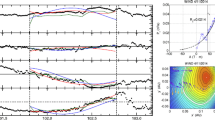
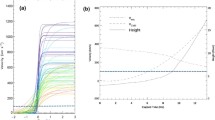
Abstract
This study aims to provide a reference for different magnetic field models and reconstruction methods for interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs). To understand the differences in the outputs of these models and codes, we analyzed 59 events from the Coordinated Data Analysis Workshop (CDAW) list, using four different magnetic field models and reconstruction techniques; force-free fitting, magnetostatic reconstruction using a numerical solution to the Grad–Shafranov equation, fitting to a self-similarly expanding cylindrical configuration and elliptical, non-force-free fitting. The resulting parameters of the reconstructions for the 59 events are compared statistically and in selected case studies. The ability of a method to fit or reconstruct an event is found to vary greatly; this depends on whether the event is a magnetic cloud or not. We find that the magnitude of the axial field is relatively consistent across models, but that the axis orientation of the ejecta is not. We also find that there are a few cases with different signs of the magnetic helicity for the same event when we leave the boundaries free to vary, which illustrates that this simplest of parameters is not necessarily always clearly constrained by fitting and reconstruction models. Finally, we examine three unique cases in depth to provide a comprehensive idea of the different aspects of how the fitting and reconstruction codes work.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Haddad, N., Roussev, I.I., Möstl, C., Jacobs, C., Lugaz, N., Poedts, S., Farrugia, C.J.: 2011, Astrophys. J. Lett. 738, L18. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/738/2/L18 .
Bothmer, V., Schwenn, R.: 1998, Ann. Geophys. 16, 1. doi: 10.1007/s00585-997-0001-x .
Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7217. doi: 10.1029/JA093iA07p07217 .
Burlaga, L.F., Plunkett, S.P., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1266.
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673.
Chané, E., van der Holst, B., Jacobs, C., Poedts, S., Kimpe, D.: 2006, Astron. Astrophys. 447, 727. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20053802 .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Farrugia, C.J.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1362. doi: 10.1029/2003JA009942 .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Luoni, M.L.: 2006, Astron. Astrophys. 455, 349. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20064806 .
Dasso, S., Nakwacki, M.S., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H.: 2007, Solar Phys. 244, 115.
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2009, Astron. Astrophys. 507, 969. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200912645 .
Farrugia, C.J., Osherovich, V.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 12293. doi: 10.1029/95JA00272 .
Farrugia, C.J., Burlaga, L.F., Osherovich, V.A., Lepping, R.P.: 1992, In: Marsch, E., Schwenn, R. (eds.) Solar Wind Seven Colloquium, 611.
Farrugia, C.J., Burlaga, L.F., Osherovich, V.A., Richardson, I.G., Freeman, M.P., Lepping, R.P., Lazarus, A.J.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 7621. doi: 10.1029/92JA02349 .
Farrugia, C.J., Berdichevsky, D.B., Möstl, C., Galvin, A.B., Leitner, M., Popecki, M.A., Simunac, K.D.C., Opitz, A., Lavraud, B., Ogilvie, K.W., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Luhmann, J.G., Sauvaud, J.A.: 2011, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1254. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2010.09.011 .
Gold, T.: 1959, J. Geophys. Res. 64, 1219. doi: 10.1029/JZ064i009p01219 .
Goldstein, H.: 1983, In: NASA Conference Publication 228, 731.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Lepping, R.P.: 2008, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 70, 245. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2007.08.070 .
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.L.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 710, 1111. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/710/2/1111 .
Gosling, J.T.: 1990, In: AGU Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 58, 343.
Gulisano, A.M., Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P.: 2005, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 67, 1761. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2005.02.026 .
Hidalgo, M.A.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1320. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009818 .
Hidalgo, M.A., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Cid, C.: 2002, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(13), 1637. doi: 10.1029/2001GL013875 .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö.: 2001, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 467. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012232 .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö.: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1142. doi: 10.1029/2001JA000293 .
Hu, Q., Smith, C.W., Ness, N.F., Skoug, R.M.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A03102. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010101 .
Isavnin, A., Kilpua, E.K.J., Koskinen, H.E.J.: 2011, Solar Phys. 273, 205. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9845-z .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Solar Phys. 239, 393. doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-0133-2 .
