Abstract
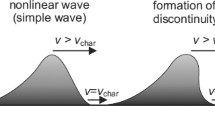
An in-depth analysis of numerical simulations is performed to obtain a deeper insight into the nature of various phenomena occurring in the solar atmosphere as a consequence of the eruption of unstable coronal structures. Although the simulations take into account only the most basic characteristics of a flux-rope eruption, the simulation analysis reveals important information on various eruption-related effects. It quantifies the relation between the eruption dynamics and the evolution of the large-amplitude coronal magnetohydrodynamic wave and the associated chromospheric downward-propagating perturbation. We show that the downward propagation of the chromospheric Moreton-wave disturbance can be approximated by a constant-amplitude switch-on shock that moves through a medium of rapidly decreasing Alfvén velocity. The presented analysis reveals the nature of secondary effects that are observed as coronal upflows, secondary shocks, various forms of wave-trains, delayed large-amplitude slow disturbances, transient coronal depletions, etc. We also show that the eruption can cause an observable Moreton wave and a secondary coronal front only if it is powerful enough and is preferably characterized by significant lateral expansion. In weaker eruptions, only the coronal and transition-region signatures of primary waves are expected to be observed. In powerful events, the primary wave moves at an Alfvén Mach number significantly larger than 1 and steepens into a shock that is due to the nonlinear evolution of the wavefront. After the eruption-driven phase, the perturbation evolves as a freely propagating simple wave, characterized by a significant deceleration, amplitude decrease, and wave-profile broadening. In weak events the coronal wave does not develop into a shock and propagates at a speed close to the ambient magnetosonic speed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanasyev, A.N., Uralov, A.M.: 2011, Coronal shock waves, EUV waves, and their relation to CMEs. II. Modeling MHD shock wave propagation along the solar surface, using nonlinear geometrical acoustics. Solar Phys. 273, 479. DOI .
Asai, A., Ishii, T.T., Isobe, H., Kitai, R., Ichimoto, K., UeNo, S., Nagata, S., Morita, S., Nishida, K., Shiota, D., Oi, A., Akioka, M., Shibata, K.: 2012, First simultaneous observation of an H\(\upalpha\) Moreton wave, EUV wave, and filament/prominence oscillations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 745, L18. DOI .
Chen, P.F., Ding, M.D., Fang, C.: 2005, Synthesis of CME-associated Moreton and EIT wave features from MHD simulations. Space Sci. Rev. 121, 201. DOI .
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., Shibata, K.: 2005, A full view of EIT waves. Astrophys. J. 622, 1202. DOI .
Chen, P.F., Wu, S.T., Shibata, K., Fang, C.: 2002, Evidence of EIT and Moreton waves in numerical simulations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 572, L99. DOI .
Cohen, O., Attrill, G.D.R., Manchester, W.B. IV, Wills-Davey, M.J.: 2009, Numerical simulation of an EUV coronal wave based on the 2009 February 13 CME event observed by STEREO. Astrophys. J. 705, 587. DOI .
Cohen, O., Attrill, G.D.R., Schwadron, N.A., Crooker, N.U., Owens, M.J., Downs, C., Gombosi, T.I.: 2010, Numerical simulation of the 12 May 1997 CME event: The role of magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A10104. DOI .
Downs, C., Roussev, I.I., van der Holst, B., Lugaz, N., Sokolov, I.V., Gombosi, T.I.: 2011, Studying extreme ultraviolet wave transients with a digital laboratory: Direct comparison of extreme ultraviolet wave observations to global magnetohydrodynamic simulations. Astrophys. J. 728, 2. DOI .
Downs, C., Roussev, I.I., van der Holst, B., Lugaz, N., Sokolov, I.V.: 2012, Understanding SDO/AIA observations of the 2010 June 13 EUV wave event: Direct insight from a global thermodynamic MHD simulation. Astrophys. J. 750, 134. DOI .
Gallagher, P.T., Long, D.M.: 2011, Large-scale bright fronts in the solar corona: A review of “EIT waves”. Space Sci. Rev. 158, 365. DOI .
