Abstract
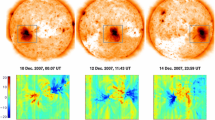
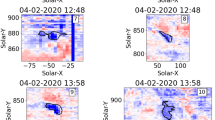
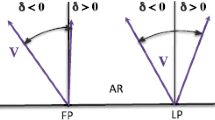
Plasma upflows have been detected in active regions using Doppler velocity maps. The origin and nature of these upflows is not well known with many of their characteristics determined from the examination of single events. In particular, some studies suggest these upflows occur along open field lines and, hence, are linked to sources of the solar wind. To investigate the relationship these upflows may have with the solar wind, and to probe what may be driving them, this paper considers seven active regions observed on the solar disc using the Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer aboard Hinode between August 2011 and September 2012. Plasma upflows are observed in all these active regions. The locations of these upflows are compared to the global potential magnetic field extrapolated from the Solar Dynamics Observatory, Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager daily synoptic magnetogram taken on the day the upflows were observed. The structure of the magnetic field is determined by constructing its magnetic skeleton in order to help identify open-field regions and also sites where magnetic reconnection at global features is likely to occur. As a further comparison, measurements of the temperature, density and composition of the plasma are taken from regions with active-region upflows. In most cases the locations of the upflows in the active regions do not correspond to areas of open field, as predicted by a global coronal potential-field model, and therefore these upflows are not always sources of the slow solar wind. The locations of the upflows are, in general, intersected by separatrix surfaces associated with null points located high in the corona; these could be important sites of reconnection with global consequences.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, D., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Murray, M.J.: 2009, Magnetic reconnection along quasi-separatrix layers as a driver of ubiquitous active region outflows. Astrophys. J. 705, 926. DOI . ADS .
Brooks, D.H., Warren, H.P.: 2011, Establishing a connection between active region outflows and the solar wind: Abundance measurements with EIS/Hinode. Astrophys. J. Lett. 727, L13. DOI . ADS .
Brooks, D.H., Warren, H.P.: 2012, The coronal source of extreme-ultraviolet line profile asymmetries in solar active region outflows. Astrophys. J. Lett. 760, L5. DOI . ADS .
Bryans, P., Young, P.R., Doschek, G.A.: 2010, Multiple component outflows in an active region observed with the EUV imaging spectrometer on Hinode. Astrophys. J. 715, 1012. DOI . ADS .
Culhane, J.L., Harra, L.K., James, A.M., Al-Janabi, K., Bradley, L.J., Chaudry, R.A., Rees, K., Tandy, J.A., Thomas, P., Whillock, M.C.R., Winter, B., Doschek, G.A., Korendyke, C.M., Brown, C.M., Myers, S., Mariska, J., Seely, J., Lang, J., Kent, B.J., Shaughnessy, B.M., Young, P.R., Simnett, G.M., Castelli, C.M., Mahmoud, S., Mapson-Menard, H., Probyn, B.J., Thomas, R.J., Davila, J., Dere, K., Windt, D., Shea, J., Hagood, R., Moye, R., Hara, H., Watanabe, T., Matsuzaki, K., Kosugi, T., Hansteen, V., Wikstol, Ø.: 2007, The EUV imaging spectrometer for Hinode. Solar Phys. 243, 19. DOI . ADS .
Culhane, J.L., Brooks, D.H., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P., Baker, D., DeRosa, M.L., Mandrini, C.H., Zhao, L., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2014, Tracking solar active region outflow plasma from its source to the near-Earth environment. Solar Phys. 289, 3799. DOI . ADS .
De Pontieu, B., McIntosh, S.W., Hansteen, V.H., Schrijver, C.J.: 2009, Observing the roots of solar coronal heating – In the chromosphere. Astrophys. J. Lett. 701, L1. DOI . ADS .
Del Zanna, G., Aulanier, G., Klein, K.-L., Török, T.: 2011, A single picture for solar coronal outflows and radio noise storms. Astron. Astrophys. 526, A137. DOI . ADS .
Dere, K.P., Landi, E., Mason, H.E., Monsignori Fossi, B.C., Young, P.R.: 1997, CHIANTI – An atomic database for emission lines. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 125, 149. DOI . ADS .
Doschek, G.A., Warren, H.P., Mariska, J.T., Muglach, K., Culhane, J.L., Hara, H., Watanabe, T.: 2008, Flows and nonthermal velocities in solar active regions observed with the EUV imaging spectrometer on Hinode: A tracer of active region sources of heliospheric magnetic fields? Astrophys. J. 686, 1362. DOI . ADS .
Edwards, S.J.: 2014, On the topology of global coronal magnetic fields. Ph.D. thesis, University of St. Andrews.
