Abstract
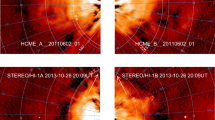
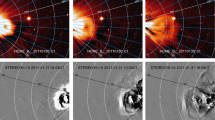
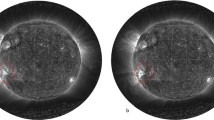
Understanding the kinematic evolution of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) in the heliosphere is important to estimate their arrival time at Earth. The kinematics of CMEs can change when they interact or collide with each other as they propagate in the heliosphere. In this article, we analyze the collision and post-interaction characteristics of two Earth-directed CMEs that were launched successively on 9 and 10 November 2012. To do this, we used white-light imaging observations from STEREO/SECCHI and in situ observations taken from the Wind spacecraft. We tracked two density-enhancement features associated with the leading and trailing edge of the 9 November CME and one density enhanced feature associated with the leading edges of the 10 November CME by constructing J-maps. We found that the leading edge of the 10 November CME interacted with the trailing edge of the 9 November CME. We also estimated the kinematics of these features of the CMEs and found a significant change in their dynamics after interaction. In in situ observations, we identified distinct structures associated with interacting CMEs and also observed heating and compression as signatures of their interaction. Our analysis shows an improvement in the arrival-time prediction of CMEs when their post-collision dynamics are used instead of the pre-collision dynamics. By estimating the true masses and speeds of these colliding CMEs, we investigated the nature of the observed collision, which is found to be almost perfectly inelastic. The investigation also places in perspective the geomagnetic consequences of the two CMEs and their interaction in terms of occurrence of geomagnetic storms and triggering of magnetospheric substorms.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billings, D.E.: 1966, A Guide to the Solar Corona, Academic Press, San Diego, 150.
Burlaga, L.F., Behannon, K.W., Klein, L.W.: 1987, Compound streams, magnetic clouds, and major geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 5725. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F., Lemaire, J.F.: 1978, Interplanetary magnetic holes – Theory. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 5157. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F., Plunkett, S.P., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2002, Successive CMEs and complex ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1266. DOI .
Cargill, P.J.: 2004, On the aerodynamic drag force acting on interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 221, 135. DOI .
Chakrabarty, D., Sekar, R., Narayanan, R., Devasia, C.V., Pathan, B.M.: 2005, Evidence for the interplanetary electric field effect on the OI 630.0 nm airglow over low latitude. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A11301. DOI .
Colaninno, R.C., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, First determination of the true mass of coronal mass ejections: A novel approach to using the two STEREO viewpoints. Astrophys. J. 698, 852. DOI .
Colaninno, R.C., Vourlidas, A., Wu, C.C.: 2013, Quantitative comparison of methods for predicting the arrival of coronal mass ejections at Earth based on multiview imaging. J. Geophys. Res. 118, 6866. DOI .
Davies, J.A., Harrison, R.A., Rouillard, A.P., Sheeley, N.R., Perry, C.H., Bewsher, D., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Crothers, S.R., Brown, D.S.: 2009, A synoptic view of solar transient evolution in the inner heliosphere using the heliospheric imagers on STEREO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, 2102. DOI .
Davies, J.A., Perry, C.H., Trines, R.M.G.M., Harrison, R.A., Lugaz, N., Möstl, C., Liu, Y.D., Steed, K.: 2013, Establishing a stereoscopic technique for determining the kinematic properties of solar wind transients based on a generalised self-similarly expanding circular geometry. Astrophys. J. 777, 167. DOI .
DeForest, C.E., Howard, T.A., McComas, D.J.: 2013, Tracking coronal features from the low corona to Earth: A quantitative analysis of the 2008 December 12 coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. 769, 43. DOI .
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, A.L.C.: 2008, Interplanetary conditions causing intense geomagnetic storms (Dst=−100 nT) during solar cycle 23 (1996 – 2006). J. Geophys. Res. 113, A05221. DOI .
Farrugia, C.J., Jordanova, V.K., Thomsen, M.F., Lu, G., Cowley, S.W.H., Ogilvie, K.W.: 2006, A two-ejecta event associated with a two-step geomagnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A11104. DOI .
Gonzalez, W.D., Gonzalez, A.L.C., Tsurutani, B.T., Smith, E.J., Tang, F.: 1989, Solar wind-magnetosphere coupling during intense magnetic storms (1978 – 1979). J. Geophys. Res. 94, 8835. DOI .
