Abstract
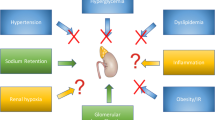
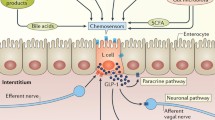
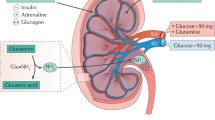
The incretin hormone, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), stimulates insulin secretion and forms the basis of a new drug class for diabetes treatment. GLP-1 has several extra-pancreatic properties which include effects on kidney function. Although renal GLP-1 receptors have been identified, their exact localization and physiological role are incompletely understood. GLP-1 increases natriuresis through inhibition of the sodium-hydrogen ion exchanger isoform 3 in the proximal tubule. This may in part explain why GLP-1 receptor agonists have antihypertensive effects. Glomerular filtration rate is regulated by GLP-1, but the mechanisms are complex and may depend on e.g. glycaemic conditions. Atrial natriuretic peptide or the renin-angiotensin system may be involved in the signalling of GLP-1-mediated renal actions. Several studies in rodents have shown that GLP-1 therapy is renoprotective beyond metabolic improvements in models of diabetic nephropathy and acute kidney injury. Inhibition of renal inflammation and oxidative stress probably mediate this protection. Clinical studies supporting GLP-1-mediated renal protection exist, but they are few and with limitations. However, acute and chronic kidney diseases are major global health concerns and measures improving renal outcome are highly needed. Therefore, the renoprotective potential of GLP-1 therapy need to be thoroughly investigated in humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANG2:
-
angiotensin II
- AKI:
-
acute kidney injury
- ANP:
-
atrial natriuretic peptide
- ARB:
-
angiotensin II receptor blocker
- CrCl:
-
creatinine clearance
- DN:
-
diabetic nephropathy
- DPP-4:
-
dipeptidyl peptidase IV
- EMA:
-
European Medicine Agency
- ESRD:
-
end-stage renal disease
- GLP-1:
-
glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLP-1R:
-
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- GFR:
-
glomerular filtration rate
- mRNA:
-
messenger ribonucleic acid
- NHE3:
-
Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3
- PKA:
-
protein kinase A
- RAS:
-
renin-angiotensin system
- RBF:
-
renal blood flow
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SGLT2:
-
sodium-glucose linked transporter 2
- STZ:
-
streptozotocin
- T2DM:
-
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TGF:
-
tubuloglomerular feedback
References
Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(4):1409–39.
Vilsboll T, Agerso H, Krarup T, Holst JJ. Similar elimination rates of glucagon-like peptide-1 in obese type 2 diabetic patients and healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(1):220–4. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-021053.
Meier JJ, Nauck MA, Kranz D, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Gaeckler D, et al. Secretion, degradation, and elimination of glucagon-like peptide 1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with chronic renal insufficiency and healthy control subjects. Diabetes. 2004;53(3):654–62.
Bullock BP, Heller RS, Habener JF. Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology. 1996;137(7):2968–78. doi:10.1210/en.137.7.2968.
Körner M, Stöckli M, Waser B, Reubi JC. GLP-1 Receptor Expression in Human Tumors and Human Normal Tissues: Potential for In Vivo Targeting. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(5):736–43. doi:10.2967/jnumed.106.038679.
Vilsboll T, Christensen M, Junker AE, Knop FK, Gluud LL. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. Bmj. 2012;344:d7771.
Wang B, Zhong J, Lin H, Zhao Z, Yan Z, He H, et al. Blood pressure-lowering effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists exenatide and liraglutide: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(8):737–49. doi:10.1111/dom.12085.
Nauck MA, Niedereichholz U, Ettler R, Holst JJ, Orskov C, Ritzel R, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibition of gastric emptying outweighs its insulinotropic effects in healthy humans. The American journal of physiology. 1997;273(5 Pt 1):E981–8.
Mendis B, Simpson E, MacDonald I, Mansell P. Investigation of the haemodynamic effects of exenatide in healthy male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74(3):437–44. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04214.x.
Ussher JR, Drucker DJ. Cardiovascular biology of the incretin system. Endocr Rev. 2012;33(2):187–215. doi:10.1210/er.2011-1052.
