Abstract
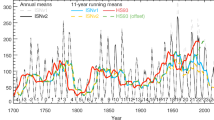
During the last few years the Sun and solar wind have shown a behavior that was so unexpected that the phenomena was described as “the strange solar minimum”. It has been speculated that the 23/24 solar cycle minimum may have indicated the onset of a Maunder-Minimum-type Grand Minimum. Here we review what is known from 1500 years of proxy data about Maunder-type Grand Minima and the minima of the cyclic Centennial Gleissberg variations. We generate criteria that distinguish between the two types of event. Applying these criteria to the observed solar terrestrial data we conclude that the unexpected behavior began well before the solar cycle 23/24 minimum. The data do not support the Maunder Minimum conjecture. However, the behavior can be understood as a minimum of the Centennial Gleissberg Cycle that previously minimized in the beginning of the 20th century. We conclude that the Centennial Gleissberg Cycle is a persistent variation that has been present 80% of the time during the last 1500 years and should be explained by solar dynamo theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aellig, M.R., Lazarus, A.J., Steinberg, J.T.: 2001, The solar wind helium abundance: variation with wind speed and the solar cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 2767 – 2770.
Ahluwalia, H.S., Ygbuhay, R.C.: 2010, Current forecast for sunspot cycle 24 parameters. In: Maksimovic, M., Issautier, K., Meyer-Vernet, N., Moncuquet, M., Pantellini, F. (eds.) Twelfth International Solar Wind Conference, AIP Conf. Proc. 1216, 671 – 674.
Bartels, J., Heck, N.H., Johnston, H.F.: 1939, The three-hour range index measuring geomagnetic activity. Geophys. Res. 44, 411 – 454.
Beer, J., Tobias, S., Weiss, N.: 1998, An active Sun throughout the Maunder minimum? Solar Phys. 181, 237 – 249.
Campbell, W.H.: 1996, Geomagnetic storms, the Dst ring-current myth and lognormal distributions. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 58, 1171 – 1187.
Chapman, S., Bartels, J.: 1940, Geomagnetism, Oxford Univ. Press, New York.
Eddy, J.A.: 1976, The Maunder Minimum. Science 18, 1189 – 1202.
Feynman, J.: 1988, Solar, geomagnetic and auroral variability observed in the historic record. In: Stephenson, F.B., Wolfendale, A.W. (eds.) Secular Solar and Geomagnetic Variations in the Last 10 000 Years, NATO ASI Series C 236, 14 – 26.
Feynman, J., Crooker, N.U.: 1978, The solar wind at the turn of the century. Nature 275, 626 – 627.
Feynman, J., Fougere, P.: 1984, Eighty-eight year cycle in solar terrestrial phenomena confirmed. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 3023 – 3027.
Feynman, J., Gu, X.Y.: 1986, Prediction of geomagnetic activity on time scales of one to ten years. Rev. Geophys. 24, 650 – 666.
Finch, I.D.: 2009, Seasonal and Daily Variations in Geomagnetic Activity. Thesis, Doctor of Philosophy, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK.
Frick, P., Galyagin, D., Hoyt, D.V., Nesme-Ribes, E., Schatten, K.H., Sokoloff, D.D., Zakharov, V.: 1997, Wavelet analysis of solar activity recorded by sunspot groups. Astron. Astrophys. 328, 670 – 681.
Gleissberg, W.: 1965, The eighty-year solar cycle in auroral frequency numbers. J. Br. Astron. Assoc. 75, 227 – 231.
Gibson, S.: 2007, Whole heliospheric interval. http://ihy2007.org/WHI/WHI.shtml .
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M., Reichmann, E.R.: 1999, A synthesis of solar cycle prediction techniques. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 22 375 – 22 388.
Hirshberg, J., Colburn, D.S.: 1969, Interplanetary field and geomagnetic variation – a unified view. Planet. Space Sci. 17, 1183 – 1206.
Kasper, J.C., Stevens, M.L., Lazarus, A.J., Steinberg, J.T., Ogilvie, K.W.: 2007, Solar wind helium abundance as a function of speed and heliographic latitude: variation through a solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 660, 901 – 910.
Keimatsu, M.A.: 1976, A chronology of aurorae and sunspots observed in China, Korea, and Japan. Ann. Sci. 13, 1 – 32.
Lee, C.O., Luhmann, J.G., Zhao, X.P., Liu, Y., Riley, P., Arge, C.N., Russell, C.T., de Pater, I.: 2009, Effects of the weak polar fields of solar cycle 23. Solar Phys. 256, 345 – 363.
Livingston, W., Penn, M.: 2009, Are sunspots different during this solar minimum? EOS 90(30).
Lockwood, M., Stamper, M.R., Wild, M.N.: 1999, A doubling of the Sun’s coronal magnetic field during the past 100 years. Nature 399, 437 – 439.
Lockwood, M., Rouillard, A.P., Finch, I., Stamper, R.: 2006, Comment on the IDV index: Its derivation and use in inferring long-term variations of the interplanetary magnetic field strength by Leif Svalgaard and Edward W. Cliver. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09109ss.
Mayaud, P.N.: 1973, A hundred year series of geomagnetic data 1868 – 1967, indices aa, storm sudden commencements. IAGA Bull. 33.