Gonzalez, W.D., Joselyn, J.A., Kamide, Y., Kroehl, H.W., Rostoker, G., Tsurutani, B.T., Vasyliunas, V.M.: 1994, What is a geomagnetic storm? J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771. DOI .
Gonzalez-Esparza, A., Santillán, A., Ferrer, J.: 2004, A numerical study of the interaction between two ejecta in the interplanetary medium: One- and two-dimensional hydrodynamic simulations. Ann. Geophys. 22, 3741. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Lepping, R.P., Kaiser, M.L., Berdichevsky, D., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2000, Interplanetary acceleration of coronal mass ejections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 145. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Radio signatures of coronal mass ejection interaction: coronal mass ejection cannibalism? Astrophys. J. Lett. 548, L91. DOI .
Gosling, J.T.: 1993, The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937. DOI .
Gosling, J.T., Bame, S.J., McComas, D.J., Phillips, J.L.: 1990, Coronal mass ejections and large geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 17, 901. DOI .
Gosling, J.T., McComas, D.J., Phillips, J.L., Bame, S.J.: 1991, Geomagnetic activity associated with earth passage of interplanetary shock disturbances and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 7831. DOI .
Harrison, R.A., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Liu, Y., Temmer, M., Bisi, M.M., Eastwood, J.P., de Koning, C.A., Nitta, N., Rollett, T., Farrugia, C.J., Forsyth, R.J., Jackson, B.V., Jensen, E.A., Kilpua, E.K.J., Odstrcil, D., Webb, D.F.: 2012, An analysis of the origin and propagation of the multiple coronal mass ejections of 2010 August 1. Astrophys. J. 750, 45. DOI .
Howard, T.A., Tappin, S.J.: 2009, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections observed in the heliosphere: 1. Review of theory. Space Sci. Rev. 147, 31. DOI .
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., Thompson, W.T., St Cyr, O.C., Mentzell, E., Mehalick, K., Lemen, J.R., Wuelser, J.P., Duncan, D.W., Tarbell, T.D., Wolfson, C.J., Moore, A., Harrison, R.A., Waltham, N.R., Lang, J., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Mapson-Menard, H., Simnett, G.M., Halain, J.P., Defise, J.M., Mazy, E., Rochus, P., Mercier, R., Ravet, M.F., Delmotte, F., Auchere, F., Delaboudiniere, J.P., Bothmer, V., Deutsch, W., Wang, D., Rich, N., Cooper, S., Stephens, V., Maahs, G., Baugh, R., McMullin, D., Carter, T.: 2008, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67. DOI .
Inhester, B.: 2006, Stereoscopy basics for the STEREO mission. arXiv .
Iyemori, T., Rao, D.R.K.: 1996, Decay of the Dst field of geomagnetic disturbance after substorm onset and its implication to storm–substorm relation. Ann. Geophys. 14, 608. DOI .
Janzhura, A., Troshichev, O., Stauning, P.: 2007, Unified PC indices: relation to isolated magnetic substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A09207. DOI .
Jurac, S., Kasper, J.C., Richardson, J.D., Lazarus, A.J.: 2002, Geomagnetic disturbances and their relationship to interplanetary shock parameters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 1463. DOI .
Kaiser, M.L., Kucera, T.A., Davila, J.M., St. Cyr, O.C., Guhathakurta, M., Christian, E.: 2008, The STEREO mission: An introduction. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 5. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Mierla, M., Rodriguez, L., Zhukov, A.N., Srivastava, N., West, M.J.: 2012, Estimating travel times of coronal mass ejections to 1 AU using multi-spacecraft coronagraph data. Solar Phys. 279, 477. DOI .
Laundal, K.M., Østgaard, N.: 2009, Asymmetric auroral intensities in the Earth’s Northern and Southern hemispheres. Nature 460, 491. DOI .
Lepping, R.P., Acũna, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Farrell, W.M., Slavin, J.A., Schatten, K.H., Mariani, F., Ness, N.F., Neubauer, F.M., Whang, Y.C., Byrnes, J.B., Kennon, R.S., Panetta, P.V., Scheifele, J., Worley, E.M.: 1995, The Wind magnetic field investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207. DOI .