Grevesse, N., Asplund, M., Sauval, A.J.: 2007, The solar chemical composition. Space Sci. Rev. 130, 105. DOI . ADS .
Handy, B.N., Acton, L.W., Kankelborg, C.C., Wolfson, C.J., Akin, D.J., Bruner, M.E., Caravalho, R., Catura, R.C., Chevalier, R., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Feinstein, C.N., Freeland, S.L., Friedlaender, F.M., Hoffmann, C.H., Hurlburt, N.E., Jurcevich, B.K., Katz, N.L., Kelly, G.A., Lemen, J.R., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., Meyer, S.B., Morrison, S.J., Morrison, M.D., Nightingale, R.W., Pope, T.P., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Shine, R.A., Shing, L., Strong, K.T., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Torgerson, D.D., Golub, L., Bookbinder, J.A., Caldwell, D., Cheimets, P.N., Davis, W.N., Deluca, E.E., McMullen, R.A., Warren, H.P., Amato, D., Fisher, R., Maldonado, H., Parkinson, C.: 1999, The Transition Region and Coronal Explorer. Solar Phys. 187, 229. DOI . ADS .
Hara, H., Watanabe, T., Harra, L.K., Culhane, J.L., Young, P.R., Mariska, J.T., Doschek, G.A.: 2008, Coronal plasma motions near footpoints of active region loops revealed from spectroscopic observations with Hinode EIS. Astrophys. J. Lett. 678, L67. DOI . ADS .
Harra, L.K., Sakao, T., Mandrini, C.H., Hara, H., Imada, S., Young, P.R., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Baker, D.: 2008, Outflows at the edges of active regions: Contribution to solar wind formation? Astrophys. J. Lett. 676, L147. DOI . ADS .
Harra, L.K., Archontis, V., Pedram, E., Hood, A.W., Shelton, D.L., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2012, The creation of outflowing plasma in the corona at emerging flux regions: Comparing observations and simulations. Solar Phys. 278, 47. DOI . ADS .
Haynes, A.L., Parnell, C.E.: 2007, A trilinear method for finding null points in a three-dimensional vector space. Phys. Plasmas 14, 082107. DOI . ADS .
Haynes, A.L., Parnell, C.E.: 2010, A method for finding three-dimensional magnetic skeletons. Phys. Plasmas 17, 092903. DOI . ADS .
He, J.-S., Marsch, E., Tu, C.-Y., Guo, L.-J., Tian, H.: 2010, Intermittent outflows at the edge of an active region – A possible source of the solar wind? Astron. Astrophys. 516, A14. DOI . ADS .
Kaiser, M.L., Kucera, T.A., Davila, J.M., St. Cyr, O.C., Guhathakurta, M., Christian, E.: 2008, The STEREO mission: An introduction. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 5. DOI . ADS .
Kashyap, V., Drake, J.J.: 1998, Markov-chain Monte Carlo reconstruction of emission measure distributions: Application to solar extreme-ultraviolet spectra. Astrophys. J. 503, 450. DOI . ADS .
Kashyap, V., Drake, J.J.: 2000, PINTofALE: Package for the interactive analysis of line emission. Bull. Astron. Soc. India 28, 475. ADS .
Kosugi, T., Matsuzaki, K., Sakao, T., Shimizu, T., Sone, Y., Tachikawa, S., Hashimoto, T., Minesugi, K., Ohnishi, A., Yamada, T., Tsuneta, S., Hara, H., Ichimoto, K., Suematsu, Y., Shimojo, M., Watanabe, T., Shimada, S., Davis, J.M., Hill, L.D., Owens, J.K., Title, A.M., Culhane, J.L., Harra, L.K., Doschek, G.A., Golub, L.: 2007, The Hinode (Solar-B) mission: An overview. Solar Phys. 243, 3. DOI . ADS .
Laming, J.M.: 2015, The FIP and inverse FIP effects in solar and stellar coronae. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12, 2. DOI .
Landi, E., Del Zanna, G., Young, P.R., Dere, K.P., Mason, H.E.: 2012, CHIANTI – An atomic database for emission lines. XII. Version 7 of the database. Astrophys. J. 744, 99. DOI . ADS .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Friedlaender, F.M., Heyman, G.F., Hurlburt, N.E., Katz, N.L., Kushner, G.D., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., McFeaters, E.L., Mitchell, S., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Springer, L.A., Stern, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Wuelser, J.-P., Wolfson, C.J., Yanari, C., Bookbinder, J.A., Cheimets, P.N., Caldwell, D., Deluca, E.E., Gates, R., Golub, L., Park, S., Podgorski, W.A., Bush, R.I., Scherrer, P.H., Gummin, M.A., Smith, P., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Soufli, R., Windt, D.L., Beardsley, S., Clapp, M., Lang, J., Waltham, N.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI . ADS .
