Abstract
Since its introduction to astro- and solar physics, the concept of helicity has proven to be useful in providing critical insights into physics of various processes from astrophysical dynamos, to magnetic reconnection and eruptive phenomena. Signature of helicity was also detected in many solar features, including orientation of solar active regions, or Joy’s law. Here we provide a summary of both solar phenomena and consider mutual relationship and its importance for the evolution of solar magnetic fields.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.I. Abramenko, T. Wang, V.B. Yurchishin, Analysis of electric current helicity in active regions on the basis of vector magnetograms. Sol. Phys. 168, 75–89 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF00145826
V.I. Abramenko, T. Wang, V.B. Yurchishin, Electric current helicity in 40 active regions in the maximum of solar cycle 22. Sol. Phys. 174, 291–296 (1997). doi:10.1023/A:1004957515498
T. Amari, J.F. Luciani, J.J. Aly, Z. Mikic, J. Linker, Coronal mass ejection: initiation, magnetic helicity, and flux ropes. I. Boundary motion-driven evolution. Astrophys. J. 585, 1073–1086 (2003a). doi:10.1086/345501
T. Amari, J.F. Luciani, J.J. Aly, Z. Mikic, J. Linker, Coronal mass ejection: initiation, magnetic helicity, and flux ropes. II. Turbulent diffusion-driven evolution. Astrophys. J. 595, 1231–1250 (2003b). doi:10.1086/377444
S.K. Antiochos, C.R. DeVore, J.A. Klimchuk, A model for solar coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 510, 485–493 (1999). doi:10.1086/306563
G. Attrill, M.S. Nakwacki, L.K. Harra, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, C.H. Mandrini, S. Dasso, J. Wang, Using the evolution of coronal dimming regions to probe the global magnetic field topology. Sol. Phys. 238, 117–139 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11207-006-0167-5
H.W. Babcock, The topology of the sun’s magnetic field and the 22-year cycle. Astrophys. J. 133, 572 (1961). doi:10.1086/147060
S. Bao, H. Zhang, Patterns of current helicity for the twenty-second solar cycle. Astrophys. J. Lett. 496, 43 (1998). doi:10.1086/311232
S.D. Bao, A.A. Pevtsov, T.J. Wang, H.Q. Zhang, Helicity computation using observations from two different polarimetric instruments. Sol. Phys. 195, 75–87 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1005244700895
I. Baumann, D. Schmitt, M. Schüssler, S.K. Solanki, Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field on the solar surface: a parameter study. Astron. Astrophys. 426, 1075–1091 (2004). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20048024
M.A. Berger, Rigorous new limits on magnetic helicity dissipation in the solar corona. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 30(1–2), 79–104 (1984). doi:10.1080/03091928408210078
M.A. Berger, Structure and stability of constant-alpha force-free fields. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 59, 433–444 (1985). doi:10.1086/191079
M.A. Berger, Magnetic helicity in space physics, in Magnetic Helicity in Space and Laboratory Plasmas. Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 111 (American Geophysical Union, Washington DC, 1999), pp. 1–11.
M.A. Berger, G.B. Field, The topological properties of magnetic helicity. J. Fluid Mech. 147, 133–148 (1984)
M.A. Berger, C. Prior, The writhe of open and closed curves. J. Phys. A, Math. Gen. 39, 8321–8348 (2006). doi:10.1088/0305-4470/39/26/005
M.A. Berger, A. Ruzmaikin, Rate of helicity production by solar rotation. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10481–10490 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999JA900392
P.N. Bernasconi, D.M. Rust, D. Hakim, Advanced automated solar filament detection and characterization code: description, performance, and results. Solar Phys. 228, 97–117 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11207-005-2766-y
A. Brandenburg, C. Sandin, Catastrophic alpha quenching alleviated by helicity flux and shear. Astron. Astrophys. 427, 13–21 (2004). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20047086
M.T. Brown, R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov (eds.), Magnetic Helicity in Space and Laboratory Plasmas. Geophysical Monograph Series (AGU, Washington, D.C., 1999)
W. Brunner, Gesetzmäßigkeiten in der Anordnung der Sonnenflecken zu Gruppen. Astron. Mitt. Eidgenöss. Sternwarte Zür. 13, 67–78 (1930)
J. Büchner, A.A. Pevtsov (eds.), Magnetic Helicity at the Sun, in Solar Wind and Magnetospheres. Advances in Space Research, vol. 32 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2003)
A.B. Burnette, R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov, Photospheric and coronal currents in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 606, 565–570 (2004). doi:10.1086/382775
P.S. Cally, M. Dikpati, P.A. Gilman, Clamshell and tipping instabilities in a two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic tachocline. Astrophys. J. 582, 1190–1205 (2003). doi:10.1086/344746
