Abstract
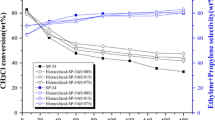
SAPO-34 molecular sieves were synthesized in the presence of soluble starch, sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as the additives under hydrothermal conditions, and the differences stemmed from the additives among all obtained SAPO-34 samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, BET, NH3-TPD and TG. Compared with the conventional SAPO-34 sample, the SAPO-34 samples modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide showed less crystalline order, enlarged mesopore volume and external surface area and a reduction in total acidity amounts. Meanwhile, the SAPO-34 modified by soluble starch exhibited more total acidity amounts than the conventional SAPO-34 samples. The SAPO-34 samples modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide showed better catalytic stability and less carbon deposition than the conventional SAPO-34 catalyst in the conversion of chloromethane to olefins due to the reduction in total acid sites and the increasing mesopore volume. The overall results of this study demonstrate that it is an effective way to modify the SAPO-34 molecular sieve with sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as the additives for improving the SAPO-34 catalyst stability in the transformation of chloromethane to olefins.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Corma A (1995) Inorganic solid acids and their use in acid-catalyzed hydrocarbon reactions. Chem Rev 95:559–614
Corma A (1997) From microporous to mesoporous molecular sieve materials and their use in catalysis. Chem Rev 97:2373–2420
Donk SV, Janssen AH, Bitter JH, Jong KPD (2003) Generation, characterization, and impact of mesopores in zeolite catalysts. Catal Rev 45:297–319
Yu J, Xu R (2010) Rational approaches toward the design and synthesis of zeolitic inorganic open-framework materials. Acc Chem Res 43:1195–1204
Wang Z, Yu J, Xu R (2012) Needs and trends in rational synthesis of zeolitic materials. Chem Soc Rev 41:1729–1741
Chen J, Li J, Wei Y, Yuan C, Li B, Xu S, Zhou Y, Wang J, Zhang M, Liu Z (2013) Spatial confinement effects of cage-type SAPO molecular sieves on product distribution and coke formation in methanol-to-olefin reaction. Catal Commun 46:36–40
Izadbakhsh A, Farhadi F, Khorasheh F, Sahebdelfar S, Asadi M, Feng Y (2009) Effect of SAPO-34′s composition on its physico-chemical properties and deactivation in MTO process. Appl Catal A 364:48–56
Nishiyama N, Kawaguchi M, Hirota Y, Vu DV, Egashira Y, Ueyama K (2009) Size control of SAPO-34 crystals and their catalyst lifetime in the methanol-to-olefin reaction. Appl Catal A 362:193–199
Venna SR, Carreon MA (2008) Synthesis of SAPO-34 crystals in the presence of crystal growth inhibitors. J Phys Chem Lett 112:16261–16265
Carreon MA, Li S, Falconer JL, Noble RD (2008) Alumina-supported SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. J Am Chem Soc 130:5412–5413
Wang D, Zhang L, Kamasamudram K, Epling WS (2013) In situ-DRIFTS study of selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 over Cu-exchanged SAPO-34. ACS Catal 3:871–881
Janchen J, Ackermann D, Weiler E, Stach H, Broesicke W (2005) Calorimetric investigation on zeolites, AlPO4′s and CaCl2 impregnated attapulgite for thermochemical storage of heat. Thermochim Acta 434:37–41
Lok BM, Messina CA, Patton RL, Gajek RT, Cannan TR, Flanigen EM (1984) Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: another new class of microporous crystalline inorganic solids. J Am Chem Soc 106:6092–6093
Prakash AM, Unnikrirhnan S (1994) Synthesis of SAPO-34: high silicon incorporation in the presence of morpholine as template. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 90:2291–2296
Tan J, Liu Z, Bao X, Liu X, Han X, He C, Zhai R (2002) Crystallization and Si incorporation mechanisms of SAPO-34. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 53:97–108
Liu G, Tian P, Liu Z (2012) Synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieves templated with diethylamine and their properties compared with other templates. Chin J Catal 33:174–182
Álvaro-Muñoz T, Márquez-Álvarez C, Sastre E (2014) Aluminium chloride: a new aluminium source to prepare SAPO-34 catalysts with enhanced stability in the MTO process. Appl Catal A 472:72–79
Liu G, Tian P, Li J, Zhang D, Zhou F, Liu Z (2008) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of SAPO-34 synthesized using diethylamine as a template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 111:143–149
Haw JF, Song W, Marcus DM, Nicholas JB (2003) The mechanism of methanol to hydrocarbon catalysis. Acc Chem Res 36:317–326
Kang M, Um MH, Park JY (1999) Synthesis and catalytic performance on methanol conversion of NiAPSO-34 crystals I : effect of preparation factors on the gel formation. J Mol Catal A-Chem 150:195–203
Kang M (1999) Synthesis and catalytic performance on methanol conversion of NiAPSO-34 crystals II : catalytic performance under various reaction conditions. J Mol Catal A-Chem 150:205–212
Kang M (2000) Methanol conversion on metal-incorporated SAPO-34 s MeAPSO-34s. J Mol Catal A-Chem 160:437–444
Wei Y, He Y, Zhang D, Xu L, Meng S, Liu Z, Su BL (2005) Study of Mn incorporation into SAPO framework: synthesis, characterization and catalysis in chloromethane conversion to light olefins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 90:188–197
