Abstract
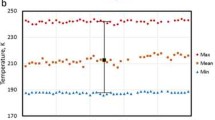
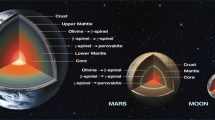
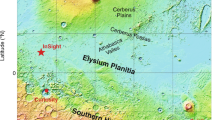
The 2018 InSight (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) Mission has the mission goal of providing insitu data for the first measurement of the geothermal heat flow of Mars. The Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3) will take thermal conductivity and thermal gradient measurements to approximately 5 m depth. By necessity, this measurement will be made within a few meters of the lander. This means that thermal perturbations from the lander will modify local surface and subsurface temperature measurements. For HP3’s sensitive thermal gradient measurements, this spacecraft influence will be important to model and parameterize. Here we present a basic 3D model of thermal effects of the lander on its surroundings. Though lander perturbations significantly alter subsurface temperatures, a successful thermal gradient measurement will be possible in all thermal conditions by proper (\(>3~\mbox{m}\) depth) placement of the heat flow probe.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.B. Banerdt, S. Smrekar, P. Lognonné, T. Spohn, S.W. Asmar, D. Banfield (The InSight Team), InSight: a discovery mission to explore the interior of Mars, in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, vol. 44 (2013), p. 1915
W.B. Banerdt et al., Insight. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue)
P.N. Desai, J.L. Prince, E.M. Queen, M.M. Schoenenberger, J.R. Cruz, M.R. Grover, Entry, descent, and landing performance of the mars phoenix lander. J. Spacecr. Rockets 48(5), 798–808 (2011)
R. Fleischner, InSight instrument deployment arm. ESMAT, http://www.esmats.eu/esmatspapers/pastpapers/pdfs/2013/fleischner.pdf (2013)
M. Golombek, D. Kipp, N. Warner, I. Daubar, R. Fergason, R. Kirk, R. Beyer, A. Huertas, S. Piqueux, N. Putzig, B.A. Campbell, G.A. Morgan, C. Constantinos, T. Pike, K. Gwinner, F. Calef, J. Ashley, D. Kass, M. Mischna, C. Bloom, N. Wigton, C. Schwartz, H. Gengl, L. Redmond, J. Sweeney, E. Sklyanskiy, M. Lisano, J. Benardino, S. Smrekar, B. Banerdt, Selection of the InSight landing site. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue)
M. Grott, Thermal disturbances caused by lander shadowing and the measurability of the martian planetary heat flow. Planet. Space Sci. 57(1), 71–77 (2009)
M. Grott, J. Helbert, R. Nadalini, The thermal structure of Martian soil and the measurability of the planetary heat flow. J. Geophys. Res. 112, E09004 (2007)
M. Grott, J. Knollenberg, C. Krause, The Apollo Lunar heat flow experiment revisited: a critical reassessment of the in-situ thermal conductivity determination. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E11005 (2010)
W.S. Kiefer, Lunar heat flow experiments: science objectives and a strategy for minimizing the effects of lander-induced perturbations. Planet. Space Sci. 60(1), 155–165 (2012)
H.H. Kieffer, Thermal model for analysis of Mars infrared mapping. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 118(3), 451–470 (2013)
M.G. Langseth, S.J. Keihm, K. Peters, Revised lunar heat-flow values, in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Proceedings, vol. 7 (1976), pp. 3143–3171
M.J. Ledlow, J.O. Burns, G.A. Gisler, J.-H. Zhao, M. Zeilik, D.N. Baker, Subsurface emissions from Mercury: VLA radio observations at 2 and 6 centimeters. Astrophys. J. 384, 640–655 (1992)
M.T. Lemmon, M.J. Wolff, J.F. Bell, M.D. Smith, B.A. Cantor, P.H. Smith, Dust aerosol, clouds, and the atmospheric optical depth record over 5 Mars years of the Mars exploration rover mission. Icarus 251, 96–111 (2015)
R.D. Lorenz, Planetary seismology—expectations for lander and wind noise with application to Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 62(1), 86–96 (2012)
D. Mimoun, P. Lognonné, D. Giardini, W.T. Pike, U. Christensen, A. van den Berg, P. Schibler (Team), The SEIS experiment: a planetary seismometer for Mars... and the Moon, in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, vol. 38 (2007), p. 2204
N. Mueller, E. Kopp, I. Walter, M. Grott, J. Knollenberg, M. Siegler, S. Smrekar, F. Hänschke, E. Kessler, T. Spohn, The HP3 radiometer for the InSight mission, in 45th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2014), p. 2375
M.D. Paton, A.M. Harri, H. Savijärvi, T. Mäkinen, A. Hagermann, O. Kemppinen, A. Johnston, Thermal and microstructural properties of fine-grained material at the Viking Lander 1 site. Icarus 271, 360–374 (2016)
S. Piqueux, P.R. Christensen, A model of thermal conductivity for planetary soils: 1. Theory for unconsolidated soils. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 114(E9), E09005 (2009)
A.C. Plesa, M. Grott, M. Lemmon, N. Mueller, S. Piqueux, M. Siegler, S. Smrekar, T. Spohn, Interannual perturbations of the Martian surface heat flow by atmospheric dust opacity variations. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 121(10), 2166–2175 (2016)
M.A. Presley, P.R. Christensen, The effect of bulk density and particle size sorting on the thermal conductivity of particulate materials under Martian atmospheric pressures. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 102(E4), 9221–9229 (1997)
J.T. Schofield, J.R. Barnes, D. Crisp, R.M. Haberle, S. Larsen, J.A. Magalhaes, J.R. Murphy, A. Seiff, G. Wilson, The Mars Pathfinder atmospheric structure investigation/meteorology (ASI/MET) experiment. Science 278(5344), 1752–1758 (1997)
M.A. Siegler, D.A. Paige, S.J. Keihm, A.R. Vasavada, R.R. Ghent, J.L. Bandfield, K.J. Snook, Apollo lunar heat flow experiments and the LRO diviner radiometer, in 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010), p. 2650
M.A. Siegler, B.G. Bills, D.A. Paige, Effects of orbital evolution on lunar ice stability. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 116(E3), E03010 (2011)
M.R. Sims et al., Beagle 2: a proposed exobiology lander for ESA’s 2003 Mars express mission. Adv. Space Res. 23(11), 1925–1928 (1999)
T. Spohn et al., INSIGHT: measuring the Martian heat flow using the heat flow and physical properties package (HP3). LPI Contrib. 1683, 1124 (2012)
W.R. Ward, Climatic variations on Mars: 1. Astronomical theory of insolation. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 3375–3386 (1974)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the InSight Project for support leading to these efforts and thank the reviewers for their helpful suggestions and corrections. Part of this research was carried out at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. This paper is InSight Contribution Number (ICN) 13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siegler, M.A., Smrekar, S.E., Grott, M. et al. The InSight Mars Lander and Its Effect on the Subsurface Thermal Environment. Space Sci Rev 211, 259–275 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0331-2