G. Călugăreanu, On isotopy classes of three dimensional knots and their invariants. Czechoslov. Math. J. 11, 588–625 (1961)
R.H. Cameron, M. Schüssler, Are the strengths of solar cycles determined by converging flows towards the activity belts? Astron. Astrophys. 548, 57 (2012). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219914
R.H. Cameron, J. Jiang, D. Schmitt, M. Schüssler, Surface flux transport modeling for solar cycles 15–21: effects of cycle-dependent tilt angles of suns pot groups. Astrophys. J. 719, 264–270 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/719/1/264
R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov, Helicity of solar active-region magnetic fields, in Synoptic Solar Physics, ed. by K.S. Balasubramaniam, J. Harvey, D. Rabin. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 140 (1998), p. 131
J. Chae, Observational determination of the rate of magnetic helicity transport through the solar surface via the horizontal motion of field line footpoints. Astrophys. J. Lett. 560, 95–98 (2001). doi:10.1086/324173
J. Chae, Y.-J. Moon, Y.-D. Park, Determination of magnetic helicity content of solar active regions from SOHO/MDI magnetograms. Sol. Phys. 223, 39–55 (2004). doi:10.1007/s11207-004-0938-9
P. Charbonneau, Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2, 2 (2005)
P. Chatterjee, A.R. Choudhuri, K. Petrovay, Development of twist in an emerging magnetic flux tube by poloidal field accretion. Astron. Astrophys. 449, 781–789 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054401
A.R. Choudhuri, On the connection between mean field dynamo theory and flux tubes. Sol. Phys. 215, 31–55 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1024874816178
A.R. Choudhuri, P. Chatterjee, D. Nandy, Helicity of solar active regions from a dynamo model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 615, 57–60 (2004). doi:10.1086/426054
K. Dalmasse, E. Pariat, G. Valori, P. Démoulin, L.M. Green, First observational application of a connectivity-based helicity flux density. Astron. Astrophys. 555, 6 (2013). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201321999
K. Dalmasse, E. Pariat, P. Démoulin, G. Aulanier, Photospheric injection of magnetic helicity: connectivity-based flux density method. Sol. Phys. 289, 107–136 (2014). doi:10.1007/s11207-013-0326-4
M. Dasi-Espuig, S.K. Solanki, N.A. Krivova, R. Cameron, T. Peñuela, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 518, 7 (2010). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014301
M. Dasi-Espuig, S.K. Solanki, N.A. Krivova, R. Cameron, T. Peñuela, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle (corrigendum). Astron. Astrophys. 556, 3 (2013). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014301e
P. Démoulin, A review of the quantitative links between CMEs and magnetic clouds. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3113–3125 (2008). doi:10.5194/angeo-26-3113-2008
P. Démoulin, M.A. Berger, Magnetic energy and helicity fluxes at the photospheric level. Sol. Phys. 215, 203–215 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1025679813955
P. Démoulin, C.H. Mandrini, L. Van Driel-Gesztelyi, M.C. Lopez Fuentes, G. Aulanier, The magnetic helicity injected by shearing motions. Sol. Phys. 207, 87–110 (2002a). doi:10.1023/A:1015531804337
P. Démoulin, C.H. Mandrini, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, B.J. Thompson, S. Plunkett, Z. Kovári, G. Aulanier, A. Young, What is the source of the magnetic helicity shed by CMEs? The long-term helicity budget of AR 7978. Astron. Astrophys. 382, 650–665 (2002b). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011634
C.R. DeVore, Magnetic helicity generation by solar differential rotation. Astrophys. J. 539, 944–953 (2000). doi:10.1086/309274
S. D’Silva, A.R. Choudhuri, A theoretical model for tilts of bipolar magnetic regions. Astron. Astrophys. 272, 621 (1993)
Y. Fan, D. Gong, On the twist of emerging flux loops in the solar convection zone. Sol. Phys. 192, 141–157 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1005260207672
Y. Fan, G.H. Fisher, A.N. McClymont, Dynamics of emerging active region flux loops. Astrophys. J. 436, 907–928 (1994). doi:10.1086/174967
J.M. Finn, T.M. Antonsen Jr., Turbulent relaxation of compressible plasmas with flow. Phys. Fluids 26, 3540–3552 (1983). doi:10.1063/1.864115
G.H. Fisher, Y. Fan, R.F. Howard, Comparisons between theory and observation of active region tilts. Astrophys. J. 438, 463–471 (1995). doi:10.1086/175090
C. Foullon, C.J. Owen, S. Dasso, L.M. Green, I. Dandouras, H.A. Elliott, A.N. Fazakerley, Y.V. Bogdanova, N.U. Crooker, Multi-spacecraft study of the 21 January 2005 ICME. Sol. Phys. 244(1–2), 139–165 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11207-007-0355-y
M.K. Georgoulis, B.J. LaBonte, Reconstruction of an inductive velocity field vector from Doppler motions and a pair of solar vector magnetograms. Astrophys. J. 636, 475–495 (2006). doi:10.1086/497978
