Abstract
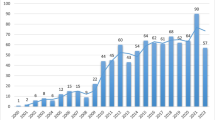
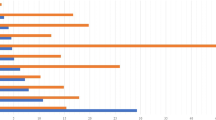
To assess endocrinologic and metabolic research productivity in East Asia (i.e., China, Japan, and South Korea) and correlations between socioeconomic factors and endocrinologic and metabolic research productivity. Articles (except editorials, conference abstracts, letters, news, and corrections) published in 134 endocrinology and metabolism journals in 2005–2014 were screened with the Web of Science database. Total and annual numbers of articles, study designs, impact factors, citations, and articles in high-impact-factor journals were determined for China, Japan, and South Korea. Annual numbers of articles were related to socioeconomic factors for each country. In 2005–2014, there were 144,660 articles from East Asia published in endocrinology and metabolism journals: 10,190, 9470, and 3124 from Japan, China, and South Korea, respectively. Japan published the most randomized controlled trials, followed by China and South Korea, respectively. China had the most articles in high-impact-factor journals, followed by Japan and South Korea, respectively. South Korea had the highest average impact factor and number of citations. During the period studied, annual numbers of articles from China and South Korea increased remarkably (P < 0.05) but remained stable for Japan. Annual numbers of articles from China and South Korea were positively correlated with gross domestic product and expenditure on health care (P < 0.05). The increase in endocrinology and metabolism articles during 2005–2014 in China and South Korea was associated with improved socioeconomic conditions. China has made progress in scientific publication in the past decade; however, there is still room for improvement.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boldt, J., Maleck, W., & Koetter, K. P. (1999). Which countries publish in important anesthesia and critical care journals? Anesthesia and Analgesia, 88(5), 1175–1180.
Chen, Z. (2009). Launch of the health-care reform plan in China. Lancet, 373(9672), 1322–1324.
de Jong, J. W., & Schaper, W. (1996). The international rank order of clinical cardiology. European Heart Journal, 17(1), 35–42.
Hu, L. H., Liao, Z., Gao, R., & Li, Z. S. (2010). Scientific publications in cardiology and cardiovasology journals from Chinese authors in various parts of North Asia: 10-year survey of literature. International Journal of Cardiology, 140(3), 304–308.
Li, J., Gao, X. H., Bian, Q., Guo, Z. Y., Mei, X. B., Yu, G., et al. (2012). Comparative study of scientific publications in urology and nephrology journals originating from USA, China and Japan (2001–2010). PLoS ONE, 7(8), e42200.
Li, G., Hu, L. H., Liao, Z., Cui, H. C., & Li, Z. S. (2010). Scientific publications in pharmacology and pharmacy journals from Chinese authors in various parts of North Asia: A 10-year survey of the literature. Journal of International Medical Research, 38(3), 750–759.
Li, M., Liu, X., & Zhang, L. (2015). Scientific publications in public, environmental and occupational health journals by authors from China, Japan and Korea in East Asia: A 10-year literature survey from 2003–2012. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 28(4), 663–673.
Man, H., Xin, S., Bi, W., Lv, C., Mauro, T. M., Elias, P. M., et al. (2014). Comparison of publication trends in dermatology among Japan, South Korea and Mainland China. BMC Dermatology, 14, 1.
Meo, S. A., Al Masri, A. A., Usmani, A. M., Memon, A. N., & Zaidi, S. Z. (2013). Impact of GDP, spending on R&D, number of universities and scientific journals on research publications among Asian countries. PLoS ONE, 8(6), e66449.
Mervis, J. (1995). Epidemiology. China’s unique environment favors large intervention trials. Science, 270(5239), 1149–1151.
Oelrich, B., Peters, R., & Jung, K. (2007). A bibliometric evaluation of publications in urological journals among European Union countries between 2000–2005. European Urology, 52(4), 1238–1248.
Rössner, S. (2002). Obesity: The disease of the twenty-first century. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 26(Suppl 4), S2–S4.
Tabish, S. A. (2007). Is diabetes becoming the biggest epidemic of the twenty-first century? International Journal of Health Sciences, 1(2), 5–8.
Wang, L. (2016). The structure and comparative advantages of China’s scientific research: Quantitative and qualitative perspectives. Scientometrics, 106(1), 435–452.
Wiysonge, C. S., Uthman, O. A., Ndumbe, P. M., & Hussey, G. D. (2013). A bibliometric analysis of childhood immunization research productivity in Africa since the onset of the Expanded Program on Immunization in 1974. BMC Medicine, 11, 66.
Xu, J., Mao, Z. G., Kong, M., Hu, L. H., Ye, C. Y., Xu, C. G., et al. (2011). Scientific publications in nephrology and urology journals from Chinese authors in East Asia: A 10-year survey of the literature. PLoS ONE, 6(4), e14781.
Yang, W., Lu, J., Weng, J., Jia, W., Ji, L., Xiao, J., et al. (2010). Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. New England Journal of Medicine, 362(12), 1090–1101.
Zhao, X., Ye, R., Zhao, L., Lin, Y., Huang, W., He, X., et al. (2015). Worldwide research productivity in the field of endocrinology and metabolism–a bibliometric analysis. Endokrynologia Polska, 66(5), 434–442.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Bo Xu for his assistance and review of the manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
Q-JL and Q-HP jointly conceived and designed the studies, and performed the experiments and the statistical analyses, and prepared the manuscript. JZ revised the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Qiu-Ju Lyu and Qiang-Hong Pu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, QJ., Pu, QH. & Zhang, J. Bibliometric analysis of scientific publications in endocrinology and metabolism from China, Japan, and South Korea. Scientometrics 110, 105–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2179-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2179-8