Kahler, S.W., Krucker, S., Szabo, A.: 2011, J. Geophys. Res. 116, A01104. doi: 10.1029/2010JA015328 .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Liewer, P.C., Farrugia, C., Luhmann, J.G., Möstl, C., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Lynch, B.J., Russell, C.T., Vourlidas, A., Acuna, M.H., Galvin, A.B., Larson, D., Sauvaud, J.A.: 2009, Solar Phys. 254, 325. doi: 10.1007/s11207-008-9300-y .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Lee, C.O., Luhmann, J.G., Li, Y.: 2011, Ann. Geophys. 29, 1455. doi: 10.5194/angeo-29-1455-2011 .
Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., Jones, J.A.: 1990, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957.
Lepping, R.P., Acuna, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Farrell, W.M.: 1995, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207.
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Wu, C.C., Szabo, A., Narock, T., Mariani, F., Lazarus, A.J., Quivers, A.J.: 2006, Ann. Geophys. 24, 215. doi: 10.5194/angeo-24-215-2006 .
Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Lynch, B.J., Kilpua, E.K.J.: 2011, Solar Phys. 270, 331. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9722-9 .
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Huttunen, K.E.J., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D., Russell, C.T., Galvin, A.B.: 2008, Astrophys. J. Lett. 677, 133. doi: 10.1086/587839 .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I.: 2005a, Astrophys. J. 627, 1019.
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I.: 2005b, Astrophys. J. 634, 651.
Lugaz, N., Vourlidas, A., Roussev, I.I., Morgan, H.: 2009, Solar Phys. 256, 269. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9339-4 .
Lundquist, S.: 1950, Ark. Fys. 2, 361.
Lynch, B.J., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Antiochos, S.K.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1239. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009591 .
Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I., Roussev, I., Ridley, A., De Zeeuw, D.L., Sokolov, I.V., Powell, K.G., Tóth, G.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A02107.
Manchester, W.B., Vourlidas, A., Tóth, G., Lugaz, N., Roussev, I.I., Sokolov, I.V., Gombosi, T.I., De Zeeuw, D.L., Opher, M.: 2008, Astrophys. J. 684, 1448. doi: 10.1086/590231 .
Marubashi, K.: 1986, Adv. Space Res. 6, 335. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(86)90172-9 .
Marubashi, K.: 2000, Adv. Space Res. 26, 55. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(99)01026-1 .
Marubashi, K., Lepping, R.P.: 2007, Ann. Geophys. 25, 2453. doi: 10.5194/angeo-25-2453-2007 .
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Barker, P., Feldman, W.C.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 563.
Möstl, C., Miklenic, C., Farrugia, C.J., Temmer, M., Veronig, A., Galvin, A.B., Vršnak, B., Biernat, H.K.: 2008, Ann. Geophys. 26, 3139. doi: 10.5194/angeo-26-3139-2008 .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Miklenic, C., Temmer, M., Galvin, A.B., Luhmann, J.G., Kilpua, E.K.J., Leitner, M., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Veronig, A., Biernat, H.K.: 2009a, J. Geophys. Res. 114, A04102. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013657 .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Biernat, H.K., Leitner, M., Kilpua, E.K.J., Galvin, A.B., Luhmann, J.G.: 2009b, Solar Phys. 256, 427. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9360-7 .
Möstl, C., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Farrugia, C.J., Liu, Y., Veronig, A.M., Leitner, M., Galvin, A.B., Biernat, H.K.: 2010, Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L24103. doi: 10.1029/2010GL045175 .
Mulligan, T., Russell, C.T.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10581. doi: 10.1029/2000JA900170 .
Nelder, J.A., Mead, R.: 1965, Comput. J. 7, 308.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Hidalgo, M.A., Sequeiros, J.: 2005, Solar Phys. 232, 105.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Colaninno, R., Vourlidas, A., Szabo, A., Lepping, R.P., Boardsen, S.A., Anderson, B.J., Korth, H.: 2012, J. Geophys. Res. 117, A06106.
Odstrčil, D., Pizzo, V.J.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104(13), 483.