Holst JJ, Burcelin R, Nathanson E. Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1: theoretical and practical applications. Current medical research and opinion. 2011;27(3):547–58. doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.549466.
Gutzwiller JP, Tschopp S, Bock A, Zehnder CE, Huber AR, Kreyenbuehl M et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces natriuresis in healthy subjects and in insulin-resistant obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89 (6):3055–61. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-03140389/6/3055 [pii]
Skov J, Dejgaard A, Frokiaer J, Holst JJ, Jonassen T, Rittig S, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1): Effect on Kidney Hemodynamics and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Healthy Men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(4):E664–71. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-3855.
Ritz E, Rychlik I, Locatelli F, Halimi S. End-stage renal failure in type 2 diabetes: A medical catastrophe of worldwide dimensions. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34(5):795–808. doi:10.1016/s0272-6386(99)70035-1.
Moreno C, Mistry M, Roman RJ. Renal effects of glucagon-like peptide in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;434(3):163–7.
Crajoinas RO, Oricchio FT, Pessoa TD, Pacheco BPM, Lessa LMA, Malnic G, et al. Mechanisms mediating the diuretic and natriuretic actions of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2011;301(2):F355–F63. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00729.2010.
Fujita H, Morii T, Fujishima H, Sato T, Shimizu T, Hosoba M et al. The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential. Kidney Int. 2013. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.427.
Carraro-Lacroix LR, Malnic G, Girardi ACC. Regulation of Na+/H + exchanger NHE3 by glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist exendin-4 in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2009;297(6):F1647–F55. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00082.2009.
Kodera R, Shikata K, Kataoka HU, Takatsuka T, Miyamoto S, Sasaki M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist ameliorates renal injury through its anti-inflammatory action without lowering blood glucose level in a rat model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011;54(4):965–78. doi:10.1007/s00125-010-2028-x.
Schlatter P, Beglinger C, Drewe J, Gutmann H. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression in primary porcine proximal tubular cells. Regul Pept. 2007;141(1–3):120–8. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2006.12.016.
Pezeshki A, Muench GP, Chelikani PK. Short communication: expression of peptide YY, proglucagon, neuropeptide Y receptor Y2, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor in bovine peripheral tissues. J Dairy Sci. 2012;95(9):5089–94. doi:10.3168/jds.2011-5311.
Pyke C, Knudsen LB. The Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor—or Not? Endocrinology. 2013;154(1):4–8. doi:10.1210/en.2012-2124.
Panjwani N, Mulvihill EE, Longuet C, Yusta B, Campbell JE, Brown TJ, et al. GLP-1 receptor activation indirectly reduces hepatic lipid accumulation but does not attenuate development of atherosclerosis in diabetic male ApoE (−/−) mice. Endocrinology. 2013;154(1):127–39. doi:10.1210/en.2012-1937.
Yu M, Moreno C, Hoagland KM, Dahly A, Ditter K, Mistry M, et al. Antihypertensive effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Hypertens. 2003;21(6):1125–35.
Thomson SC, Kashkouli A, Singh P. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation increases GFR and suppresses proximal reabsorption in the rat. Am J Physiol-Renal Physiol. 2013;304(2):F137–F44. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00064.2012.
Hirata K, Kume S. Araki S-i, Sakaguchi M, Chin-Kanasaki M, Isshiki K et al. Exendin-4 has an anti-hypertensive effect in salt-sensitive mice model. Biochemical and Biophysical Research. Communications. 2009;380(1):44–9.
Liu Q, Adams L, Broyde A, Fernandez R, Baron A, Parkes D. The exenatide analogue AC3174 attenuates hypertension, insulin resistance, and renal dysfunction in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010;9(1):32.
Rieg T, Gerasimova M, Murray F, Masuda T, Tang T, Rose M, et al. Natriuretic effect by exendin-4, but not the DPP-4 inhibitor alogliptin, is mediated via the GLP-1 receptor and preserved in obese type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;303(7):F963–71. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00259.2012.
