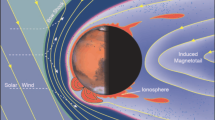
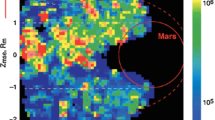
Abstract
The Mars thermosphere-ionosphere-exosphere (TIE) system constitutes the atmospheric reservoir (i.e. available cold and hot planetary neutral and thermal ion species) that regulates present day escape processes from the planet. The characterization of this TIE system, including its spatial and temporal (e.g., solar cycle, seasonal, diurnal, episodic) variability is needed to determine present day escape rates. Without knowledge of the physics and chemistry creating this TIE region and driving its variations, it is not possible to constrain either the short term or long term histories of atmosphere escape from Mars. MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission) will make both in-situ and remote measurements of the state variables of the Martian TIE system. A full characterization of the thermosphere (∼100–250 km) and ionosphere (∼100–400 km) structure (and its variability) will be conducted with the collection of spacecraft in-situ measurements that systematically span most local times and latitudes, over a regular sampling of Mars seasons, and throughout the bottom half of the solar cycle. Such sampling will far surpass that available from existing spacecraft and ground-based datasets. In addition, remote measurements will provide a systematic mapping of the composition and structure of Mars neutral upper atmosphere and coronae (e.g. H, C, N, O), as well as probe lower altitudes. Such a detailed characterization is a necessary first step toward answering MAVEN’s three main science questions (see Jakosky et al. 2014, this issue). This information will be used to determine present day escape rates from Mars, and provide an estimate of integrated loss to space throughout Mars history.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Angelats i Coll, F. Forget, M.A. López-Valverde et al., Upper atmosphere of Mars up to 120 km: Mars Global Surveyor data analysis with the LMD general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 109, E01011 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JE002163
D.T. Baird, R. Tolson, S.W. Bougher, B. Steers, Zonal wind calculation from MGS Accelerometer and rate data. AIAA J. Spacecr. Rockets 44(6), 1180–1187 (2007)
C.A. Barth, A.I.F. Stewart, S.W. Bougher et al., Aeronomy of the current martian atmosphere, in Mars, ed. by H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, M.S. Matthews (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992), pp. 1054–1089
J.-L. Bertaux, E. Chassefiere, V.G. Kurt, Vensu EUV measurements of hydrogen and helium from Venera 11 and Venera 12. Adv. Space Res. 5, 119–124 (1985)
J.-L. Bertaux, F. Leblanc, S. Perrier et al., Nightglow in the upper atmosphere of Mars and implications for atmospheric transport. Science 307, 566–569 (2005a). doi:10.1126/science.1106957
J.-L. Bertaux, F. Leblanc, O. Witasse et al., Discovery of an aurora on Mars. Nature 435, 790–794 (2005b)
S.W. Bougher, Comparative thermospheres: Venus and Mars. Adv. Space Res. 15(4), 21–25 (1995)
S.W. Bougher, Coupled MGCM-MTGCM Mars thermosphere simulations and resulting data products in support of the MAVEN mission. JPL/CDP report, pp. 1–9, 6 August 2012 (2012)
S.W. Bougher, M.J. Alexander, H.G. Mayr, Upper atmosphere dynamics: global circulation and gravity waves, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere, and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Phillips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997), pp. 259–291
S.W. Bougher, G. Keating, R. Zurek et al., Mars global surveyor aerobraking: Atmospheric trends and model interpretation. Adv. Space Res. 23, 1887–1897 (1999a). doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(99)00272-0
S.W. Bougher, S. Engel, R.G. Roble, B. Foster, Comparative terrestrial planet thermospheres 2. Solar cycle variation of global structure and winds at equinox. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 16591–16611 (1999b). doi:10.1029/1998JE001019
S.W. Bougher, S. Engel, R.G. Roble, B. Foster, Comparative terrestrial planet thermospheres 3. Solar cycle variation of global structure and winds at solstices. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 17669–17692 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999JE001232
S.W. Bougher, R.G. Roble, T.J. Fuller-Rowell, Simulations of the upper atmospheres of the terrestrial planets, in Atmospheres in the Solar System, Comparative Aeronomy, ed. by M. Mendillo, A.F. Nagy, J.H. Waite Jr. AGU Monograph, vol. 130 (American Geophysical Union, Washington, 2002), pp. 261–288