M.K. Georgoulis, B.J. LaBonte, Magnetic energy and helicity budgets in the active region solar corona. I. Linear force-free approximation. Astrophys. J. 671, 1034–1050 (2007). doi:10.1086/521417
M.K. Georgoulis, D.M. Rust, A.A. Pevtsov, P.N. Bernasconi, K.M. Kuzanyan, Solar magnetic helicity injected into the heliosphere: magnitude, balance, and periodicities over solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. Lett. 705, 48–52 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/705/1/L48
M.K. Georgoulis, K. Tziotziou, N.-E. Raouafi, Magnetic energy and helicity budgets in the active-region solar corona. II. Nonlinear force-free approximation. Astrophys. J. 759, 1 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/759/1/1
P.A. Gilman, M. Dikpati, Joint instability of latitudinal differential rotation and concentrated toroidal fields below the solar convection zone. II. Instability of narrow bands at all latitudes. Astrophys. J. 528, 552–572 (2000). doi:10.1086/308146
P.A. Gilman, P.A. Fox, Joint instability of latitudinal differential rotation and toroidal magnetic fields below the solar convection zone. Astrophys. J. 484, 439 (1997). doi:10.1086/304330
S. Gosain, A.A. Pevtsov, G.V. Rudenko, S.A. Anfinogentov, First synoptic maps of photospheric vector magnetic field from SOLIS/VSM: non-radial magnetic fields and hemispheric pattern of helicity. Astrophys. J. 772, 52 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/772/1/52
L.M. Green, M.C. López fuentes, C.H. Mandrini, P. Démoulin, L. Van Driel-Gesztelyi, J.L. Culhane, The magnetic helicity budget of a CME-prolific active region. Sol. Phys. 208, 43–68 (2002). doi:10.1023/A:1019658520033
L.M. Green, B. Kliem, T. Török, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, G.D.R. Attrill, Transient coronal sigmoids and rotating erupting flux ropes. Sol. Phys. 246, 365–391 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11207-007-9061-z
A.M. Gulisano, S. Dasso, C.H. Mandrini, P. Démoulin, Magnetic clouds: a statistical study of magnetic helicity. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 67, 1761–1766 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2005.02.026
M. Hagino, T. Sakurai, Latitude variation of helicity in solar active regions. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 56, 831–843 (2004). doi:10.1093/pasj/56.5.831
M. Hagino, T. Sakurai, Solar-cycle variation of magnetic helicity in active regions. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 57, 481–485 (2005). doi:10.1093/pasj/57.3.481
M.J. Hagyard, A.A. Pevtsov, Studies of solar helicity using vector magnetograms. Sol. Phys. 189, 25–43 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005215001514
G.E. Hale, F. Ellerman, S.B. Nicholson, A.H. Joy, The magnetic polarity of sun-spots. Astrophys. J. 49, 153 (1919). doi:10.1086/142452
J. Hao, M. Zhang, Hemispheric helicity trend for solar cycle 24. Astrophys. J. Lett. 733, 27 (2011). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/733/2/L27
Z.A. Holder, R.C. Canfield, R.A. McMullen, D. Nandy, R.F. Howard, A.A. Pevtsov, On the tilt and twist of solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 611, 1149–1155 (2004). doi:10.1086/422247
R.F. Howard, Axial tilt angles of sunspot groups. Sol. Phys. 136, 251–262 (1991). doi:10.1007/BF00146534
R.F. Howard, Axial tilt angles of active regions. Sol. Phys. 169, 293–301 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF00190606
V.G. Ivanov, Joy’s law and its features according to the data of three sunspot catalogs. Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 999–1004 (2012). doi:10.1134/S0016793212080130
C. Jacobs, S. Poedts, B. van der Holst, The effect of the solar wind on CME triggering by magnetic foot point shearing. Astron. Astrophys. 450, 793–803 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054670
B. Kliem, S. Rust, N. Seehafer, Helicity transport in a simulated coronal mass ejection, in IAU Symposium, ed. by A. Bonanno, E. de Gouveia Dal Pino, A.G. Kosovichev IAU Symposium, vol. 274 (2011), pp. 125–128. doi:10.1017/S1743921311006715
B. Kliem, T. Török, W.T. Thompson, A parametric study of erupting flux rope rotation. Modeling the “Cartwheel CME” on 9 April 2008. Sol. Phys. 281, 137–166 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11207-012-9990-z
A.G. Kosovichev, J.O. Stenflo, Tilt of emerging bipolar magnetic regions on the sun. Astrophys. J. Lett. 688, 115–118 (2008). doi:10.1086/595619
K. Kusano, T. Maeshiro, T. Yokoyama, T. Sakurai, Measurement of magnetic helicity injection and free energy loading into the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 577, 501–512 (2002). doi:10.1086/342171
K. Kusano, T. Yokoyama, T. Maeshiro, T. Sakurai, Annihilation of magnetic helicity: a new model for solar flare onset. Adv. Space Res. 32, 1931–1936 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(03)90628-4
K. Kusano, T. Maeshiro, T. Yokoyama, T. Sakurai, The trigger mechanism of solar flares in a coronal arcade with reversed magnetic shear. Astrophys. J. 610, 537–549 (2004). doi:10.1086/421547
