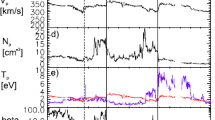
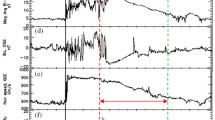
Abstract
In this work a total of 266 interplanetary coronal mass ejections observed by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory/Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph (SOHO/LASCO) and then studied by in situ observations from Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft, are presented in a new catalog for the time interval 1996 – 2009 covering Solar Cycle 23. Specifically, we determine the characteristics of the CME which is responsible for the upcoming ICME and the associated solar flare, the initial/background solar wind plasma and magnetic field conditions before the arrival of the CME, the conditions in the sheath of the ICME, the main part of the ICME, the geomagnetic conditions of the ICME’s impact at Earth and finally we remark on the visual examination for each event. Interesting results revealed from this study include the high correlation coefficient values of the magnetic field \(B_{z}\) component against the Ap index (\(r = 0.84\)), as well as against the Dst index (\(r = 0.80\)) and of the effective acceleration against the CME linear speed (\(r = 0.98\)). We also identify a north–south asymmetry for X-class solar flares and an east–west asymmetry for CMEs associated with strong solar flares (magnitude ≥ M1.0) which finally triggered intense geomagnetic storms (with \(\mathrm{Ap} \geq179\)). The majority of the geomagnetic storms are determined to be due to the ICME main part and not to the extreme conditions which dominate inside the sheath. For the intense geomagnetic storms the maximum value of the Ap index is observed almost 4 hours before the minimum Dst index. The amount of information makes this new catalog the most comprehensive ICME catalog for Solar Cycle 23.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, M.D.: 2003, Solar Phys. 218, 261. DOI .
Bartels, J.: 1932, Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. 37, 1. DOI .
Bochsler, P., Geiss, J., Joos, R.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 10779. DOI .
Borrini, G., Gosling, J.T., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C.: 1982, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 7370. DOI .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Scwhenn, R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673. DOI .
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3591. DOI .
Chi, Y., Shen, C., Wang, Y., Xu, M., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 2419. DOI .
Chowdhury, P., Kudela, K., Dwivedi, B.N.: 2013, Solar Phys. 286, 577. DOI .
Cortie, A.L.: 1912, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 73, 52. DOI .
Crooker, N.U., Cliver, E.W., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1992, Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 429. DOI .
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, A.L.C.: 2008, J. Geophys. Res. 113, A05221. DOI .
Georgoulis, M.K.: 2008, Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L06S02. DOI .
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1992, In: Svestka, Z., Jackson, B.V., Machado, M.E. (eds.) Eruptive Solar Flares, Springer, New York, 277. DOI .
Gonzalez, W.D., Clua de Gonzalez, A.L., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1993, Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1659. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2004, In: Poletto, G., Suess, S.T. (eds.) The Sun and the Heliosphere as an Integrated System 317, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 201. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, J. Astrophys. Astron. 27, 243. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2009, Earth Planets Space 61, 595. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 112, A06112. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Lepping, R.P., Kaiser, M.L., Berdichevsky, D., Cyr, O.C.St.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 145. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Makela, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 710, 1111. DOI .
Gosling, J.T.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937. DOI .
Gushchina, R.T., Belov, A.V., Eroshenko, E.A., Obridko, V.N., Paouris, E., Shelting, B.D.: 2014, Geomagn. Aeron. 54, 430. DOI .
Harrison, R.A.: 1995, Astron. Astrophys. 304, 585.
Huttunen, K.E.J., Schwenn, R., Bothmer, V., Koskinen, H.E.J.: 2005, Ann. Geophys. 23, 625. DOI .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Solar Phys. 239, 393. DOI .
Loewe, C.A., Prölss, G.W.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 14209. DOI .
Mavromichalaki, H., Gerontidou, M., Paschalis, P., Papaioannou, A., Paouris, E., Papailiou, M., Souvatzoglou, G.: 2015, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 632, 012071. DOI .
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Barker, P., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Riley, P., Griffee, J.W.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 563. DOI .
McIntosh, D.H.: 1959, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 251, 525. DOI .
McPherron, R.L.: 1999, Phys. Chem. Earth 24, 45. DOI .
Mitsakou, E., Moussas, X.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 3137. DOI .
Mullan, D.J., Smith, C.W.: 2006, Solar Phys. 234, 325. DOI .
Newbury, J.A., Russell, C.T., Phillips, J.L., Gary, S.P.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 9553. DOI .
Paouris, E.: 2013, Solar Phys. 284, 589. DOI .
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Belov, A., Gushchina, R., Yanke, V.: 2012, Solar Phys. 280, 255. DOI .
Papailiou, M., Mavromichalaki, H., Abunina, M., et al.: 2013, Solar Phys. 283, 557. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Solar Phys. 264, 189. DOI .
Russell, C.T., McPherron, R.L.: 1973, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 92. DOI .
Schwenn, R., Dal Lago, A., Huttunen, E., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2005, Ann. Geophys. 23, 1033. DOI .
Smith, C.W., Acuna, M.H., Burlaga, L., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Scheifele, J.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 613. DOI .
Svalgaard, L.: 1977, In: Zirker, J.B. (ed.) Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams, Colorado Associated Univ. Press, Boulder, 371.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 1997, In: Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Kamide, Y., Arballo, J.K. (eds.) Magnetic Storms, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 98, AGU, Washington, 77. DOI .
Vourlidas, A., Buzasi, D., Howard, R.A., Esfandiari, E.: 2002, In: Wilson, A. (ed.) Solar Variability: From Core to Outer Frontiers SP-506, ESA, Noordwijk, 91. 92-9092-816-6.
Wang, Y., Zhang, J.: 2007, Astrophys. J. 665, 1428. DOI .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Michalek, G., Howard, R.A.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S05. DOI .
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, M.Yu.: 2015, J. Geophys. Res. 120, 7094. DOI .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., et al.: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 112, A10102. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the providers of the solar, interplanetary, and geomagnetic data used in this work. The coronal mass ejection data are taken from the SOHO/LASCO CME list ( http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/ ). This CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. Thanks are also due to Dr. N. Gopalswamy for useful suggestions and to the anonymous referee for comments improving this paper significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H. Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections Resulting from Earth-Directed CMEs Using SOHO and ACE Combined Data During Solar Cycle 23. Sol Phys 292, 30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1050-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1050-2