Lindsay, G.M., Luhmann, J.G., Russell, C.T., Gosling, J.T.: 1999, Relationships between coronal mass ejection speeds from coronagraph images and interplanetary characteristics of associated interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12515. DOI .
Liu, Y., Davies, J.A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2010a, Geometric triangulation of imaging observations to track coronal mass ejections continuously out to 1 AU. Astrophys. J. Lett. 710, L82. DOI .
Liu, Y., Thernisien, A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D.: 2010b, Reconstructing coronal mass ejections with coordinated imaging and in situ observations: Global structure, kinematics, and implications for space weather forecasting. Astrophys. J. 722, 1762. DOI .
Liu, Y.D., Luhmann, J.G., Möstl, C., Martinez-Oliveros, J.C., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P., Harrison, R.A., Temmer, M., Webb, D.F., Odstrcil, D.: 2012, Interactions between coronal mass ejections viewed in coordinated imaging and in situ observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 746, L15. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B. IV, Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, Numerical simulation of the interaction of two coronal mass ejections from Sun to Earth. Astrophys. J. 634, 651. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Vourlidas, A., Roussev, I.I.: 2009, Deriving the radial distances of wide coronal mass ejections from elongation measurements in the heliosphere – Application to CME–CME interaction. Ann. Geophys. 27, 3479. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Hernandez-Charpak, J.N., Roussev, I.I., Davis, C.J., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Determining the azimuthal properties of coronal mass ejections from multi-spacecraft remote-sensing observations with STEREO SECCHI. Astrophys. J. 715, 493. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Davis, C.J., Roussev, I.I., Temmer, M.: 2012, The deflection of the two interacting coronal mass ejections of 2010 May 23 – 24 as revealed by combined in situ measurements and heliospheric imaging. Astrophys. J. 759, 68. DOI .
Manoharan, P.K.: 2006, Evolution of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere: A study using white-light and scintillation images. Solar Phys. 235, 345. DOI .
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Dumbović, M., Žic, T., Roša, D., Hržina, D., Lulić, S., Romštajn, I., Bušić, I., Salamon, K., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Veronig, A., Bostanjyan, N., Chilingarian, A., Mailyan, B., Arakelyan, K., Hovhannisyan, A., Mujić, N.: 2014, Kinematics of interacting ICMEs and related forbush decrease: case study. Solar Phys. 289, 351. DOI .
Martínez Oliveros, J.C., Raftery, C.L., Bain, H.M., Liu, Y., Krupar, V., Bale, S., Krucker, S.: 2012, The 2010 August 1 type II burst: A CME–CME interaction and its radio and white-light manifestations. Astrophys. J. 748, 66. DOI .
Mays, M.L., Horton, W., Kozyra, J., Zurbuchen, T.H., Huang, C., Spencer, E.: 2007, Effect of interplanetary shocks on the AL and Dst indices. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L11104. DOI .
Mierla, M., Davila, J., Thompson, W., Inhester, B., Srivastava, N., Kramar, M., St. Cyr, O.C., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2008, A quick method for estimating the propagation direction of coronal mass ejections using STEREO-COR1 images. Solar Phys. 252, 385. DOI .
Minnaert, M.: 1930, On the continuous spectrum of the corona and its polarisation. Z. Astrophys. 1, 209.
Mishra, W., Srivastava, N.: 2013, Estimating the arrival time of Earth-directed coronal mass ejections at in situ spacecraft using COR and HI observations from STEREO. Astrophys. J. 772, 70. DOI .
Mishra, W., Srivastava, N.: 2014, Morphological and kinematic evolution of three interacting coronal mass ejections of 2011 February 13 – 15. Astrophys. J. 794, 64. DOI . ADS . arXiv .
Mishra, W., Srivastava, N., Davies, J.A.: 2014, A comparison of reconstruction methods for the estimation of coronal mass ejections kinematics based on SECCHI/HI observations. Astrophys. J. 784, 135. DOI . ADS .
Möstl, C., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Farrugia, C.J., Liu, Y., Veronig, A.M., Leitner, M., Galvin, A.B., Biernat, H.K.: 2010, STEREO and Wind observations of a fast ICME flank triggering a prolonged geomagnetic storm on 5 – 7 April 2010. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, 24103. DOI .