Gary, G.A.: 2001, Plasma beta above a solar active region: Rethinking the paradigm. Solar Phys. 203, 71. DOI .
Goedbloed, J.P., Keppens, R., Poedts, S.: 2003, Computer simulations of solar plasmas. Space Sci. Rev. 107, 63. DOI .
Grechnev, V.V., Uralov, A.M., Chertok, I.M., Kuzmenko, I.V., Afanasyev, A.N., Meshalkina, N.S., Kalashnikov, S.S., Kubo, Y.: 2011, Coronal shock waves, EUV waves, and their relation to CMEs. I. Reconciliation of “EIT waves”, type II radio bursts, and leading edges of CMEs. Solar Phys. 273, 433. DOI .
Hoilijoki, S., Pomoell, J., Vainio, R., Palmroth, M., Koskinen, H.E.J.: 2013, Interpreting solar EUV wave observations from different viewing angles using an MHD model. Solar Phys. 286, 493. DOI .
Kienreich, I.W., Veronig, A.M., Muhr, N., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Nitta, N.: 2011, Case study of four homologous large-scale coronal waves observed on 2010 April 28 and 29. Astrophys. J. Lett. 727, L43. DOI .
Kienreich, I.W., Muhr, N., Veronig, A.M., Berghmans, D., De Groof, A., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Seaton, D.B.: 2013, Solar TErrestrial Relations Observatory-A (STEREO-A) and PRoject for On-Board Autonomy 2 (PROBA2) quadrature observations of reflections of three EUV waves from a coronal hole. Solar Phys. 286, 201. DOI .
Klimchuk, J.A., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Schrijver, C.J., Melrose, D.B., Fletcher, L., Gopalswamy, N., Harrison, R.A., Mandrini, C.H., Peter, H., Tsuneta, S., Vršnak, B., Wang, J.-X.: 2009, Commission 10: Solar activity. In: van der Hucht, K.A. (ed.) Trans. IAU 27A, 79. DOI .
Kozarev, K.A., Korreck, K.E., Lobzin, V.V., Weber, M.A., Schwadron, N.A.: 2011, Off-limb solar coronal wavefronts from SDO/AIA extreme-ultraviolet observations – implications for particle production. Astrophys. J. Lett. 733, L25. DOI .
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: 1987, Fluid Mechanics, 2nd edn. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 385.
Liu, W., Ofman, L.: 2014, Advances in observing various coronal EUV waves in the SDO era and their seismological applications (invited review). Solar Phys. 289, 3233. DOI .
Long, D.M., DeLuca, E.E., Gallagher, P.T.: 2011, The wave properties of coronal bright fronts observed using SDO/AIA. Astrophys. J. Lett. 741, L21. DOI .
Low, B.C., Hundhausen, J.R.: 1995, Magnetostatic structures of the solar corona. 2: The magnetic topology of quiescent prominences. Astrophys. J. 443, 818. DOI .
Lulić, S., Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Kienreich, I.W., Muhr, N., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M.: 2013, Formation of coronal shock waves. Solar Phys. 286, 509. DOI .
Ma, S., Raymond, J.C., Golub, L., Lin, J., Chen, H., Grigis, P., Testa, P., Long, D.: 2011, Observations and interpretation of a low coronal shock wave observed in the EUV by the SDO/AIA. Astrophys. J. 738, 160. DOI .
Mei, Z., Udo, Z., Lin, J.: 2012, Numerical experiments of disturbance to the solar atmosphere caused by eruptions. Sci. China Ser. A 55, 1316. DOI .
Moreton, G.E.: 1960, H\(\upalpha\) observations of flare-initiated disturbances with velocities \({\sim}\,1000~\mbox{km}/\mbox{sec}\). Astron. J. 65, 494. DOI .
Moreton, G.E., Ramsey, H.E.: 1960, Recent observations of dynamical phenomena associated with solar flares. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 72, 357. DOI .