Mackay, D., Yeates, A.: 2012, The Sun’s global photospheric and coronal magnetic fields: Observations and models. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 9(6). DOI . ADS .
Mandrini, C.H., Schmieder, B., Démoulin, P., Guo, Y., Cristiani, G.D.: 2014, Topological analysis of emerging bipole clusters producing violent solar events. Solar Phys. 289, 2041. DOI . ADS .
Parnell, C.E., Smith, J.M., Neukirch, T., Priest, E.R.: 1996, The structure of three-dimensional magnetic neutral points. Phys. Plasmas 3, 759. DOI . ADS .
Platten, S.J., Parnell, C.E., Haynes, A.L., Priest, E.R., Mackay, D.H.: 2014, The solar cycle variation of topological structures in the global solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 565, A44. DOI . ADS .
Sakao, T., Kano, R., Narukage, N., Kotoku, J., Bando, T., DeLuca, E.E., Lundquist, L.L., Tsuneta, S., Harra, L.K., Katsukawa, Y., Kubo, M., Hara, H., Matsuzaki, K., Shimojo, M., Bookbinder, J.A., Golub, L., Korreck, K.E., Su, Y., Shibasaki, K., Shimizu, T., Nakatani, I.: 2007, Continuous plasma outflows from the edge of a solar active region as a possible source of solar wind. Science 318, 1585. DOI . ADS .
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) investigation for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 207. DOI . ADS .
Slemzin, V., Harra, L., Urnov, A., Kuzin, S., Goryaev, F., Berghmans, D.: 2013, Signatures of slow solar wind streams from active regions in the inner corona. Solar Phys. 286, 157. DOI . ADS .
Ugarte-Urra, I., Warren, H.P.: 2011, Temporal variability of active region outflows. Astrophys. J. 730, 37. DOI . ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Cartledge, N.P., Priest, E.R.: 1998, Magnetic flux transport and the formation of filament channels on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 501, 866. DOI . ADS .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Culhane, J.L., Baker, D., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H., DeRosa, M.L., Rouillard, A.P., Opitz, A., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Brooks, D.H.: 2012, Magnetic topology of active regions and coronal holes: Implications for coronal outflows and the solar wind. Solar Phys. 281, 237. DOI . ADS .
Verbeeck, C., Delouille, V., Mampaey, B., De Visscher, R.: 2014, The SPoCA-suite: Software for extraction, characterization, and tracking of active regions and coronal holes on EUV images. Astron. Astrophys. 561, A29. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Young, P.R., Muglach, K.: 2014, Evidence for two separate heliospheric current sheets of cylindrical shape during mid-2012. Astrophys. J. 780, 103. DOI . ADS .
Warren, H.P., Ugarte-Urra, I., Young, P.R., Stenborg, G.: 2011, The temperature dependence of solar active region outflows. Astrophys. J. 727, 58. DOI . ADS .
Wilhelm, K., Curdt, W., Marsch, E., Schühle, U., Lemaire, P., Gabriel, A., Vial, J.-C., Grewing, M., Huber, M.C.E., Jordan, S.D., Poland, A.I., Thomas, R.J., Kühne, M., Timothy, J.G., Hassler, D.M., Siegmund, O.H.W.: 1995, SUMER – Solar ultraviolet measurements of emitted radiation. Solar Phys. 162, 189. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
S.J. Edwards acknowledges the financial support of the Isle of Man Government during her Ph.D. and the support of the STFC. C.E. Parnell acknowledges the support of the St. Andrews SMTG’s STFC consolidated grant. The work of DHB was performed under contract with the Naval Research Laboratory and was funded by the NASA Hinode program. Hinode is a Japanese mission developed and launched by ISAS/JAXA, collaborating with NAOJ as a domestic partner, NASA and STFC (UK) as international partners. The Hinode science team organised at ISAS/JAXA conducts the scientific operation of Hinode mission: this team mainly consists of scientists from institutes in the partner countries. Support for the post-launch operation is provided by JAXA and NAOJ (Japan), STFC (UK), NASA, ESA, and NSC (Norway). Courtesy of NASA/SDO and the AIA, EVE, and HMI science teams. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme under the grant agreement No. 284461 (eHEROES project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, S.J., Parnell, C.E., Harra, L.K. et al. A Comparison of Global Magnetic Field Skeletons and Active-Region Upflows. Sol Phys 291, 117–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0807-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0807-8