B.J. LaBonte, M.K. Georgoulis, D.M. Rust, Survey of magnetic helicity injection in regions producing X-class flares. Astrophys. J. 671, 955–963 (2007). doi:10.1086/522682
R.J. Leamon, R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov, Properties of magnetic clouds and geomagnetic storms associated with eruption of coronal sigmoids. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1234 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000313
R.B. Leighton, A magneto-kinematic model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 156, 1 (1969). doi:10.1086/149943
J. Li, R.K. Ulrich, Long-term measurements of sunspot magnetic tilt angles. Astrophys. J. 758, 115 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/758/2/115
E.-K. Lim, J. Chae, Chirality of intermediate filaments and magnetic helicity of active regions. Astrophys. J. 692, 104–108 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/692/1/104
E.-K. Lim, H. Jeong, J. Chae, Y.-J. Moon, A check for consistency between different magnetic helicity measurements based on the helicity conservation principle. Astrophys. J. 656, 1167–1172 (2007). doi:10.1086/510575
Y. Liu, P.W. Schuck, Magnetic energy and helicity in two emerging active regions in the sun. Astrophys. J. 761, 105 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/761/2/105
Y. Liu, P.W. Schuck, A note on computation of relative magnetic-helicity flux across the photosphere. Sol. Phys. 283, 283–294 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11207-012-0219-y
Y. Liu, J.T. Hoeksema, X. Sun, Test of the hemispheric rule of magnetic helicity in the sun using the helioseismic and magnetic imager (HMI) data. Astrophys. J. Lett. 783, 1 (2014). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/783/1/L1
D.W. Longcope, Inferring a photospheric velocity field from a sequence of vector magnetograms: the minimum energy fit. Astrophys. J. 612, 1181–1192 (2004). doi:10.1086/422579
D.W. Longcope, G.H. Fisher, The effects of convection zone turbulence on the tilt angles of magnetic bipoles. Astrophys. J. 458, 380 (1996). doi:10.1086/176821
D.W. Longcope, A. Malanushenko, Defining and calculating self-helicity in coronal magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 674(2), 1130 (2008). http://stacks.iop.org/0004-637X/674/i=2/a=1130
D.W. Longcope, B.T. Welsch, A model for the emergence of a twisted magnetic flux tube. Astrophys. J. 545, 1089–1100 (2000). doi:10.1086/317846
D.W. Longcope, G.H. Fisher, A.A. Pevtsov, Flux-tube twist resulting from helical turbulence: the sigma-effect. Astrophys. J. 507, 417–432 (1998). doi:10.1086/306312
D.W. Longcope, M.G. Linton, A.A. Pevtsov, G.H. Fisher, I. Klapper, Twisted flux tubes and how they get that way, in Magnetic Helicity in Space and Laboratory Plasmas, ed. by M.R. Brown, R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov Geophysical Monographs Series, vol. 111 (AGU, Washington, D.C., 1999), pp. 93–101
M.C. López Fuentes, P. Démoulin, C.H. Mandrini, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, The counterkink rotation of a non-Hale active region. Astrophys. J. 544, 540–549 (2000). doi:10.1086/317180
M.C. López Fuentes, P. Démoulin, C.H. Mandrini, A.A. Pevtsov, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, Magnetic twist and writhe of active regions. On the origin of deformed flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 397, 305–318 (2003). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021487
B.C. Low, Solar activity and the corona. Sol. Phys. 167, 217–265 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF00146338
B.C. Low, Magnetic helicity in a two-flux partitioning of an ideal hydromagnetic fluid. Astrophys. J. 646(2), 1288 (2006). http://stacks.iop.org/0004-637X/646/i=2/a=1288
B.C. Low, M. Zhang, The hydromagnetic origin of the two dynamical types of solar coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 564, 53–56 (2002). doi:10.1086/338798
M.L. Luoni, P. Démoulin, C.H. Mandrini, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, Twisted flux tube emergence evidenced in longitudinal magnetograms: magnetic tongues. Sol. Phys. 270, 45–74 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11207-011-9731-8
P. MacNeice, S.K. Antiochos, A. Phillips, D.S. Spicer, C.R. DeVore, K. Olson, A numerical study of the breakout model for coronal mass ejection initiation. Astrophys. J. 614, 1028–1041 (2004). doi:10.1086/423887
C.H. Mandrini, S. Pohjolainen, S. Dasso, L.M. Green, P. Démoulin, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, C. Copperwheat, C. Foley, Interplanetary flux rope ejected from an X-ray bright point. The smallest magnetic cloud source-region ever observed. Astron. Astrophys. 434, 725–740 (2005). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041079
S.F. Martin, Observational criteria for filament models, in Solar Active Region Evolution: Comparing Models with Observations, ed. by K.S. Balasubramaniam, G.W. Simon. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 68 (1994), p. 264