S.W. Bougher, S. Engel, D.P. Hinson, J.R. Murphy, MGS Radio Science electron density profiles: Interannual variability and implications for the martian neutral atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 109, E03010 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JE002154
S.W. Bougher, J.M. Bell, J.R. Murphy et al., Polar warming in the Mars thermosphere: Seasonal variations owing to changing isolation and dust distributions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L02203 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005GL024059
S.W. Bougher, P.-L. Blelly, M. Combi et al., Neutral upper atmosphere and ionosphere modeling. Space Sci. Rev. 139, 107–141 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11214-008-9401-9
S.W. Bougher, A. Valeille, M.R. Combi, V. Tenishev, Solar cycle and seasonal variability of the martian thermosphere-ionosphere and associated impacts upon atmospheric escape. SAE Technical Paper #2009-01-2386, SAE International (2009a)
S.W. Bougher, T.M. McDunn, K.A. Zoldak, J.M. Forbes, Solar cycle variability of Mars dayside exospheric temperatures: Model evaluation of underlying thermal balances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L05201 (2009b). doi:10.1029/2008GL036376
S.W. Bougher, A. Ridley, D. Pawlowski et al., Development and validation of the ground-to-exosphere Mars GITM code: solar cycle and seasonal variations of the upper atmosphere, in The Fourth International Workshop on the Mars Atmosphere: Modeling and Observations, Paris, France (2011a)
S.W. Bougher, D.J. Pawlowski, J.R. Murphy, Toward an understanding of the time-dependent responses of the martian upper atmosphere to dust storm events, in 2011 Fall AGU Meeting, San Francisco, California (2011b)
S.W. Bougher, D.A. Brain, J.L. Fox, F. Gonzalez-Galindo, C. Simon-Wedlund, P.G. Withers, Upper neutral atmosphere and ionosphere, in Mars Book II (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2014), accepted, Chap. 14
D.A. Brain, S. Barabash, S.W. Bougher, F. Duru, B.M. Jakosky, R. Modolo, Solar wind interaction and atmospheric escape, in Mars Book II (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2014), accepted, Chap. 15
P.C. Chamberlain, T.N. Woods, F.G. Eparvier, Flare irradiance spectral model (FISM): Daily component algorithms and results. Space Weather 6(S05), 001 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007SW000372
S. Chapman, The absorption and dissociation of ionizing effect of monochromatic radiation in an atmosphere on a rotating Earth. Proc. Phys. Soc. 43, 26–45 (1931)
E. Chassefiere, F. Leblanc, Mars atmospheric escape and evolution: Interaction with the solar wind. Planet. Space Sci. 52, 1039–1058 (2004)
J.Y. Chaufray, R. Modolo, F. Leblanc, G. Chanteur, R.E. Johnson, J.G. Luhmann, Mars solar wind interaction: Formation of the Martian corona and atmospheric loss to space. J. Geophys. Res. 112, E09009 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JE002915
J.Y. Chaufray, F. Leblanc, E. Quémerais, J.L. Bertaux, Martian oxygen density at the exobase deduced from O I 130.4-nm observations by spectroscopy for the investigation of the characteristics of the atmosphere of Mars on Mars Express. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E02006 (2009)
F. Cipriani, F. Leblanc, J.J. Berthelier, Martian corona: Nonthermal sources of hot heavy species. J. Geophys. Res. 112, E07001 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JE002818
J.E.P. Connerney et al., The Magnetometer (MAG) (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/mag
D.H. Crider, D.A. Brain, M.A. Acuña, D. Vignes, C. Mazelle, C. Bertucci, Mars global surveyor observations of solar wind magnetic field draping around Mars. Space Sci. Rev. 111(1), 203–221 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:SPAC.0000032714.66124.4e
Z. Dobe, A.F. Nagy, J.L. Fox, A theoretical study concerning the solar cycle dependence of the nightside ionosphere of Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 14507–14513 (1995)
C. Dong, S.W. Bougher, Y. Ma, G. Toth, A.F. Nagy, D. Najib, Solar wind interaction with Mars upper atmosphere: Results from the one-way coupling between the multi-fluid MHD model and the MTGCM model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 1–8 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014GL059515
F. Duru, D.A. Gurnett, D.D. Morgan, R. Modolo, A.F. Nagy, D. Najib, Electron densities in the upper ionosphere of Mars from the excitation of electron plasma oscillations. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A07302 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JA013073