Larsen PJ, Fledelius C, Knudsen LB, Tang-Christensen M. Systemic administration of the long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 induces lasting and reversible weight loss in both normal and obese rats. Diabetes. 2001;50(11):2530–9.
Kim M, Platt MJ, Shibasaki T, Quaggin SE, Backx PH, Seino S, et al. GLP-1 receptor activation and Epac2 link atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to control of blood pressure. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):567–75. doi:10.1038/nm.3128.
Girardi AC, Fukuda LE, Rossoni LV, Malnic G, Reboucas NA. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition downregulates Na + − H + exchanger NHE3 in rat renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294(2):F414–22. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00174.2007.
Gutzwiller JP, Hruz P, Huber AR, Hamel C, Zehnder C, Drewe J, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 is involved in sodium and water homeostasis in humans. Digestion. 2006;73(2–3):142–50. doi:10.1159/000094334.
Pacheco BP, Crajoinas RO, Couto GK, Davel AP, Lessa LM, Rossoni LV, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition attenuates blood pressure rising in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2011;29(3):520–8. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328341939d.
Thomsen K. Lithium Clearance: A New Method for Determining Proximal and Distal Tubular Reabsorption of Sodium and Water. Nephron. 1984;37(4):217–23.
Girardi AC, Di Sole F. Deciphering the mechanisms of the Na+/H + exchanger-3 regulation in organ dysfunction. American journal of physiology Cell physiology. 2012;302(11):C1569–87. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00017.2012.
Girardi AC, Knauf F, Demuth HU, Aronson PS. Role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in regulating activity of Na+/H + exchanger isoform NHE3 in proximal tubule cells. American journal of physiology Cell physiology. 2004;287(5):C1238–45. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00186.2004.
Girardi AC, Degray BC, Nagy T, Biemesderfer D, Aronson PS. Association of Na (+)-H (+) exchanger isoform NHE3 and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the renal proximal tubule. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(49):46671–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106897200.
Park CW, Kim HW, Ko SH, Lim JH, Ryu GR, Chung HW, et al. Long-Term Treatment of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analog Exendin-4 Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy through Improving Metabolic Anomalies in db/dB Mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(4):1227–38. doi:10.1681/asn.2006070778.
Persson P, Hansell P, Palm F. Tubular reabsorption and diabetes-induced glomerular hyperfiltration. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010;200(1):3–10. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02147.x.
Yu M, Moreno C, Hoagland KM, Dahly A, Ditter K, Mistry M, et al. Antihypertensive effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Hypertens. 2003;21(6):1125–35. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000059046.65882.49.
Varanasi A, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa S, Arora A, Lohano T, Vora MR, et al. Durability of effects of exenatide treatment on glycemic control, body weight, systolic blood pressure, C-reactive protein, and triglyceride concentrations. Endocrine practice : official journal of the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. 2011;17(2):192–200. doi:10.4158/ep10199.or.
Liu WJ, Xie SH, Liu YN, Kim W, Jin HY, Park SK, et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor Attenuates Kidney Injury in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;340(2):248–55. doi:10.1124/jpet.111.186866.
Skov J, Holst JJ, Goetze JP, Frokiaer J, Christiansen JS. Glucagon-like peptide-1: effect on pro-atrial natriuretic peptide in healthy males. Endocrine connections. 2013. doi:10.1530/ec-13-0087.
Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Ojima A, Nishino Y, Nakashima S, Maeda S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced mesangial cell damage via protein kinase A. Microvasc Res. 2012;84(3):395–8. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2012.06.008.
Mima A, Hiraoka-Yamomoto J, Li Q, Kitada M, Li C, Geraldes P, et al. Protective effects of GLP-1 on glomerular endothelium and its inhibition by PKCbeta activation in diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2967–79. doi:10.2337/db11-1824.
van der Zijl NJ, Moors CC, Goossens GH, Hermans MM, Blaak EE, Diamant M. Valsartan improves {beta}-cell function and insulin sensitivity in subjects with impaired glucose metabolism: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(4):845–51. doi:10.2337/dc10-2224.
Wang HW, Mizuta M, Saitoh Y, Noma K, Ueno H, Nakazato M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and candesartan additively improve glucolipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells. Metabolism. 2011;60(8):1081–9. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2010.11.004.