Muhr, N., Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Magdalenić, J.: 2010, Analysis of a global Moreton wave observed on 2003 October 28. Astrophys. J. 708, 1639. DOI .
Muhr, N., Veronig, A.M., Kienreich, I.W., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B.: 2011, Analysis of characteristic parameters of large-scale coronal waves observed by the solar-terrestrial relations observatory/extreme ultraviolet imager. Astrophys. J. 739, 89. DOI .
Olmedo, O., Vourlidas, A., Zhang, J., Cheng, X.: 2012, Secondary waves and/or the “reflection” from and “transmission” through a coronal hole of an extreme ultraviolet wave associated with the 2011 February 15 X2.2 flare observed with SDO/AIA and STEREO/EUVI. Astrophys. J. 756, 143. DOI .
Ontiveros, V., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, Quantitative measurements of coronal mass ejection-driven shocks from LASCO observations. Astrophys. J. 693, 267. DOI .
Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2012, On the nature and genesis of EUV waves: A synthesis of observations from SOHO, STEREO, SDO, and Hinode (invited review). Solar Phys. 281, 187. DOI .
Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A., Stenborg, G.: 2010, The genesis of an impulsive coronal mass ejection observed at ultra-high cadence by AIA on SDO. Astrophys. J. Lett. 724, L188. DOI .
Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A., Wang, Y.M., Stenborg, G., Thernisien, A.: 2009, What is the nature of EUV waves? First STEREO 3D observations and comparison with theoretical models. Solar Phys. 259, 49. DOI .
Payne-Scott, R., Yabsley, D.E., Bolton, J.G.: 1947, Relative times of arrival of solar noise on different radio frequencies. Nature 160, 256. DOI .
Pomoell, J., Vainio, R., Kissmann, R.: 2008, MHD modeling of coronal large-amplitude waves related to CME lift-off. Solar Phys. 253, 249. DOI .
Priest, E.R.: 1982, Solar Magneto-hydrodynamics, Reidel, Dordrecht, 203.
Schmidt, J.M., Ofman, L.: 2010, Global simulation of an extreme ultraviolet imaging telescope wave. Astrophys. J. 713, 1008. DOI .
Schrijver, C.J., Aulanier, G., Title, A.M., Pariat, E., Delannée, C.: 2011, The 2011 February 15 X2 flare, ribbons, coronal front, and mass ejection: Interpreting the three-dimensional views from the solar dynamics observatory and STEREO guided by magnetohydrodynamic flux-rope modeling. Astrophys. J. 738, 167. DOI .
Selwa, M., Poedts, S., DeVore, C.R.: 2012, Dome-shaped EUV waves from rotating active regions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 747, L21. DOI .
Selwa, M., Poedts, S., DeVore, C.R.: 2013, Numerical simulations of dome-shaped EUV waves from different active-region configurations. Solar Phys. 284, 515. DOI .
Shen, Y., Liu, Y.: 2012a, Evidence for the wave nature of an extreme ultraviolet wave observed by the atmospheric imaging assembly on board the solar dynamics observatory. Astrophys. J. 754, 7. DOI .
Shen, Y., Liu, Y.: 2012b, Simultaneous observations of a large-scale wave event in the solar atmosphere: From photosphere to corona. Astrophys. J. Lett. 752, L23. DOI .
Shen, Y., Liu, Y., Su, J., Li, H., Zhao, R., Tian, Z., Ichimoto, K., Shibata, K.: 2013, Diffraction, refraction, and reflection of an extreme-ultraviolet wave observed during its interactions with remote active regions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 773, L33. DOI .
Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Veronig, A.M.: 2013, The wave-driver system of the off-disk coronal wave of 17 January 2010. Solar Phys. 287, 441. DOI .
Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Veronig, A.M.: 2009, Analytic modeling of the Moreton wave kinematics. Astrophys. J. 702, 1343. DOI .
Tóth, G.: 1996, A general code for modeling MHD flows on parallel computers: Versatile advection code. Astrophys. Lett. Commun. 34, 245.