F. Duru, D.A. Gurnett, R.A. Frahm, J.D. Winningham, D.D. Morgan, G.G. Howes, Steep transient density gradients in the Martian ionosphere similar to the ionopause at Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 114(A), 12310 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009JA014711
F. Duru, D.A. Gurnett, J.D. Winningham, R. Frahm, R. Modolo, A plasma flow velocity boundary at Mars from the disappearance of electron plasma oscillations. Icarus 206(1), 74–82 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2009.04.012
S.L. England, R.J. Lillis, On the nature of the variability of the Martian thermospheric mass density: Results from the electron reflectometry with Mars Global Surveyor. J. Geophys. Res. 117, E02008 (2012). doi:10.1029/2011JE003998
F.G. Eparvier et al., The extreme ultraviolet (EUV) monitor (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/lpw/extreme-ultraviolet-euv-monitor
R.E. Ergun et al., The Langmuir probe and waves (LPW) instrument (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/lpw
X. Fang, S.W. Bougher, et al., The importance of pickup oxygen ion precipitation to the Mars upper atmosphere under extreme solar wind conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40 (2013). doi:10.1029/grl.50415.2013
P.D. Feldman et al., Rosetta-Alice observations of exospheric hydrogen and oxygen on Mars. Icarus 214, 394–399 (2011)
M.O. Fillingim, L.M. Peticolas, R.J. Lillis et al., Model calculations of electron precipitation induced ionization patches on the nightside of Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L12101 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007GL029986
G. Fjeldbo, V.R. Eshleman, The atmosphere of Mars analyzed by integral inversion of the Mariner IV occultation data. Planet. Space Sci. 16, 1035–1059 (1968)
J.M. Forbes, M.E. Hagan, Diurnal Kelvin wave in the atmosphere of Mars: Towards an understanding of “stationary” density structures observed by the MGS Accelerometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 21 (2000). doi:10.1029/2000GL011850
J.M. Forbes, A.F.C. Bridger, S.W. Bougher et al., Nonmigrating tides in the thermosphere of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 5113 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JE001582
J.M. Forbes, F.G. Lemoine, S.L. Bruinsma et al., Solar flux variability of Mars’ exosphere densities and temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L01201 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007GL031904
F. Forget, F. Montmessin, J.-L. Bertaux et al., Density and temperatures of the upper martian atmosphere measured by stellar occultations with Mars Express SPICAM. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E01004 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JE003086
J.L. Fox, Morphology of the dayside ionosphere of Mars: Implication for ion outflows. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E12005 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009JE003432
J.L. Fox, A.B. Hać, Photochemical escape of oxygen from Mars: A comparison of the exobase approximation to a Monte Carlo method. Icarus 204, 527–544 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2009.07.005
J.L. Fox, A.B. Hać, Isotope fractionation in the photochemical escape of O from Mars. Icarus 208, 176–191 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2010.01.019
J.L. Fox, A.J. Kliore, Ionosphere: solar cycle variations, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Phillips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997)
J.L. Fox, J.F. Brannon, H.S. Porter, Upper limits to the nightside ionosphere of Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1339–1342 (1993)
J.L. Fox, P. Zhou, S.W. Bougher, The thermosphere/ionosphere of Mars at high and low solar activities. Adv. Space Res. 17, (11)203–(11)218 (1996)
M. Fränz, E. Dubinin, E. Nielsen et al., Transterminator ion flow in the martian ionosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 58, 1442–1454 (2010)
T. Fuller-Rowell, S.C. Solomon, Flares, coronal mass ejections, and atmospheric responses, in Heliophysics—Space Storms and Radiation: Causes and Effects, ed. by C.J. Schrijver, G.L. Siscoe (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010), pp. 321–357