Möstl, C., Rollett, T., Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Davies, J.A., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Harrison, R.A., Crothers, S., Luhmann, J.G., Galvin, A.B., Zhang, T.L., Baumjohann, W., Biernat, H.K.: 2011, Arrival time calculation for interplanetary coronal mass ejections with circular fronts and application to STEREO observations of the 2009 February 13 eruption. Astrophys. J. 741, 34. DOI .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Kilpua, E.K.J., Jian, L.K., Liu, Y., Eastwood, J.P., Harrison, R.A., Webb, D.F., Temmer, M., Odstrcil, D., Davies, J.A., Rollett, T., Luhmann, J.G., Nitta, N., Mulligan, T., Jensen, E.A., Forsyth, R., Lavraud, B., de Koning, C.A., Veronig, A.M., Galvin, A.B., Zhang, T.L., Anderson, B.J.: 2012, Multi-point shock and flux rope analysis of multiple interplanetary coronal mass ejections around 2010 August 1 in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 758, 10. DOI .
Munro, R.H., Gosling, J.T., Hildner, E., MacQueen, R.M., Poland, A.I., Ross, C.L.: 1979, The association of coronal mass ejection transients with other forms of solar activity. Solar Phys. 61, 201. DOI .
Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Arge, C.N.: 2005, Propagation of the 12 May 1997 interplanetary coronal mass ejection in evolving solar wind structures. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A02106. DOI .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., Miller, G., Scudder, J.D., Sittler, E.C. Jr., Torbert, R.B., Bodet, D., Needell, G., Lazarus, A.J., Steinberg, J.T., Tappan, J.H., Mavretic, A., Gergin, E.: 1995, SWE, a comprehensive plasma instrument for the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55. DOI .
Poland, A.I., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Michels, D.J., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1981, Coronal transients near sunspot maximum. Solar Phys. 69, 169. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2011, Geoeffectiveness (Dst and Kp) of interplanetary coronal mass ejections during 1995 – 2009 and implications for storm forecasting. Space Weather 9, 7005. DOI .
Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Farrugia, C.J., Biernat, H.K.: 2012, Constraining the kinematics of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere with in-situ signatures. Solar Phys. 276, 293. DOI .
Rollett, T., Temmer, M., Möstl, C., Lugaz, N., Veronig, A.M., Möstl, U.V.: 2013, Assessing the constrained harmonic mean method for deriving the kinematics of ICMEs with a numerical simulation. Solar Phys. 283, 541. DOI .
Sheeley, N.R., Walters, J.H., Wang, Y.-M., Howard, R.A.: 1999, Continuous tracking of coronal outflows: two kinds of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 24739. DOI .
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Liu, Y., Liu, R., Vourlidas, A., Miao, B., Ye, P., Liu, J., Zhou, Z.: 2012, Super-elastic collision of large-scale magnetized plasmoids in the heliosphere. Nature 8, 923. DOI .
Srivastava, N., Inhester, B., Mierla, M., Podlipnik, B.: 2009, 3D reconstruction of the leading edge of the 20 May 2007 partial halo CME. Solar Phys. 259, 213. DOI .
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., Rybák, J., Gömöry, P., Stoiser, S., Maričić, D.: 2008, Acceleration in fast halo CMEs and synchronized flare HXR bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 673, L95. DOI .
Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., Odstrčil, D.: 2011, Influence of the ambient solar wind flow on the propagation behavior of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 743, 101. DOI .
Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Rollett, T., Bein, B., de Koning, C.A., Liu, Y., Bosman, E., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Žic, T., Veronig, A.M., Bothmer, V., Harrison, R., Nitta, N., Bisi, M., Flor, O., Eastwood, J., Odstrcil, D., Forsyth, R.: 2012, Characteristics of kinematics of a coronal mass ejection during the 2010 August 1 CME–CME interaction event. Astrophys. J. 749, 57. DOI .
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Peinhart, V., Vršnak, B.: 2014, Asymmetry in the CME–CME interaction process for the events from 2011 February 14 – 15. Astrophys. J. 785, 85. DOI .
Thernisien, A.: 2011, Implementation of the graduated cylindrical shell model for the three-dimensional reconstruction of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 194, 33. DOI .
Thernisien, A., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2009, Forward modeling of coronal mass ejections using STEREO/SECCHI data. Solar Phys. 256, 111. DOI .
