Abstract
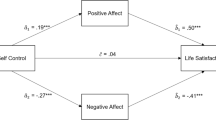
The present study aimed at analyzing the important role of forgiveness in life satisfaction and to extend the previous literature by investigating the potential mediating effects of social support and affect balance in this relationship. Self-report measures of forgiveness, social support, positive affect, negative affect and life satisfaction were administrated to 430 Chinese university students. Path analysis indicated that forgiveness exerted its indirect effect on life satisfaction through the mediating effects of social support and affect balance and the three-path mediating effect of social support–affect balance. Furthermore, a multi-group analysis showed that the mediational model was not moderated by gender. Therefore, this study makes a contribution to the complex nature of the association between forgiveness and life satisfaction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H. (1987). Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika, 52, 317–332.
Allemand, M., Hill, P. L., Ghaemmaghami, P., & Martin, M. (2012). Forgivingness and subjective well-being in adulthood: The moderating role of future time perspective. Journal of Research in Personality, 46, 32–39.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103, 411–423.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2003). AMOS 5.0 update to the AMOS user’s guide. Chicago, IL: Smallwaters.
Bono, G., McCullough, M. E., & Root, L. M. (2008). Forgiveness, feeling connected to others, and well-being: Two longitudinal studies. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 34, 182–195.
Brannan, D., Biswas-Diener, R., Mohr, C. D., Mortazavi, S., & Stein, N. (2012). Friends and family: A cross-cultural investigation of social support and subjective well-being among college students. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 8, 65–75.
Brown, R. P. (2003). Measuring individual differences in the tendency to forgive: Construct validity and links with depression. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 29, 759–771.
Brown, R. P., & Phillips, A. (2005). Letting bygones be bygones: Further evidence for the validity of the Tendency to Forgive scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 38, 627–638.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Cohen, S., Gottlieb, B., & Underwood, L. (2000). Theoretical and historical perspectives. In S. Cohen, L. Underwood, & B. Gottlieb (Eds.), Social support measurement and intervention: A guide for health and social scientists (pp. 3–28). New York: Oxford University Press.
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49, 71–75.
Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2003). Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: Emotional and cognitive evaluations of life. Annual Review of Psychology, 54, 403–425.
Gallagher, E. N., & Vella-Brodrick, D. A. (2008). Social support and emotional intelligence as predictors of subjective well-being. Personality and Individual Differences, 44, 1551–1561.
Green, M., DeCourville, N., & Sadava, S. (2012). Positive affect, negative affect, stress, and social support as mediators of the forgiveness-health relationship. The Journal of social Psychology, 152, 288–307.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Hu, S., Zhong, H., Ja, Y., & Zhang, A. (2005). A study on interpersonal forgive and revenge of undergraduates and their links with depression. Psychological Development and Education, 1, 101–108.
Kong, F., Ding, K., & Zhao, J. (2014). The Relationships among gratitude, self-esteem, social support and life satisfaction among undergraduate students. Journal of Happiness Studies, 1–13.
Kong, F., Wang, X., & Zhao, J. (2014b). Dispositional mindfulness and life satisfaction: The role of core self-evaluations. Personality and Individual Differences, 56, 165–169.
Kong, F., & You, X. (2013). Loneliness and self-esteem as mediators between social support and life satisfaction in late adolescence. Social Indicators Research, 110, 271–279.
Kong, F., & Zhao, J. (2013). Affective mediators of the relationship between trait emotional intelligence and life satisfaction in young adults. Personality and Individual Differences, 54, 197–201.
Kong, F., Zhao, J., & You, X. (2012a). Emotional intelligence and life satisfaction in Chinese university students: The mediating role of self-esteem and social support. Personality and Individual Differences, 53, 1039–1043.
Kong, F., Zhao, J., & You, X. (2012b). Social support mediates the impact of emotional intelligence on mental distress and life satisfaction in Chinese young adults. Personality and Individual Differences, 53, 513–517.
Kong, F., Zhao, J., & You, X. (2013). Self-esteem as mediator and moderator of the relationship between social support and subjective well-being among Chinese university students. Social Indicators Research, 112, 151–161.
Koydemir, S., & Schütz, A. (2012). Emotional intelligence predicts components of subjective well-being beyond personality: A two-country study using self-and informant reports. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 7, 107–118.
Kuppens, P., Realo, A., & Diener, E. (2008). The role of positive and negative emotions in life satisfaction judgment across nations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95, 66–75.
Lawler, K. A., Younger, J. W., Piferi, R. L., Jobe, R. L., Edmondson, K. A., & Jones, W. H. (2005). The unique effects of forgiveness on health: An exploration of pathways. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 28, 157–167.
Lawler-Row, K. A., & Piferi, R. L. (2006). The forgiving personality: Describing a life well lived? Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 1009–1020.
McCullough, M. E., Fincham, F. D., & Tsang, J. A. (2003). Forgiveness, forbearance, and time: The temporal unfolding of transgression-related interpersonal motivations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(3), 540–557.