F. González-Galindo, F. Forget, M.A. López-Valverde et al., A ground-to-exosphere martian general circulation model: 1. Seasonal, diurnal, and solar cycle variation of thermospheric temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E04001 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JE003246
G. Gronoff, C. Simon-Wedlund, C.J. Mertens et al., Computing uncertainties in ionosphere-airglow models. II. The martian airglow. J. Geophys. Res. 117, A05309 (2012). doi:10.1029/2011JA017308
D.A. Gurnett, R.L. Huff, D.D. Morgan et al., An overview of radar soundings of the martian ionosphere from the Mars Express spacecraft. Adv. Space Res. 41, 1335–1346 (2008)
S.A. Haider, K.K. Mahajan, E. Kallio, Mars ionosphere: A review of experimental results and modeling studies. Rev. Geophys. 49, RG4001 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011RG000357
W.B. Hanson, G.P. Mantas, Viking electron temperature measurements—Evidence for a magnetic field in the martian ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7538–7544 (1988)
W.B. Hanson, S. Sanatani, D.R. Zuccaro, The martian ionosphere as observed by the Viking retarding potential analyzers. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4351–4363 (1977)
J.S. Halekas et al., The solar wind ion analyzer for MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. (2013, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-013-0029-z
D.P. Hinson, R.A. Simpson, J.D. Twicken et al., Initial results from radio occultation measurements with Mars Global Surveyor. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 26997–27012 (1999)
R.R. Hodges, The rate of loss of water from Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(3), 1038 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001GL013853
D.L. Huestis, T.G. Slanger, B.D. Sharpee, J.L. Fox, Chemical origins of the Mars ultraviolet dayglow. Faraday Discuss. 147, 307–322 (2010)
B.M. Jakosky, MAVEN: A Mars Scout Phase A Concept Study Report. Version 2: No Cost Edited, 1–109 (2008)
B.M. Jakosky et al., The MAVEN mission to Mars: exploring Mars’ climate history, in 6th Alfven Conference, Abstract, 7–11 July (UCL, London, 2014)
W.T. Kasprzak, G.M. Keating, N.C. Hsu, A.I.F. Stewart, W.B. Colwell, S.W. Bougher, Solar activity behavior of the thermosphere, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere, and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Phillips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997), pp. 225–257
G.M. Keating, S.W. Bougher, R.W. Zurek et al., The structure of the upper atmosphere of Mars: In situ accelerometer measurements from Mars Global Surveyor. Science 279, 1672–1676 (1998)
G.M. Keating, M. Theriot, R. Tolson et al., Brief review on the results obtained with the MGS and Mars Odyssey 2001 accelerometer experiments, in Mars Atmosphere: Modeling and Observations Workshop, Granada, Spain (2003)
G.M. Keating, S.W. Bougher, M.E. Theriot et al., Atmospheric structure from Mars reconnaissance orbiter accelerometer measurements, in Proceedings of European Planetary Science Congress, Berlin, Germany (2006)
G.M. Keating, S.W. Bougher, M.E. Theriot, R.H. Tolson, Properties of the Mars upper atmosphere derived from accelerometer measurements, in Proceedings of 37th COSPAR Scientific Assembly 2008 and 50th Anniversary, Montreal, Canada (2008)
Y.H. Kim, S. Son, Y. Yi, J. Kim, A non-spherical model for the hot oxygen corona of Mars. J. Korean Astron. Soc. 34, 25–29 (2001)
A.J. Kliore, D.L. Cain, G. Fjeldbo et al., The atmosphere of Mars from Mariner 9 radio occultation measurements. Icarus 17, 484–516 (1972)
V.A. Krasnopolsky, Solar activity variations of thermospheric temperatures on Mars and a problem of CO in the lower atmosphere. Icarus 207, 638–647 (2010)
V.A. Krasnopolsky, P.D. Feldman, Far ultraviolet spectrum of Mars. Icarus 160, 86–94 (2002)
M.A. Krestyanikova, V.I. Shematovitch, Stochastic models of hot planetary and satellite coronas: A photochemical source of hot oxygen in the upper atmosphere of Mars. Sol. Syst. Res. 39, 22–32 (2005)
T.P. Larson et al., The solar energetic particle (SEP) instrument (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/sep
F. Leblanc, J.Y. Chaufray, J. Lilensten et al., Martian dayglow as seen by the SPICAM UV spectrograph on Mars Express. J. Geophys. Res. 111(9) (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JE002664
C. Lee et al., Thermal tides in the Martian middle atmosphere as seen by the Mars Climate Sounder. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E03005 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JE003285