Thompson, W.T.: 2009, 3D triangulation of a Sun-grazing comet. Icarus 200, 351. DOI .
Troshichev, O.A., Lukianova, R.Y., Papitashvili, V.O., Rich, F.J., Rasmussen, O.: 2000, Polar cap index (PC) as a proxy for ionospheric electric field in the near-pole region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3809. DOI .
Tsurutani, B.T., Smith, E.J., Gonzalez, W.D., Tang, F., Akasofu, S.I.: 1988, Origin of interplanetary southward magnetic fields responsible for major magnetic storms near solar maximum (1978 – 1979). J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8519. DOI .
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Gonzalez, A.L.C., Guarnieri, F.L., Gopalswamy, N., Grande, M., Kamide, Y., Kasahara, Y., Lu, G., Mann, I., McPherron, R., Soraas, F., Vasyliunas, V.: 2006, Corotating solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic activity: A review. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A07S01. DOI .
Vandas, M., Odstrcil, D.: 2004, Acceleration of electrons by interacting CMEs. Astron. Astrophys. 415, 755. DOI .
Vandas, M., Fischer, S., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Detman, T., Geranios, A.: 1997, MHD simulation of an interaction of a shock wave with a magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 22295. DOI .
Vourlidas, A., Subramanian, P., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A.: 2000, Large-angle spectrometric coronagraph measurements of the energetics of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 534, 456. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Falkenberg, T.V., Möstl, C., Vennerstrom, S., Vrbanec, D.: 2010, The role of aerodynamic drag in propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 512, A43. DOI .
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Vrbanec, D., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A., Čalogović, J., Dumbović, M., Lulić, S., Moon, Y.-J., Shanmugaraju, A.: 2013, Propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: the drag-based model. Solar Phys. 285, 295. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S.: 2003, Multiple magnetic clouds: Several examples during March–April 2001. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1370. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S., Xue, X.H.: 2003, An interplanetary cause of large geomagnetic storms: Fast forward shock overtaking preceding magnetic cloud. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 1700. DOI .
Wang, Y., Zheng, H., Wang, S., Ye, P.: 2005, MHD simulation of the formation and propagation of multiple magnetic clouds in the heliosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 434, 309. DOI .
Webb, D.F., Möstl, C., Jackson, B.V., Bisi, M.M., Howard, T.A., Mulligan, T., Jensen, E.A., Jian, L.K., Davies, J.A., de Koning, C.A., Liu, Y., Temmer, M., Clover, J.M., Farrugia, C.J., Harrison, R.A., Nitta, N., Odstrcil, D., Tappin, S.J., Yu, H.-S.: 2013, Heliospheric imaging of 3D density structures during the multiple coronal mass ejections of late July to early August 2010. Solar Phys. 285, 317. DOI .
Xiong, M., Zheng, H., Wang, S.: 2009, Magnetohydrodynamic simulation of the interaction between two interplanetary magnetic clouds and its consequent geoeffectiveness: 2. Oblique collision. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A11101. DOI .
Xiong, M., Zheng, H., Wang, Y., Wang, S.: 2006, Magnetohydrodynamic simulation of the interaction between interplanetary strong shock and magnetic cloud and its consequent geoeffectiveness: 2. Oblique collision. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A11102. DOI .
Xiong, M., Zheng, H., Wu, S.T., Wang, Y., Wang, S.: 2007, Magnetohydrodynamic simulation of the interaction between two interplanetary magnetic clouds and its consequent geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A11103. DOI .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev. 123, 31. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the UK Solar System Data Centre for providing the processed Level-2 STEREO/HI data. The in situ measurements of solar wind data from ACE and Wind spacecraft were obtained from the NASA CDAweb ( http://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/ ). We also acknowledge the use of DBM, developed by Bojan Vršnak and available at http://oh.geof.unizg.hr/CADBM/cadbm.php , in this study. We also thank the referee for useful comments that helped us improve the manuscript. The work by N.S. partially contributes to the research for European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) for the Coronal Mass Ejections and Solar Energetic Particles (COMESEP) project under Grant Agreement No. 263252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, W., Srivastava, N. & Chakrabarty, D. Evolution and Consequences of Interacting CMEs of 9 – 10 November 2012 Using STEREO/SECCHI and In Situ Observations. Sol Phys 290, 527–552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0625-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0625-4