S.F. Martin, Conditions for the formation and maintenance of filaments (invited review). Sol. Phys. 182, 107–137 (1998). doi:10.1023/A:1005026814076
S.F. Martin, R. Bilimoria, P.W. Tracadas, Magnetic field configurations basic to filament channels and filaments, in Solar Surface Magnetism, ed. by R.J. Rutten, C.J. Schrijver (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1994), p. 303
S.F. Martin, O. Panasenco, M.A. Berger, O. Engvold, Y. Lin, A.A. Pevtsov, N. Srivastava, The build-up to eruptive solar events viewed as the development of chiral systems, in Second ATST-EAST Meeting: Magnetic Fields from the Photosphere to the Corona, ed. by T.R. Rimmele, A. Tritschler, F. Wöger, M. Collados Vera, H. Socas-Navarro, R. Schlichenmaier, M. Carlsson, T. Berger, A. Cadavid, P.R. Gilbert, P.R. Goode, M. Knölker. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 463 (2012), p. 157
B.H. McClintock, A.A. Norton, Recovering Joy’s law as a function of solar cycle, hemisphere, and longitude. Sol. Phys. 287, 215–227 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11207-013-0338-0
H.K. Moffatt, The degree of knottedness of tangled vortex lines. J. Fluid Mech. 35, 117 (1969)
H.K. Moffatt, R.L. Ricca, Helicity and the Calugareanu invariant. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 439, 411–429 (1992). doi:10.1098/rspa.1992.0159
Y.-J. Moon, J. Chae, G.S. Choe, H. Wang, Y.D. Park, H.S. Yun, V. Yurchyshyn, P.R. Goode, Flare activity and magnetic helicity injection by photospheric horizontal motions. Astrophys. J. 574, 1066–1073 (2002a). doi:10.1086/340975
Y.-J. Moon, J. Chae, H. Wang, G.S. Choe, Y.D. Park, Impulsive variations of the magnetic helicity change rate associated with eruptive flares. Astrophys. J. 580, 528–537 (2002b). doi:10.1086/343130
R.L. Moore, A.C. Sterling, H.S. Hudson, J.R. Lemen, Onset of the magnetic explosion in solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 552, 833–848 (2001). doi:10.1086/320559
D. Nandy, Magnetic helicity and flux tube dynamics in the solar convection zone: comparisons between observation and theory. J. Geophys. Res. 111(A10), 12 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006JA011882
A. Nindos, M.D. Andrews, The association of big flares and coronal mass ejections: what is the role of magnetic helicity? Astrophys. J. Lett. 616, 175–178 (2004). doi:10.1086/426861
A. Nindos, H. Zhang, Photospheric motions and coronal mass ejection productivity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 573, 133–136 (2002). doi:10.1086/341937
A. Nindos, J. Zhang, H. Zhang, The magnetic helicity budget of solar active regions and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 594, 1033–1048 (2003). doi:10.1086/377126
A. Nindos, S. Patsourakos, T. Wiegelmann, On the role of the background overlying magnetic field in solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 748, 6 (2012). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/748/1/L6
A.A. Norton, P.A. Gilman, Recovering solar toroidal field dynamics from sunspot location patterns. Astrophys. J. 630, 1194–1205 (2005). doi:10.1086/431961
L.J. November, G.W. Simon, Precise proper-motion measurement of solar granulation. Astrophys. J. 333, 427–442 (1988). doi:10.1086/166758
S. Ortolani, D.D. Schnack, Magnetohydrodynamics of Plasma Relaxation (World Scientific, Singapore, 1993)
E. Pariat, P. Démoulin, M.A. Berger, Photospheric flux density of magnetic helicity. Astron. Astrophys. 439, 1191–1203 (2005). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20052663
E. Pariat, A. Nindos, P. Démoulin, M.A. Berger, What is the spatial distribution of magnetic helicity injected in a solar active region? Astron. Astrophys. 452, 623–630 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054643
E. Pariat, P. Démoulin, A. Nindos, How to improve the maps of magnetic helicity injection in active regions? Adv. Space Res. 39, 1706–1714 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.02.047
G.J.D. Petrie, Evolution of active and polar photospheric magnetic fields during the rise of cycle 24 compared to previous cycles. Sol. Phys. 281, 577–598 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11207-012-0117-3
K. Petrovay, U.R. Christensen, The magnetic sun: reversals and long-term variations. Space Sci. Rev. 155, 371–385 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11214-010-9657-8
A.A. Pevtsov, Transequatorial loops in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 531, 553–560 (2000). doi:10.1086/308467
A.A. Pevtsov, Sinuous coronal loops at the sun, in Multi-Wavelength Observations of Coronal Structure and Dynamics, ed. by P.C.H. Martens, D.P. Cauffman. COSPAR Colloquia Series, vol. 13 (Pergamon, Dordrecht, 2002), pp. 125–134
A.A. Pevtsov, Helicity generation and signature in the solar atmosphere, in IAU Joint Discussion. IAU Joint Discussion, vol. 3 (2003)