Mayaud, P.N.: 1980, Derivation, Meaning, and Use of Geomagnetic Indices, AGU Geophys. Monogr. 22, American Geophysical Union, Washington.
Mewaldt, R.A., Davis, A.J., Lave, K.A., Leske, R.A., Stone, E.C., Wiedenbeck, M.E., Binns, W.R., Christian, E.R., Cummings, A.C., de Nolfo, G.A., Israel, M.H., Labrador, A.W., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 2010, Record-setting cosmic-ray intensities in 2009 and 2010. Astrophys. J. Lett. 723, 1 – 6.
Milan, S.E., Hutchinson, J.P., Boakes, D., Hubert, B.: 2009a, Influences on the radius of the auroral oval. Ann. Geophys. 27, 2913 – 2924.
Milan, S.E.: 2009b, Both solar wind-magnetosphere coupling and ring current intensity control the size of the auroral oval. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L18101.
Miyahara, H., Masuda, K., Muraki, Y., Furuzawa, H., Menjo, H., Nakamura, T.: 2004, Cyclicity of solar activity during the Maunder Minimum deduced from radiocarbon content. Solar Phys. 234, 317 – 322.
Nakai, H., Kamida, Y.: 2003, Substorm-associated largescale magnetic field chnages in the magnetotail. Ann. Geophys. 21, 869 – 879.
Pulkkinen, T.I., Nevanlinna, H., Pulkkinen, P.J., Lockwood, M.: 2001, The Sun-Earth connection in time scales from years to decades and centuries. Space Sci. Rev. 95, 625 – 637.
Richardson, I.E., Cliver, E.W., Cane, H.V.: 2002, Long-term trends in interplanetary magnetic field strength and solar wind structure during the twentieth century. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A10), SSH 12-1.
Rouillard, A.P., Lockwood, M., Finch, I.: 2007, Centennial changes in the solar wind speed and in the open solar flux. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A05103.
Ruzmaikin, A.: 1981, Solar cycle as strange attractor. Comments Astrophys. 9, 85 – 93.
Schlamminger, L.: 1991, Aurora Borealis lag during the Maunder Minimum. Solar Phys. 131, 411 – 414.
Silverman, S., Feynman, J.: 1980, The changing aurora of the past three centuries. In: Deehr, C.S., Holtet, J.A. (eds.) Exploration of the Polar Upper Atmosphere, Reidel, Dordrecht, 407 – 420.
Silverman, S.: 1992, Secular variation of the aurora for the past 500 years. Rev. Geophys. 30, 333 – 351.
Siscoe, G.L.: 1978, A quasi-self-consistent axially symmetric model for the growth of a ring current through Earthward motion from a pre-storm configuration. Planet. Space Sci. 27, 285 – 295.
Siscoe, G.L.: 1980, Evidence in the auroral record for secular solar variability. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 18, 647 – 658.
Siscoe, G.L., Verosub, K.L.: 1983, High medieval auroral incidence over China and Japan: Implications for the medieaval site of the geomagnetic pole. Geophys. Res. Lett. 10, 345 – 348.
Sokoloff, D.: 2004, The Maunder Minimum and the solar dynamo. Solar Phys. 224, 145 – 152.
Steinberg, J.T., Skoug, R.M., Ryland, P., Kasper, J.C., Maruca, B., Lepri, S.T.: 2010, The recent weakening solar wind as observed by ACE and Wind. AGU Fall Meeting, SH11B-1670.
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W.: 2005, The IDV index: Its derivation and use in inferring long-term variations of the interplanetary magnetic field strength. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12103.
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W.: 2006, Reply to the comment by M. Lockwood et al. on the IDV index: Its derivation and use in inferring long-term variations of the interplanetary magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09110.
Troshichev, O., Hayakawa, H., Matsuoka, A., Mukai, T., Tsuruda, K.: 1996, Cross polar cap diameter and voltage as a function of PC index and interplanetary quantities. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 13429 – 13435.
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2001, Heliospheric modulation of cosmic rays and solar activity during the Maunder Minimum. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 16039 – 16046.
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2007, Grand minima and maxima of solar activity: new observational constraints. Astron. Astrophys. 471, 301 – 309.
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K., Taricco, C., Bhandari, N., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2006, Direct test by cosmogenic 44 T i in meteorites. Astron. Astrophys. 457, L25 – L27.
Usoskin, I.G., Sokoloff, D.D., Moss, D.: 2009, Grand Minima of solar activity and the mean-field dynamo. Solar Phys. 254, 345 – 355.
Vaquero, J.M., Gallego, M.C., Usoskin, I.G., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2011, Revisited sunspot number data: a new scenario for the onset of the Maunder Minimum. Astrophys. J. Lett. 731, L24.
Vestine, E.H., Laporte, L., Lange, I., Scott, W.E.: 1947, The Geomagnetic Field, Its Description and Analysis. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication 580.
Wang, Y.-M.: 2008, Relating the solar wind helium abundance to the coronal magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 683, 499 – 509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feynman, J., Ruzmaikin, A. The Sun’s Strange Behavior: Maunder Minimum or Gleissberg Cycle?. Sol Phys 272, 351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9828-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9828-0