MacKinnon, D. P., Fairchild, A. J., & Fritz, M. S. (2007). Mediation analysis. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 593–614.
Maltby, J., Day, L., & Barber, L. (2004). Forgiveness and mental health variables: Interpreting the relationship using an adaptational-continuum model of personality and coping. Personality and Individual Differences, 37, 1629–1641.
Maxwell, S. E., & Cole, D. A. (2007). Bias in cross-sectional analyses of longitudinal mediation. Psychological Methods, 12, 23–44.
Maxwell, S. E., Cole, D. A., & Mitchell, M. A. (2011). Bias in cross-sectional analyses of longitudinal mediation: Partial and complete mediation under an autoregressive model. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 46, 816–841.
Orth, U., Berking, M., Walker, N., Meier, L. L., & Znoj, H. (2008). Forgiveness and psychological adjustment following interpersonal transgressions: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Research in Personality, 42, 365–385.
Park, H., Paul Heppner, P., & Lee, D. (2010). Maladaptive coping and self-esteem as mediators between perfectionism and psychological distress. Personality and Individual Differences, 48, 469–474.
Proctor, C. L., Linley, P. A., & Maltby, J. (2009). Youth life satisfaction: A review of the literature. Journal of Happiness Studies, 10, 583–630.
Salovey, P., Rothman, A. J., Detweiler, J. B., & Steward, W. T. (2000). Emotional states and physical health. American Psychologist, 55, 110–121.
Sastre, M. T. M., Vinsonneau, G., Neto, F., Girard, M., & Mullet, E. (2003). Forgivingness and satisfaction with life. Journal of Happiness Studies, 4, 323–335.
Schimmack, U. (2008). The structure of subjective wellbeing. In M. Eid & R. J. Larsen (Eds.), The science of subjective well-being (pp. 97–123). New York: Guilford.
Shrout, P. E. (2011). Commentary: Mediation analysis, causal process, and cross-sectional data. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 46, 852–860.
Shrout, P. E., & Bolger, N. (2002). Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 7, 422–445.
Song, G., Kong, F., & Jin, W. (2013). Mediating effects of core self-evaluations on the relationship between social support and life satisfaction. Social Indicators Research, 114, 1161–1169.
Sun, P., & Kong, F. (2013). Affective mediators of the influence of gratitude on life satisfaction in late adolescence. Social Indicators Research, 114, 1361–1369.
Taylor, A. B., MacKinnon, D. P., & Tein, J.-Y. (2008). Tests of the three-path mediated effect. Organizational Research Methods, 11, 241–269.
Tellegen, A., Watson, D., & Clark, L. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 1063–1070.
Thoreson, C. E., Harris, A. H. S., & Luskin, F. (2000). Forgiveness and health: An unanswered question. In M. E. McCullough, K. L. Pargament, & C. E. Thoreson (Eds.), Forgiveness: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 254–280). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Toussaint, L., & Friedman, P. (2009). Forgiveness, gratitude, and well-being: The mediating role of affect and beliefs. Journal of Happiness Studies, 10, 635–654.
Wang, Y., & Kong, F. (2014). The role of emotional intelligence in the impact of mindfulness on life satisfaction and mental distress. Social Indicators Research, 116, 843–852.
Worthington, E. L, Jr, Berry, J. W., Parrott, L, I. I. I., Plante, T. G., & Sherman, A. C. (2001). Unforgiveness, forgiveness, religion, and health. In T. G. Plante & A. C. Sherman (Eds.), Faith and health: Psychological perspectives. New York: Guilford Press.
Worthington, E. L., & Scherer, M. (2004). Forgiveness is an emotion-focused coping strategy that can reduce health risks and promote health resilience: Theory, review, and hypotheses. Psychology & Health, 19, 385–405.
Zhang, W., Jing, D., & Schick, C. J. (2004). The cross-cultural measurement of positive and negative affect examining the dimensionality of PANAS. Psychological Science (China), 27, 77–79.
Zhang, L., & Leung, J. P. (2002). Moderating effects of gender and age on the relationship between self-esteem and life satisfaction in mainland Chinese. International Journal of Psychology, 37(2), 83–91.
Zhao, J., Kong, F., & Wang, Y. (2013). The role of social support and self-esteem in the relationship between shyness and loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 54(5), 577–581.
Zhao, J., Wang, Y., & Kong, F. (2014). Exploring the mediation effect of social support and self-esteem on the relationship between humor style and life satisfaction in Chinese college students. Personality and Individual Differences, 64, 126–130.
Zimet, G. D., Dahlem, N. W., Zimet, S. G., & Farley, G. K. (1988). The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. Journal of Personality Assessment, 52, 30–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, H. Social Support and Affect Balance Mediate the Association Between Forgiveness and Life Satisfaction. Soc Indic Res 124, 671–681 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0790-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0790-8