A.A. Pevtsov, What helicity can tell us about solar magnetic fields. J. Astrophys. Astron. 29, 49–56 (2008). doi:10.1007/s12036-008-0006-1
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, Helicity of the photospheric magnetic field, in Magnetic Helicity in Space and Laboratory Plasmas, ed. by M.R. Brown, R.C. Canfield, A.A. Pevtsov. Geophysical Monographs Series, vol. 111 (AGU, Washington, D.C., 1999), pp. 103–110
A.A. Pevtsov, S.M. Latushko, Current helicity of the large-scale photospheric magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 528, 999–1003 (2000). doi:10.1086/308227
A.A. Pevtsov, D.W. Longcope, NOAA 7926: a kinked omega-loop? Astrophys. J. 508, 908–915 (1998). doi:10.1086/306414
A.A. Pevtsov, D.W. Longcope, Origin of helicity in the quiet sun, in Advanced Solar Polarimetry—Theory, Observation, and Instrumentation, ed. by M. Sigwarth. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 236 (2001), p. 423
A.A. Pevtsov, D.W. Longcope, Helicity as the ultimate test to the surface dynamo problem, in New Solar Physics with Solar-B Mission, ed. by K. Shibata, S. Nagata, T. Sakurai. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 369 (2007), p. 99
A.A. Pevtsov, N.L. Peregud, Electric currents in a unipolar sunspot, in Physics of Magnetic Flux Ropes. Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 58 (American Geophysical Union, Washington DC, 1990), pp. 161–165
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, T.R. Metcalf, Patterns of helicity in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 425, 117–119 (1994). doi:10.1086/187324
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, T.R. Metcalf, Latitudinal variation of helicity of photospheric magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 440, 109–112 (1995). doi:10.1086/187773
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, A.N. McClymont, On the subphotospheric origin of coronal electric currents. Astrophys. J. 481, 973 (1997). doi:10.1086/304065
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, S.M. Latushko, Hemispheric helicity trend for solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. Lett. 549, 261–263 (2001). doi:10.1086/319179
A.A. Pevtsov, K.S. Balasubramaniam, J.W. Rogers, Chirality of chromospheric filaments. Astrophys. J. 595, 500–505 (2003). doi:10.1086/377339
A.A. Pevtsov, V.M. Maleev, D.W. Longcope, Helicity evolution in emerging active regions. Astrophys. J. 593, 1217–1225 (2003a). doi:10.1086/376733
A.A. Pevtsov, R.C. Canfield, T. Sakurai, M. Hagino, On the solar cycle variation of the hemispheric helicity rule. Astrophys. J. 677, 719–722 (2008). doi:10.1086/533435
A.A. Pevtsov, M. Berger, A. Nindos, A. Norton, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, Magnetic helicity, tilt, and twist, in The Solar Activity Cycle: Physical Causes and Consequences, ed. by A. Balogh, H. Hudson, K. Petrovay, R. von Steiger. Space Science Series of ISSI, vol. 53 (Springer, Heidelberg, 2014)
A.D. Phillips, P.J. MacNeice, S.K. Antiochos, The role of magnetic helicity in coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 624, 129–132 (2005). doi:10.1086/430516
K.G. Puschmann, B. Ruiz Cobo, V. Martínez Pillet, The electrical current density vector in the inner penumbra of a sunspot. Astrophys. J. Lett. 721, 58–61 (2010). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/721/1/L58
B. Ravindra, D.W. Longcope, W.P. Abbett, Inferring photospheric velocity fields using a combination of minimum energy fit, local correlation tracking, and Doppler velocity. Astrophys. J. 677, 751–768 (2008). doi:10.1086/528363
R.L. Ricca, B. Nipoti, Gauss linking number revisited. J. Knot Theory Ramif. 20, 1325–1343 (2011)
P. Romano, F. Zuccarello, Flare occurrence and the spatial distribution of the magnetic helicity flux. Astron. Astrophys. 535, 1–5 (2011). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117594
P. Romano, L. Contarino, F. Zuccarello, Eruption of a helically twisted prominence. Sol. Phys. 214, 313–323 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1024257603143
G.V. Rudenko, I.I. Myshyakov, Gauge-invariant helicity for force-free magnetic fields in a rectangular box. Sol. Phys. 270, 165–173 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11207-011-9743-4
B. Ruiz Cobo, K.G. Puschmann, Twist, writhe, and helicity in the inner penumbra of a sunspot. Astrophys. J. 745, 141 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/745/2/141
D.M. Rust, Spawning and shedding helical magnetic fields in the solar atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 241–244 (1994). doi:10.1029/94GL00003
D.M. Rust, A. Kumar, Evidence for helically kinked magnetic flux ropes in solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 464, 199 (1996). doi:10.1086/310118
D.M. Rust, S.F. Martin, A correlation between sunspot whirls and filament type, in Solar Active Region Evolution: Comparing Models with Observations, ed. by K.S. Balasubramaniam, G.W. Simon. Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 68 (1994), p. 337