Y. Lee, M. Combi, V. Tenishev, S.W. Bougher, Hot carbon corona in Mars’ upper thermosphere and exosphere: 1. Mechanisms and structure of the hot corona for low solar activity at Equinox. J. Geophys. Res. (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JE004552
R.J. Lillis, S.W. Bougher, F. González-Galindo et al., Four martian years of nightside upper thermospheric mass densities derived from electron reflectometry: Method extension and comparison with GCM simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E07014 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JE003529
R.J. Lillis et al., Photochemical escape of the Martian atmosphere: looking forward to MAVEN, in 6th Alfven Conference, Abstract, 7–11 July (UCL, London, 2014)
J. Liu, M.I. Richardson, R.J. Wilson, An assessment of the global, seasonal, and interannual spacecraft record of Martian climate in the thermal infrared. J. Geophys. Res. 108(E8), 5089 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JE001921
R. Lundin et al., A comet-like escape of ionospheric plasma from Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L18203 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008GL034811
Y. Ma, A.F. Nagy, Ion escape fluxes from Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L08201 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GL029208
Y. Ma, A.F. Nagy, I.V. Sokolov, K.C. Hansen, Three-dimensional, multispecies, high spatial resolution MHD studies of the solar wind interaction with Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07211 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JA010367
Y.J. Ma, X. Fang, A.F. Nagy, C.T. Russell, G. Toth, Martian ionospheric responses to dynamic pressure enhancements in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 1272–1286 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JA019402
P.R. Mahaffy et al., Space Sci. Rev. (2014, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0043-9
M. Matta, P. Withers, M. Mendillo, The composition of Mars’ topside ionosphere: Effects of hydrogen. J. Geophys. Res. 118, 1–13 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50104
W. McClintock et al., The imaging ultraviolet spectrograph (IUVS) (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/iuvs
T.L. McDunn, S.W. Bougher, J. Murphy et al., Simulating the density and thermal structure of the middle atmosphere (80–130 km) of Mars using the MGCM-MTGCM: A comparison with MEX/SPICAM observations. Icarus 206, 5–17 (2010)
J. McFadden et al., The suprathermal and thermal ion composition (STATIC) instrument (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/static
M. Mendillo, S. Smith, J. Wroten et al., Simultaneous ionospheric variability on Earth and Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1432 (2003). doi:10.1029/2003JA009961
M. Mendillo, P. Withers, D. Hinson et al., Effects of solar flares on the ionosphere of Mars. Science 311, 1135–1138 (2006)
M. Mendillo, A.G. Marusiak, P. Withers, D. Morgan, D. Gurnett, A new semi-empirical model of the peak electron density of the martian ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 5361–5365 (2013). doi:10.1002/2013GL057631
D.L. Mitchell, R.P. Lin, H. Rème, D.H. Crider, P.A. Cloutier, J.E.P. Connerney, M.H. Acuña, N.F. Ness, Oxygen Auger electrons observed in Mars’ ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(1), 1871–1874 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999GL010754
D.L. Mitchell, R.P. Lin, C. Mazelle et al., Probing Mars’ crustal magnetic field and ionosphere with the MGS electron reflectometer. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 23419–23428 (2001)
D.G. Mitchell et al., The Solar Wind Electron Analyzer (SWEA) (2014). http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/maven/science/instrument-package/swea
D.D. Morgan, D.A. Gurnett, D.L. Kirchner et al., Variation of the Martian ionospheric electron density from Mars Express radar soundings. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A09303 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JA013313
Y. Moudden, J.M. Forbes, Effects of vertically propagating thermal tides on the mean structure and dynamics of Mars’ lower thermosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L23805 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008GL036086
Y. Moudden, J.M. Forbes, A new interpretation of Mars aerobraking variability: Planetary wave-tide interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E09005 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JE003542
I.C.F. Müeller-Wodarg, D.F. Strobel, J.I. Moses et al., Neutral atmospheres. Space Sci. Rev. 139 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11214-008-9404-6