Wei Y, Zhang D, Xu L, Chang F, He Y, Meng S, Su BL, Liu Z (2008) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of metal-incorporated SAPO-34 for chloromethane transformation to light olefins. Catal Today 131:262–269
Zhang D, Wei Y, Xu L, Chang F, Liu Z, Meng S, Su BL, Liu Z (2008) MgAPSO-34 molecular sieves with various Mg stoichiometries: synthesis, characterization and catalytic behavior in the direct transformation of chloromethane into light olefins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 116:684–692
Tosheva L, Valtchev VP (2005) Nanozeolites: synthesis, crystallization mechanism, and applications. Chem Mater 17:2494–2513
Heyden HV, Mintova S, Bein T (2008) Nanosized SAPO-34 synthesized from colloidal solutions. Chem Mater 20:2956–2963
Sun Q, Wang N, Xi D, Yang M, Yu J (2014) Organosilane surfactant-directed synthesis of hierarchical porous SAPO-34 catalysts with excellent MTO performance. Chem Commun 50:6502–6505
Yang G, Wei Y, Xu S, Chen J, Li J, Liu Z, Yu J, Xu R (2013) Nanosize-enhanced lifetime of SAPO-34 catalysts in methanol-to-olefin reactions. J Phys Chem C 117:8214–8222
Schmidt F, Paasch S, Brunner E, Kaskel S (2014) Carbon templated SAPO-34 with improved adsorption kinetics and catalytic performance in the MTO-reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 164:214–221
Yang H, Liu Z, Gao H, Xie Z (2010) Synthesis and catalytic performances of hierarchical SAPO-34 monolith. J Mater Chem 20:3227–3231
Yang ST, Kim JY, Chae HJ, Kim M, Jeong SY, Ahn WS (2012) Microwave synthesis of mesoporous SAPO-34 with a hierarchical pore structure. Mater Res Bull 47:3888–3892
Singh AK, Yadav R, Sakthivel A (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic application of mesoporous SAPO-34 (MESO-SAPO-34) molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 181:166–174
Mei C, Wen P, Liu Z, Liu H, Wang Y, Yang W, Xie Z, Hua W, Gao Z (2008) Selective production of propylene from methanol: mesoporosity development in high silica HZSM-5. J Catal 258:243–249
Gu F, Wei F, Yang J, Lin N, Lin W, Wang Y, Zhu J (2006) New strategy to synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous zeolites. Chem Mater 22:2442–2450
Zhang D, Wei Y, Xu L, Du A, Chang F, Su BL, Liu Z (2006) Chloromethane conversion to higher hydrocarbons over zeolites and SAPOs. Catal Lett 109:97–101
Olah GA, Gupta B, Farina M, Felberg JD, Wai MP, Husain A, Karpeles R, Lammertsma K, Melhotra AK, Trivedi NJ (1985) Selective monohalogenation of methane over supported acid or platinum metal catalysts and hydrolysis of methyl halides over y-alumina-supported metal oxide/hydroxide catalysts. A feasible path for the oxidative conversion of methane into methyl alcohol/dimethyl ether. J Am Chem Soc 107:7097
Taylor CE, Noceti RP (1988) Direct conversion of methane to liquid hydrocarbons through chlorocarbon intermediates. Stud Surf Sci Catal 36:483–489
Wei Y, Zhang D, Liu Z, Su BL (2006) Highly efficient catalytic conversion of chloromethane to light olefins over HSAPO-34 as studied by catalytic testing and in situ FTIR. J Catal 238:46–57
Wei Y, Zhang D, Chang F, Xia Q, Su BL, Liu Z (2009) Ultra-short contact time conversion of chloromethane to olefins over pre-coked SAPO-34: direct insight into the primary conversion with coke deposition. Chem Commun 40:5999–6001
Svelle S, Aravinthan S, Bjørgen M, Lillerud KP, Kolboe S, Dahl IM, Olsbye U (2006) The methyl halide to hydrocarbon reaction over H-SAPO-34. J Catal 241:243–254
Olsbye U, Saure OV, Muddada NB, Bordiga S, Lamberti C, Nilsen MH, Lillerud KP, Svelle S (2011) Methane conversion to light olefins-how does the methyl halide route differ from the methanol to olefins (MTO) route? Catal Today 171:211–220
Zhang A, Sun S, Komon ZJA, Osterwalder N, Gadewar S, Stoimenov P, Auerbach DJ, Stucky GD, McFarland EW (2011) Improved light olefin yield from methyl bromide coupling over modified SAPO-34 molecular sieves. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:2550–2555
Wang P, Lv A, Hu J, Xu J, Lu G (2008) The synthesis of SAPO-34 with mixed template and its catalytic performance for methanol to olefins reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 152:178–184
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Pure Appl Chem 57:603
Dahl IM, Kolboe S (1993) On the reaction mechanism for propene formation in the MTO reaction over SAPO-34. Catal Lett 20:329–336
Dahl IM, Kolboe S (1994) On the reaction mechanism for hydrocarbon formation from Methanol over SAPO-34: I. isotopic labeling studies of the co-reaction of ethene and methanol. J Catal 149:458–464
Ilias S, Bhan A (2013) Mechanism of the catalytic conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons. ACS Catal 3:18–31
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank the analysis and test center of the State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering in East China University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Lt., Shen, Bx., Jiang, Z. et al. Synthesis of SAPO-34 with the presence of additives and their catalytic performance in the transformation of chloromethane to olefins. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 114, 697–710 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-014-0812-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-014-0812-1