H.U. Schmidt, Magnetohydrodynamics of an active region, in Structure and Development of Solar Active Regions, ed. by K.O. Kiepenheuer. IAU Symposium, vol. 35 (1968), p. 95
P.W. Schuck, Tracking vector magnetograms with the magnetic induction equation. Astrophys. J. 683, 1134–1152 (2008). doi:10.1086/589434
M. Schüssler, P. Caligari, A. Ferriz-Mas, F. Moreno-Insertis, Instability and eruption of magnetic flux tubes in the solar convection zone. Astron. Astrophys. 281, 69–72 (1994)
N. Seehafer, Electric current helicity in the solar atmosphere. Sol. Phys. 125, 219–232 (1990). doi:10.1007/BF00158402
K.R. Sivaraman, S.S. Gupta, R.F. Howard, Measurement of Kodaikanal white-light images—IV. Axial tilt angles of sunspot groups. Sol. Phys. 189, 69–83 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005277515551
J.O. Stenflo, A.G. Kosovichev, Bipolar magnetic regions on the sun: global analysis of the SOHO/MDI data set. Astrophys. J. 745, 129 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/745/2/129
J.K. Thalmann, B. Inhester, T. Wiegelmann, Estimating the relative helicity of coronal magnetic fields. Sol. Phys. 272, 243–255 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11207-011-9826-2
J.K. Thalmann, S.K. Tiwari, T. Wiegelmann, Force-free field modeling of twist and braiding-induced magnetic energy in an active-region corona. Astrophys. J. 780(1), 102 (2014). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/780/1/102
L. Tian, Y. Liu, Tilt and α best of major flare-producing active regions. Astron. Astrophys. 407, 13–16 (2003). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030977
L. Tian, S. Bao, H. Zhang, H. Wang, Relationship in sign between tilt and twist in active region magnetic fields. Astron. Astrophys. 374, 294–300 (2001). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010701
A.G. Tlatov, A.A. Pevtsov, Bimodal distribution of magnetic fields and areas of sunspots. Sol. Phys. 289, 1143–1152 (2014). doi:10.1007/s11207-013-0382-9
A.G. Tlatov, V.V. Vasil’eva, A.A. Pevtsov, Distribution of magnetic bipoles on the sun over three solar cycles. Astrophys. J. 717, 357–362 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/717/1/357
T. Török, B. Kliem, Confined and ejective eruptions of kink-unstable flux ropes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 630, 97–100 (2005). doi:10.1086/462412
T. Török, M.A. Berger, B. Kliem, The writhe of helical structures in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 516, 49 (2010). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913578
T. Török, B. Kliem, M.A. Berger, M.G. Linton, P. Demoulin, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, The evolution of writhe in kink-unstable flux ropes and erupting filaments. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion, 56(6), 064012 (2014)
K. Tziotziou, M.K. Georgoulis, N.-E. Raouafi, The magnetic energy-helicity diagram of solar active regions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 759, 4 (2012). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/759/1/L4
K. Tziotziou, M.K. Georgoulis, Y. Liu, Interpreting eruptive behavior in NOAA AR 11158 via the region’s magnetic energy and relative-helicity budgets. Astrophys. J. 772, 115 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/772/2/115
L. Upton, D.H. Hathaway, Predicting the sun’s polar magnetic fields with a surface flux transport model. Astrophys. J. 780, 5 (2014). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/780/1/5
G. Valori, P. Démoulin, E. Pariat, Comparing values of the relative magnetic helicity in finite volumes. Sol. Phys. 278, 347–366 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11207-012-0044-3
A.A. van Ballegooijen, P.C.H. Martens, Formation and eruption of solar prominences. Astrophys. J. 343, 971–984 (1989). doi:10.1086/167766
B. Vršnak, V. Ruždjak, B. Rompolt, Stability of prominences exposing helical-like patterns. Sol. Phys. 136, 151–167 (1991). doi:10.1007/BF00151701
Y.-M. Wang, On the strength of the hemispheric rule and the origin of active-region helicity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 775, 46 (2013). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/775/2/L46
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Average properties of bipolar magnetic regions during sunspot cycle 21. Sol. Phys. 124, 81–100 (1989). doi:10.1007/BF00146521
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Magnetic flux transport and the sun’s dipole moment—new twists to the Babcock-Leighton model. Astrophys. J. 375, 761–770 (1991). doi:10.1086/170240
C. Wang, M. Zhang, A hemispheric helicity sign rule indicated by large-scale photospheric magnetic fields at three phases of solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. 720, 632–638 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/720/1/632
M.A. Weber, Y. Fan, M.S. Miesch, The rise of active region flux tubes in the turbulent solar convective envelope. Astrophys. J. 741, 11 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/1/11