Lu HL, Wang ZY, Huang X, Han YF, Wu YS, Guo X, et al. Excitatory regulation of angiotensin II on gastric motility and its mechanism in guinea pig. Regul Pept. 2011;167(2–3):170–6. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2011.01.004.
Fogari R, Derosa G, Zoppi A, Rinaldi A, Lazzari P, Fogari E, et al. Comparison of the effects of valsartan and felodipine on plasma leptin and insulin sensitivity in hypertensive obese patients. Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension. 2005;28(3):209–14. doi:10.1291/hypres.28.209.
Malm-Erjefalt M, Bjornsdottir I, Vanggaard J, Helleberg H, Larsen U, Oosterhuis B, et al. Metabolism and excretion of the once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide in healthy male subjects and its in vitro degradation by dipeptidyl peptidase IV and neutral endopeptidase. Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals. 2010;38(11):1944–53. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.034066.
Simonsen L, Holst JJ, Deacon CF. Exendin-4, but not glucagon-like peptide-1, is cleared exclusively by glomerular filtration in anaesthetised pigs. Diabetologia. 2006;49(4):706–12. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-0128-9.
Vejakama P, Thakkinstian A, Lertrattananon D, Ingsathit A, Ngarmukos C, Attia J. Reno-protective effects of renin-angiotensin system blockade in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2012;55(3):566–78.
Rossing P, de Zeeuw D. Need for better diabetes treatment for improved renal outcome. Kidney Int Suppl. 2011;120:S28–32. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.513.
Ojima A, Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Maeda S, Nishino Y, Takeuchi M et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Inhibits Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Generation in the Kidney of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats by Blocking Advanced Glycation End Product–Induced Protein Arginine Methyltranferase-1 Expression. The American journal of pathology. 2013;182 (1):132–41. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.016.
Hendarto H, Inoguchi T, Maeda Y, Ikeda N, Zheng J, Takei R, et al. GLP-1 analog liraglutide protects against oxidative stress and albuminuria in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via protein kinase A-mediated inhibition of renal NAD (P)H oxidases. Metabolism. 2012;61(10):1422–34. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2012.03.002.
Alter ML, Ott IM, von Websky K, Tsuprykov O, Sharkovska Y, Krause-Relle K, et al. DPP-4 inhibition on top of angiotensin receptor blockade offers a new therapeutic approach for diabetic nephropathy. Kidney & blood pressure research. 2012;36(1):119–30. doi:10.1159/000341487.
Kodera R, Shikata K, Takatsuka T, Oda K, Miyamoto S, Kajitani N et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor ameliorates early renal injury through its anti-inflammatory action in a rat model of type 1 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.049.
Shiraki A, Oyama J, Komoda H, Asaka M, Komatsu A, Sakuma M, et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-alpha-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2012;221(2):375–82. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.12.039.
Liu L, Liu J, Wong WT, Tian XY, Lau CW, Wang YX, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor sitagliptin protects endothelial function in hypertension through a glucagon-like peptide 1-dependent mechanism. Hypertension. 2012;60(3):833–41. doi:10.1161/hypertensionaha.112.195115.
Ishibashi Y, Nishino Y, Matsui T, Takeuchi M, Yamagishi S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 suppresses advanced glycation end product-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in mesangial cells by reducing advanced glycation end product receptor level. Metabolism. 2011;60(9):1271–7. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2011.01.010.
Li W, Cui M, Wei Y, Kong X, Tang L, Xu D. Inhibition of the expression of TGF-beta1 and CTGF in human mesangial cells by exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology. 2012;30(3):749–57. doi:10.1159/000341454.
Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, et al. Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1317–26. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1307684.
Zhang H, Zhang X, Hu C, Lu W. Exenatide reduces urinary transforming growth factor-beta1 and type IV collagen excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Kidney & blood pressure research. 2012;35(6):483–8. doi:10.1159/000337929.
Fujita H, Taniai H, Murayama H, Ohshiro H, Hayashi H, Sato S et al. DPP-4 inhibition with alogliptin on top of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade ameliorates albuminuria via up-regulation of SDF-1alpha in type 2 diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. Endocrine journal. 2013.