A.F. Nagy, T.E. Cravens, Hot oxygen atoms in the upper atmospheres of Venus and Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 15(5), 433–435 (1988)
A.F. Nagy, T.E. Cravens, J.H. Lee, A.I.F. Stewart, Hot oxygen atoms in the upper atmosphere of Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 629–632 (1981)
D. Najib, A.F. Nagy, G. Toth, Y. Ma, Three-dimensional, multi-fluid, high spatial resolution MHD model studies of the solar wind interaction with Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 116, A05204 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JA016272
F. Němec, D.D. Morgan, D.A. Gurnett, F. Duru, Nightside ionosphere of Mars: Radar soundings by the Mars Express spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E12009 (2010). doi:10.1029/2010JE003663
F. Němec, D.D. Morgan, D.A. Gurnett, D.A. Brain, Areas of enhanced ionization in the deep nightside ionosphere of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 116, E06006 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011JE003804
E. Nielsen, M. Fraenz, H. Zou et al., Local plasma processes and enhanced electron densities in the lower ionosphere in magnetic cusp regions on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 55, 2164–2172 (2007)
A.O. Nier, M.B. McElroy, Composition and structure of Mars’ upper atmosphere: Results from the Neutral Mass Spectrometers on Viking 1 and 2. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4341–4349 (1977)
M. Pätzold, S. Tellmann, B. Häusler et al., A sporadic third layer in the ionosphere of Mars. Science 310, 837–839 (2005)
D.J. Pawlowski, S.W. Bougher, Comparative aeronomy: the effects of solar flares at Earth and Mars, in Comparative Climatology of Terrestrial Planets Conference, Boulder, Colorado (2012)
D.J. Pawlowski, S.W. Bougher, P. Chamberlain, Modeling the response of the martian upper atmosphere to solar flares, in 2011 Fall AGU Meeting, San Francisco, California (2011)
L.J. Paxton, Pioneer Venus Orbiter ultraviolet spectrometer limb observations: Analysis and interpretation of the 166- and 156-nm data. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 5089–5096 (1985)
T. Penz, I. Arshukova, N. Terada, H. Shinagawa, N.V. Erkaev, H.K. Biernat, H. Lammer, A comparison of magnetohydrodynamic instabilities at the Martian ionopause. Adv. Space Res. 36(1), 2049–2056 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2004.11.039
A. Safaeinili, W. Kofman, J. Mouginot et al., Estimation of the total electron content of the martian ionosphere using radar sounder surface echoes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L23204 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007GL032154
R. Schunk, A. Nagy, Ionospheres: Physics, Plasma Physics, and Chemistry, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2009)
A. Seiff, D.B. Kirk, Structure of the atmosphere of Mars in summer at mid-latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4364–4378 (1977)
M.D. Smith, Interannual variability in TES atmospheric observations of Mars during 1999–2003. Icarus 167, 148–165 (2004)
M.D. Smith, THEMIS observations of Mars aerosol optical depth from 2002–2008. Icarus 202, 444–452 (2009)
M.D. Smith, S.W. Bougher, T. Encrenaz, F. Forget, A. Kleinbohl, Thermal structure and composition, in Mars Book II (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2014), accepted, Chap. 4
A. Stewart, Mariner 6 and 7 ultraviolet spectrometer experiment: Implications of \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}^{+}\), CO and O airglow. J. Geophys. Res. 77, 1 (1972). doi:10.1029/JA077i001p00054
A.I.F. Stewart, Revised time dependent model of the martian atmosphere for use in orbit lifetime and sustenance studies. LASP-JPL Internal Report, NQ-802429, Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, California (1987)
A.I. Stewart, C.A. Barth, C.W. Hord, A.L. Lane, Mariner 9 ultraviolet spectrometer experiment: Structure of Mars’s upper atmosphere. Icarus 17, 469–474 (1972)
A.I. Stewart, M.J. Alexander, R.R. Meier et al., Atomic oxygen in the martian thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 91–102 (1992)
A. Stiepen, J.-C. Gerard, S. Bougher, F. Montmessin, B. Hubert, Mars thermospheric temperatures from CO Cameron and \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}^{+}\) dayglow observations from Mars Express. Icarus (2014, submitted)
D.J. Strickland, G.E. Thomas, P.R. Sparks, Mariner 6 and 7 ultraviolet spectrometer experiment: Analysis of the O I 1304- and 1356-Å emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 77, 4052–4068 (1972)