Uchida, Y.: 1968, Propagation of hydromagnetic disturbances in the solar corona and Moreton’s wave phenomenon. Solar Phys. 4, 30. DOI .
Uchida, Y.: 1974, Behavior of the flare produced coronal MHD wavefront and the occurrence of type II radio bursts. Solar Phys. 39, 431. DOI .
Uchida, Y., Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1973, Flare-produced coronal MHD-fast-mode wavefronts and Moreton’s wave phenomenon. Solar Phys. 28, 495. DOI .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Schrijver, C.J., Klimchuk, J.A., Charbonneau, P., Fletcher, L., Hasan, S.S., Hudson, H.S., Kusano, K., Mandrini, C.H., Peter, H., Vršnak, B., Yan, Y.: 2012, Commission 10: Solar activity. In: van der Hucht, K.A. (ed.) Trans. IAU 28A, 69. DOI .
Vernazza, J.E., Avrett, E.H., Loeser, R.: 1981, Structure of the solar chromosphere. III – Models of the EUV brightness components of the quiet-sun. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 45, 635. DOI .
Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B.: 2008, High-cadence observations of a global coronal wave by STEREO EUVI. Astrophys. J. Lett. 681, L113. DOI .
Veronig, A.M., Muhr, N., Kienreich, I.W., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B.: 2010, First observations of a dome-shaped large-scale coronal extreme-ultraviolet wave. Astrophys. J. Lett. 716, L57. DOI .
Veronig, A.M., Gömöry, P., Kienreich, I.W., Muhr, N., Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Warren, H.P.: 2011, Plasma diagnostics of an EIT wave observed by Hinode/EIS and SDO/AIA. Astrophys. J. Lett. 743, L10. DOI .
Vršnak, B.: 2001, Solar flares and coronal shock waves. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25291. DOI .
Vršnak, B.: 2005, Terminology of large-scale waves in the solar atmosphere. Eos Trans. AGU 86, 112. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Cliver, E.W.: 2008, Origin of coronal shock waves. invited review. Solar Phys. 253, 215. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Lulić, S.: 2000a, Formation of coronal MHD shock waves – I. The basic mechanism. Solar Phys. 196, 157. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Lulić, S.: 2000b, Formation of coronal MHD shock waves – II. The pressure pulse mechanism. Solar Phys. 196, 181. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Aurass, H., Mann, G.: 2002a, Band-splitting of coronal and interplanetary type II bursts. II. Coronal magnetic field and Alfvén velocity. Astron. Astrophys. 396, 673. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Warmuth, A., Brajša, R., Hanslmeier, A.: 2002b, Flare waves observed in helium I 10 830 Å. A link between H\(\upalpha\) Moreton and EIT waves. Astron. Astrophys. 394, 299. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Maričić, D., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.: 2004, Coronal mass ejection of 15 May 2001: II. Coupling of the CME acceleration and the flare energy release. Solar Phys. 225, 355. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Warmuth, A., Temmer, M., Veronig, A., Magdalenić, J., Hillaris, A., Karlický, M.: 2006, Multi-wavelength study of coronal waves associated with the CME-flare event of 3 November 2003. Astron. Astrophys. 448, 739. DOI .
Wang, H., Shen, C., Lin, J.: 2009, Numerical experiments of wave-like phenomena caused by the disruption of an unstable magnetic configuration. Astrophys. J. 700, 1716. DOI .
Wang, H., Liu, S., Gong, J., Wu, N., Lin, J.: 2015, Contribution of velocity vortices and fast shock reflection and refraction to the formation of EUV waves in solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. 805, 114. DOI .
Warmuth, A.: 2007, Large-scale waves and shocks in the solar corona. In: Klein, K.-L., MacKinnon, A.L. (eds.) The High Energy Solar Corona: Waves, Eruptions, Particles, Lecture Notes in Physics, 725, Springer, Berlin, 107.
Warmuth, A.: 2010, Large-scale waves in the solar corona: The continuing debate. Adv. Space Res. 45, 527. DOI .