Imamura S, Hirai K, Hirai A. The glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist, liraglutide, attenuates the progression of overt diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2013;231(1):57–61.
Abd El Motteleb DM, Elshazly SM. Renoprotective effect of sitagliptin against hypertensive nephropathy induced by chronic administration of l-NAME in rats: Role of GLP-1 and GLP-1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;720(1–3):158–65. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.033.
Joo KW, Kim S, Ahn SY, Chin HJ, Chae DW, Lee J, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor attenuates kidney injury in rat remnant kidney. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14:98. doi:10.1186/1471-2369-14-98.
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012;380(9843):756–66. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61454-2.
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer J, Endre Z, Kellum JA, et al. Acute kidney injury: an increasing global concern. Lancet. 2013;382(9887):170–9. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60647-9.
Yang H, Li H, Wang Z, Shi Y, Jiang G, Zeng F. Exendin-4 ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. The Journal of surgical research. 2013;185(2):825–32. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.042.
Glorie LL, Verhulst A, Matheeussen V, Baerts L, Magielse J, Hermans N, et al. DPP4 inhibition improves functional outcome after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;303(5):F681–8. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00075.2012.
Vaghasiya J, Sheth N, Bhalodia Y, Manek R. Sitagliptin protects renal ischemia reperfusion induced renal damage in diabetes. Regul Pept. 2011;166(1–3):48–54. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2010.08.007.
Chen YT, Tsai TH, Yang CC, Sun CK, Chang LT, Chen HH, et al. Exendin-4 and sitagliptin protect kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction. J Transl Med. 2013;11(1):270. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-11-270.
Katagiri D, Hamasaki Y, Doi K, Okamoto K, Negishi K, Nangaku M et al. Protection of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 in Cisplatin-Induced Renal Injury Elucidates Gut-Kidney Connection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. doi:10.1681/asn.2013020134.
Linnebjerg H, Kothare PA, Park S, Mace K, Reddy S, Mitchell M, et al. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of exenatide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;64(3):317–27. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02890.x.
Davidson JA, Brett J, Falahati A, Scott D. Mild renal impairment and the efficacy and safety of liraglutide. Endocrine practice : official journal of the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. 2011;17(3):345–55. doi:10.4158/ep10215.ra.
Jacobsen LV, Hindsberger C, Robson R, Zdravkovic M. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;68(6):898–905. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03536.x.
Idorn T, Knop FK, Jorgensen M, Jensen T, Resuli M, Hansen PM et al. Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end-stage renal disease: protocol for an investigator-initiated prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, parallel intervention study. BMJ Open. 2013;3 (4). doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002764.
Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetics of dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(8):648–58. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01212.x.
Weise WJ, Sivanandy MS, Block CA, Comi RJ. Exenatide-associated ischemic renal failure. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(2):e22–3. doi:10.2337/dc08-1309.
Narayana SK, Talab SK, Elrishi MA. Liraglutide-induced acute kidney injury. Practical Diabetes. 2012;29(9):380–2. doi:10.1002/pdi.1727.
Filippatos TD, Elisaf MS. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on renal function. World journal of diabetes. 2013;4(5):190–201. doi:10.4239/wjd.v4.i5.190.
Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2011;32(4):515–31. doi:10.1210/er.2010-0029.
Thomson SC, Rieg T, Miracle C, Mansoury H, Whaley J, Vallon V, et al. Acute and chronic effects of SGLT2 blockade on glomerular and tubular function in the early diabetic rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012;302(1):R75–83. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00357.2011.
Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Maione M, Lai V, Lee A et al. The Renal Hemodynamic Effect of SGLT2 Inhibition in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Circulation. 2013. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.113.005081.
Lonborg J, Vejlstrup N, Kelbaek H, Botker HE, Kim WY, Mathiasen AB, et al. Exenatide reduces reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(12):1491–9. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr309.
Conflict of interest
J.S. has a PhD fellowship in a joint collaboration between Aarhus University Hospital and Novo Nordisk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skov, J. Effects of GLP-1 in the Kidney. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15, 197–207 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-014-9287-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-014-9287-7