D.J. Strickland, A.I. Stewart, C.A. Barth et al., Mariner 9 ultraviolet spectrometer experiment: Mars atomic oxygen 1304-Å emission. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 4547–4559 (1973)
R.H. Tolson, G.M. Keating, G.J. Cancro et al., Application of accelerometer data to Mars Global Surveyor aerobraking operations. J. Spacecr. Rockets 36(3), 323–329 (1999)
R.H. Tolson, A.M. Dwyer, J.L. Hanna et al., Application of accelerometer data to Mars aerobraking and atmospheric modeling. J. Spacecr. Rockets 42(3), 435–443 (2005)
R.H. Tolson, G.M. Keating, R.W. Zurek et al., Application of accelerometer data to atmospheric modeling during Mars aerobraking operations. J. Spacecr. Rockets 44(6), 1172–1179 (2007)
R.H. Tolson, E. Bemis, S. Hough et al., Atmospheric modeling using accelerometer data during Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter aerobraking operations. J. Spacecr. Rockets 45(3), 511–518 (2008)
A. Valeille, M.R. Combi, S.W. Bougher et al., Three-dimensional study of Mars upper thermosphere/ionosphere and hot oxygen corona: 1. General description and results at equinox for solar low conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E11005 (2009a). doi:10.1029/2009JE003388
A. Valeille, M.R. Combi, S.W. Bougher et al., Three-dimensional study of Mars upper thermosphere/ionosphere and hot oxygen corona: 2. Solar cycle, seasonal variations and evolution over history. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E11006 (2009b). doi:10.1029/2009JE003389
A. Valeille, M.R. Combi, V. Tenishev et al., A study of suprathermal oxygen atoms in Mars upper thermosphere and exosphere over the range of limiting conditions. Icarus 206, 18–27 (2010a)
A. Valeille, S.W. Bougher, V. Tenishev, M.R. Combi, A.F. Nagy, Water loss and evolution of the upper atmosphere and exosphere over Martian history. Icarus 206, 28–39 (2010b)
Y.-C. Wang, J.G. Luhmann, F. Leblanc, X. Fang, R.E. Johnson, Y. Ma, W.-H. Ip, L. Li, Modeling of the sputtering efficiency for Martian atmosphere, in Abstract P23A-1907 Presented at 2012 Fall Meeting, AGU, San Francisco, CA, 3–7 Dec. 2012 (2012)
R.J. Wilson, Evidence for non-migrating thermal tides in the Mars upper atmosphere from the Mars Global Surveyor Accelerometer Experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(7) (2002). doi:10.1029/2001GL013975
P.G. Withers, Mars Gobal Surveyor and Mars Odyssey accelerometer observations of the martian upper atmosphere during aerobraking. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L02201 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005GL024447
P.G. Withers, A review of observed variability in the dayside ionosphere of Mars. Adv. Space Res. 44, 277–307 (2009)
P.G. Withers, R. Pratt, An observational study of the response of the upper atmosphere of Mars to lower atmospheric dust storms. Icarus 225, 378–389 (2013)
P.G. Withers, S.W. Bougher, G.M. Keating, The effects of topographically controlled thermal tides in the martian upper atmosphere as seen by the MGS accelerometer. Icarus 164, 14–32 (2003)
P.G. Withers, M. Mendillo, H. Risbeth et al., Ionospheric characteristics above martian crustal magnetic anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L16204 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005GL023483
M. Yagi, F. Leblanc, J.Y. Chaufray, F. Gonzalez-Galindo, S. Hess, R. Modolo, Mars exospheric thermal and non-thermal components: Seasonal and local variations. Icarus 221, 682–693 (2012)
M.H.G. Zhang, J.G. Luhmann, A.J. Kliore, J. Kim, A post-Pioneer Venus reassessment of the martian dayside ionosphere as observed by radio occultation methods. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14829–14839 (1990a)
M.H.G. Zhang, J.G. Luhmann, A.J. Kliore, An observational study of the nightside ionospheres of Mars and Venus with radio occultation methods. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 17095–17102 (1990b)
R.W. Zurek et al., Application of MAVEN accelerometer and attitude control data to Mars atmospheric characterization. Space Sci. Rev. (2014, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0053-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bougher, S.W., Cravens, T.E., Grebowsky, J. et al. The Aeronomy of Mars: Characterization by MAVEN of the Upper Atmosphere Reservoir That Regulates Volatile Escape. Space Sci Rev 195, 423–456 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0053-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0053-7