Warmuth, A., Mann, G.: 2011, Kinematical evidence for physically different classes of large-scale coronal EUV waves. Astron. Astrophys. 532, A151. DOI .
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Aurass, H., Hanslmeier, A.: 2001, Evolution of two EIT/H\(\upalpha\) Moreton waves. Astrophys. J. 560, L105. DOI .
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Hanslmeier, A., Otruba, W. 2004a, A multiwavelength study of solar flare waves. I. Observations and basic properties. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 1101. DOI .
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Hanslmeier, A., Otruba, W. 2004b, A multiwavelength study of solar flare waves. II. Perturbation characteristics and physical interpretation. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 1117. DOI .
Wild, J.P., McCready, L.L.: 1950, Observations of the spectrum of high-intensity solar radiation at metre wavelengths. I. The apparatus and spectral types of solar burst observed. Aust. J. Phys. A 3, 387.
Wills-Davey, M.J., Attrill, G.D.R.: 2009, EIT waves: A changing understanding over a solar cycle. Space Sci. Rev. 149, 325. DOI .
Wu, S.T., Wu, C.-C., Liou, K.: 2013, Evidence of the correspondence of EIT waves and coronal mass ejections induced waves using a three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic simulation. In: Pogorelov, N.V., Audit, E., Zank, G.P. (eds.) Numerical Modeling of Space Plasma Flows, ASTRONUM2012, ASP Conf. Ser. 474, 185.
Wu, S.T., Zheng, H., Wang, S., Thompson, B.J., Plunkett, S.P., Zhao, X.P., Dryer, M.: 2001, Three-dimensional numerical simulation of MHD waves observed by the extreme ultraviolet imaging telescope. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25089. DOI .
Wu, S.T., Li, B., Wang, S., Zheng, H.: 2005, A three-dimensional analysis of global propagation of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves in a structured solar atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A11102. DOI .
Xue, Z.K., Qu, Z.Q., Yan, X.L., Zhao, L., Ma, L.: 2013, Deformation and deceleration of coronal wave. Astron. Astrophys. 556, A152. DOI .
Yang, L., Zhang, J., Liu, W., Li, T., Shen, Y.: 2013, SDO/AIA and Hinode/EIS observations of interaction between an EUV wave and active region loops. Astrophys. J. 775, 39. DOI .
Zhukov, A.N.: 2011, EIT wave observations and modeling in the STEREO era. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1096. DOI .
Žic, T., Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Jacobs, C.: 2008, Cylindrical and spherical pistons as drivers of MHD shocks. Solar Phys. 253, 73. DOI .
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by Croatian Science Foundation under the project 6212 “Solar and Stellar Variability” and the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) projects under the grant agreement No. 263252 (project COMESEP, www.comesep.eu ) and No. 284461 (project eHEROES, soteria-space.eu/eheroes/html/ ). M.T. and A.M.V. acknowledge the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): FWF V195-N16 and P24092-N16. The Versatile Advection Code (VAC) was developed by Gábor Tóth at the Astronomical Institute at Utrecht. The project is a collaboration with the FOM Institute for Plasma Physics, the Mathematics department at Utrecht and the CWI at Amsterdam. In particular, Rony Keppens (FOM), Mikhail Botchev (Mathematics Dept.), and Auke van der Ploeg (CWI) contributed significantly to the development of the code. G. Tóth and R. Keppens share the responsibility and work associated with the development, maintenance, distribution, and management of the software. We are grateful to Tayeb Aiouaz and Tibor Török for help in getting acquainted with VAC. B.V. and A.M.V. thank ISSI (International Space Science Institute, Bern) for the hospitality provided to the team “The Nature of Coronal Bright Fronts” led by D. Long and S. Bloomfield, where many of the ideas presented in this work have been discussed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Lulić, S. et al. Formation of Coronal Large-Amplitude Waves and the Chromospheric Response. Sol Phys 291, 89–115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0822-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0822-9