M.A. Weber, Y. Fan, M.S. Miesch, Comparing simulations of rising flux tubes through the solar convection zone with observations of solar active regions: constraining the dynamo field strength. Sol. Phys. 287, 239–263 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11207-012-0093-7
B.T. Welsch, D.W. Longcope, Magnetic helicity injection by horizontal flows in the quiet sun. I. Mutual-helicity flux. Astrophys. J. 588, 620–629 (2003). doi:10.1086/368408
B.T. Welsch, G.H. Fisher, W.P. Abbett, S. Regnier, ILCT: recovering photospheric velocities from magnetograms by combining the induction equation with local correlation tracking. Astrophys. J. 610, 1148–1156 (2004). doi:10.1086/421767
B.T. Welsch, W.P. Abbett, M.L. De Rosa, G.H. Fisher, M.K. Georgoulis, K. Kusano, D.W. Longcope, B. Ravindra, P.W. Schuck, Tests and comparisons of velocity-inversion techniques. Astrophys. J. 670, 1434–1452 (2007). doi:10.1086/522422
D.R. Williams, T. Török, P. Démoulin, L. van Driel-Gesztelyi, B. Kliem, Eruption of a kink-unstable filament in NOAA active region 10696. Astrophys. J. Lett. 628, 163–166 (2005). doi:10.1086/432910
P.R. Wilson, R.C. Altrocki, K.L. Harvey, S.F. Martin, H.B. Snodgrass, The extended solar activity cycle. Nature 333, 748–750 (1988). doi:10.1038/333748a0
A. Wright, M.A. Berger, The effect of reconnection upon the linkage and interior structure of magnetic flux tubes. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 1295–1302 (1989)
S. Yang, H. Zhang, Large-scale magnetic helicity fluxes estimated from MDI magnetic synoptic charts over the solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. 758, 61 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/758/1/61
A.R. Yeates, D.H. Mackay, A.A. van Ballegooijen, Modelling the global solar corona: filament chirality observations and surface simulations. Sol. Phys. 245, 87–107 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11207-007-9013-7
M. Zhang, Helicity observations of weak and strong fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 646, 85–88 (2006). doi:10.1086/506560
M. Zhang, N. Flyer, The dependence of the helicity bound of force-free magnetic fields on boundary conditions. Astrophys. J. 683, 1160–1167 (2008). doi:10.1086/589993
M. Zhang, B.C. Low, Magnetic flux emergence into the solar corona. I. Its role for the reversal of global coronal magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 561, 406–419 (2001). doi:10.1086/323238
M. Zhang, B.C. Low, Magnetic flux emergence into the solar corona. III. The role of magnetic helicity conservation. Astrophys. J. 584, 479–496 (2003). doi:10.1086/345615
M. Zhang, B.C. Low, The hydromagnetic nature of solar coronal mass ejections. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 43, 103–137 (2005). doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.43.072103.150602
M. Zhang, N. Flyer, B.C. Low, Magnetic field confinement in the corona: the role of magnetic helicity accumulation. Astrophys. J. 644, 575–586 (2006). doi:10.1086/503353
H. Zhang, T. Sakurai, A. Pevtsov, Y. Gao, H. Xu, D.D. Sokoloff, K. Kuzanyan, A new dynamo pattern revealed by solar helical magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 30–33 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00793.x
M. Zhang, N. Flyer, B. Chye Low, Magnetic helicity of self-similar axisymmetric force-free fields. Astrophys. J. 755, 78 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/755/1/78
Y. Zhang, R. Kitai, K. Takizawa, Magnetic helicity transported by flux emergence and shuffling motions in solar active region NOAA 10930. Astrophys. J. 751, 85 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/751/2/85
F.P. Zuccarello, C. Jacobs, A. Soenen, S. Poedts, B. van der Holst, F. Zuccarello, Modelling the initiation of coronal mass ejections: magnetic flux emergence versus shearing motions. Astron. Astrophys. 507, 441–452 (2009). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912541
Acknowledgements
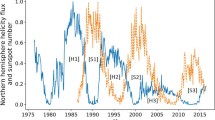
The National Solar Observatory (NSO) is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, AURA Inc under cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation (NSF). AN’s research has been partly co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund—ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF)—Research Funding Program: “Thales. Investing in knowledge society through the European Social Fund.” LvDG acknowledges support by STFC Consolidated Grant ST/H00260/1 and the Hungarian Research grants OTKA K-081421 and K-109276. AAP acknowledges support by NASA’s NNH09AL04I inter agency transfer. Data used in Fig. 9 were acquired by SOLIS instruments operated by NISP/NSO/AURA/NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pevtsov, A.A., Berger, M.A., Nindos, A. et al. Magnetic Helicity, Tilt, and Twist. Space Sci Rev 186, 285–324 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0082-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0082-2