Odstrčil, D., Pizzo, V.J.: 2009, Solar Phys. 259, 297. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9449-z .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F.: 1995, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55.
Owens, M.J., Merkin, V.G., Riley, P.: 2006, J. Geophys. Res. 111, A03104. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011460 .
Owens, M.J., Démoulin, P., Savani, N.P., Lavraud, B., Ruffenach, A.: 2012, Solar Phys., 278, 435. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-9939-2 .
Rees, A., Forsyth, R.J.: 2004, Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L06804. doi: 10.1029/2003GL018330 .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Solar Phys. 264, 189. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9568-6 .
Riley, P., Gosling, J.T., Pizzo, V.J.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 14677. doi: 10.1029/97JA01131 .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Odstrcil, D., Zurbuchen, T.H., Lario, D., Lepping, R.P.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1272. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009760 .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Odstrcil, D., Hidalgo, M.A., Cid, C., Hu, Q., Lepping, R.P., Lynch, B.J., Rees, A.: 2004, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1321. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2004.03.019 .
Riley, P., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Linker, J.: 2008, Astrophys. J. 672, 1221. doi: 10.1086/523893 .
Romashets, E.P., Vandas, M.: 2003, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(20), 2065. doi: 10.1029/2003GL017692 .
Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1201.
Ruffenach, A.B., Lavraud, B., Owens, M.J., et al.: 2012, J. Geophys. Res. doi: 10.1029/2012JA017624
Savani, N.P., Rouillard, A.P., Davies, J.A., Owens, M.J., Forsyth, R.J., Davis, C.J., Harrison, R.A.: 2009, Ann. Geophys. 27, 4349 – 4358. doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-4349-2009 .
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Astrophys. J. Lett. 714, 128. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/714/1/L128 .
Shen, F., Feng, X., Wu, S.T., Xiang, C.: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 112, A06109. doi: 10.1029/2006JA012164 .
Shimazu, H., Vandas, M.: 2002, Earth Planets Space 54, 783.
Smith, C.W., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Acuna, M.H.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 613.
Sonnerup, B.U.Ö., Scheible, M.: 1998, ISSI Sci. Rep. Ser. 1, 185.
Steed, K., Owen, C.J., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2011, J. Geophys. Res. 116, A01106. doi: 10.1029/2010JA015940 .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E.P.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 398, 801. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20021691 .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E.P., Watari, S., Geranios, A., Antoniadou, E., Zacharopoulou, O.: 2006, Adv. Space Res. 38, 441. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2004.11.026 .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1370.
Yurchyshyn, V.B., Wang, H., Goode, P.R., Deng, Y.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 563, 381. doi: 10.1086/323778 .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., Nitta, N.V., Poomvises, W., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.C., Yashiro, S., Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 112. A10102. doi: 10.1029/2007JA012321 .
Zhao, X.P., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 2077. doi: 10.1029/97JA03234 .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, Space Sci. Rev. 123, 31. doi: 10.1007/s11214-006-9010-4 .
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the referee for his/her very useful comments, which helped improve and clarify our study and manuscript.
N. A. and I. R. were supported by a NSF grant AGS-0639335 (CAREER). This work was initiated at two Coordinated Data Analysis Workshops (CDAWs) held at Predictive Science Inc. in San Diego, CA and at the University of Alcala in Alcala de Henares, Spain with support from NASA and from Spain. N. P. S. was supported by the NASA LWS Jack Eddy Postdoctoral Fellowship Program, administrated by the UCAR Visiting Scientist Program and hosted by the Naval Research Laboratory. C. M. was supported by a Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship within the 7th European Community Framework Programme. The presented work has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n∘263252 [COMESEP]. C. J. F. acknowledges support from NASA grant NNX10AQ29G and NAS5-0313. N. A. would like to thank the Space Science Center at the University of New Hampshire for providing a nice work environment during the final revisions of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Flux-Rope Structure of Coronal Mass Ejections
Guest Editors: N. Gopalswamy, T. Nieves-Chinchilla, M. Hidalgo, J. Zhang and P. Riley
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Haddad, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Savani, N.P. et al. Magnetic Field Configuration Models and Reconstruction Methods for Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections. Sol Phys 284, 129–149 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0244-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0244-5