), 803–815. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2010.10.011.
Mishra, A., Rozner, E., Banerjee, S., & Arbaugh, W. (2005). Exploiting partially overlapping channels in wireless networks: turning a peril into an advantage. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, (p. 29). Berkeley, CA, USA, 2005.
Mohsenian Rad, A. H., & Wong, V. W. S. (2007). Partially overlapped channel assignment for multi-channel wireless mesh networks. In IEEE International Conference on Communications, (pp. 3770–3775). Glasgow, Scotland, 2007.
MATLAB (2012). Version 7.14.0 (R2012a) The MathWorks Inc. Natick, Massachusetts, USA.
CPLEX-12.0 (2014). IBM ILOG CPLEX 12.0 Users Manual.: IBM.
Fourer, R., Gay, D. M., & Kernighan, B. W. (1990). A modeling language for mathematical programming. Management Science, 36(5), 519–554. doi:10.1287/mnsc.36.5.519.
Ramachandran, K. N., Belding, E. M., Almeroth, K. C., & Buddhikot, M. M. (2006). Interference-aware channel assignment in multi-radio wireless mesh networks. In Proceedings of the INFOCOM 2006. 25th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, (pp. 1–12). 2006.
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by MOHE/FRGS/4F568 Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. Authors are thankful to Dr. Anjum Naveed from the Department of Electrical Engineering, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan for his valuable suggestions. Further, the authors are grateful to the reviewers and the editor for their excellent comments that improved the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Ngadi, M.A. Optimized interference aware joint channel assignment model for wireless mesh network. Telecommun Syst 62, 215–230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0076-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0076-8