Abstract
Purpose
To review data on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in individuals with childhood trauma, including psychological maltreatment, physical maltreatment, sexual abuse, and neglect.
Methods
The literature search was conducted with pre-defined keywords using the following electronic bibliographic databases: EMBASE, PubMed, MEDLINE, CINAHL, PsyINFO, PSYNDEX, and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Further databases were searched for relevant dissertations. Study selection and data extraction were completed by two independent reviewers.
Results
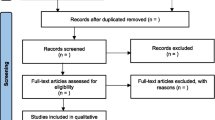
The literature search yielded 1568 entries. Nineteen articles met all inclusion criteria and were retained for further analysis. Findings quite consistently showed significant negative associations between child maltreatment and both self- and proxy-rated HRQoL. Effect sizes range from small to large. Number of types of maltreatment and HRQoL were found to be negatively related.
Conclusion
Data on HRQoL for maltreated children are still rare. Studies often investigate adult survivors of child maltreatment. Considering HRQoL in children and adolescents who suffered maltreatment would allow the planning of effective interventions and the evaluation of treatments to improve HRQoL of these children.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leeb, R. T., Paulozzi, L. J., Melanson, C., Simon, T. R., & Arias, I. (2008). Child Maltreatment surveillance: Uniform definitions for public health and recommended data elements, version 1.0. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
Runyan, D. K., Dunne, M. P., Zolotor, A. J., Madrid, B., Jain, D., Gerbaka, B., et al. (2009). The development and piloting of the ISPCAN Child Abuse Screening Tool—Parent version (ICAST-P). Child Abuse and Neglect, 33(11), 826–832.
Mohler-Kuo, M., Landolt, M. A., Maier, T., Meidert, U., Schonbucher, V., & Schnyder, U. (2014). Child sexual abuse revisited: A population-based cross-sectional study among swiss adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 54(3), 304–311.
Stoltenborgh, M., Bakermans- Kranenburg, M. J., Alink, L. R. A., & van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2014). The prevalence of child maltreatment across the globe: Review of a series of meta-analyses. Child Abuse Review, 24, 37–50.
Fang, X. M., Brown, D. S., Florence, C. S., & Mercy, J. A. (2012). The economic burden of child maltreatment in the United States and implications for prevention. Child Abuse and Neglect, 36(2), 156–165.
Corso, P. S., & Fertig, A. R. (2010). The economic impact of child maltreatment in the United States: Are the estimates credible? Child Abuse and Neglect, 34(5), 296–304.
De Bellis, M. D., & Keshavan, M. S. (2003). Sex differences in brain maturation in maltreatment-related pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 27(1), 103–117.
Gilbert, R., Widom, C. S., Browne, K., Fergusson, D., Webb, E., & Janson, S. (2009). Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet, 373(9657), 68–81.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention A. (2011). HRQOL concepts (Vol. 2014). Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Aaronson, N. K., Meyerowitz, B. E., Bard, M., Bloom, J. R., Fawzy, F. I., Feldstein, M., et al. (1991). Quality-of-life research in oncology—Past achievements and future priorities. Cancer, 67(3), 839–843.
Landolt, M. A., & Sennhauser, F. H. (2007). Gesundheitsbezogene Lebensqualität. In M. J. Lentze, J. Schaub, F. J. Schulte, & J. H. Spranger (Eds.), Pädiatrie—Grundlagen und Praxis (Vol. 3, pp. 125–128). Heidelberg: Springer.
O’Hagan, K. P. (1995). Emotional and psychological abuse: Problems of definition. Child Abuse and Neglect, 19(4), 449–461.
Durlak, J. A. (2009). How to select, calculate, and interpret effect sizes. Jounal of Pediatric Psychology, 34(9), 917–928.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Converting among effect sizes. In Introduction to Meta-Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Afifi, T. O., Enns, M. W., Cox, B. J., de Graaf, R., ten Have, M., & Sareen, J. (2007). Child abuse and health-related quality of life in adulthood. The Jounal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 195(10), 797–804.
Agorastos, A., Pittman, J. O., Angkaw, A. C., Nievergelt, C. M., Hansen, C. J., Aversa, L. H., et al. (2014). The cumulative effect of different childhood trauma types on self-reported symptoms of adult male depression and PTSD, substance abuse and health-related quality of life in a large active-duty military cohort. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 58, 46–54.
Bonomi, A. E., Cannon, E. A., Anderson, M. L., Rivara, F. R., & Thompson, R. S. (2008). Association between self-reported health and physical and/or sexual abuse experienced before age 18. Child Abuse and Neglect, 32(7), 693–701.
Chan, K. L. (2013). Victimization and poly-victimization among school-aged Chinese adolescents: Prevalence and associations with health. Preventive Medicine, 56(3–4), 207–210.
Draper, B., Pfaff, J. J., Pirkis, J., Snowdon, J., Lautenschlager, N. T., Wilson, I., et al. (2008). Long-term effects of childhood abuse on the quality of life and health of older people: Results from the depression and early prevention of suicide in general practice project. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 56(2), 262–271. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01537.x.
Gospodarevskaya, E. (2013). Post-traumatic stress disorder and quality of life in sexually abused Australian children. Journal of Child Sexual Abuse, 22(3), 277–296.
Jud, A., Landolt, M. A., Tatalias, A., Lach, L. M., & Lips, U. (2013). Health-related quality of life in the aftermath of child maltreatment: Follow-up study of a hospital sample. Quality of Life Research, 22(6), 1361–1369.
Nickel, M. K., Tritt, K., Mitterlehner, F. O., Leiberich, P., Nickel, C., Lahmann, C., et al. (2004). Sexual abuse in childhood and youth as psychopathologically relevant life occurrence: Cross-sectional survey. Croatian Medical Journal, 45(4), 483–489.
Scigliano, C. E. (2008). The effect of mental distress, history of childhood trauma, and spiritual wellness on health-related quality of life in a New Hampshire primary care setting. Dissertation, Spalding University, Louisville, Kentucky.
Walker, E. A., Gelfand, A., Katon, W. J., Koss, M. P., Von Korff, M., Bernstein, D., et al. (1999). Adult health status of women with histories of childhood abuse and neglect. American Journal of Medicine, 107(4), 332–339.
Zafar, M., Kashikar-Zuck, S. M., Slater, S. K., Allen, J. R., Barnett, K. A., Lecates, S. L., et al. (2012). Childhood abuse in pediatric patients with chronic daily headache. Clinical Pediatrics, 51(6), 590–593.
Zak, E. N. (2001). Coping Styles, Quality of Life, and Sexual Trauma in Women Veterans. Dissertation, University of North Texas, Denton, Texas.
Al-Fayez, G. A., Ohaeri, J. U., & Gado, O. M. (2012). Prevalence of physical, psychological, and sexual abuse among a nationwide sample of Arab high school students: Association with family characteristics, anxiety, depression, self-esteem, and quality of life. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 47(1), 53–66.
Corso, P. S., Edwards, V. J., Fang, X. M., & Mercy, J. A. (2008). Health-related quality of life among adults who experienced maltreatment during childhood. American Journal of Public Health, 98(6), 1094–1100.
Cuijpers, P., Smit, F., Unger, F., Stikkelbroek, Y., ten Have, M., & de Graaf, R. (2011). The disease burden of childhood adversities in adults: A population-based study. Child Abuse and Neglect, 35(11), 937–945.
Dickinson, L. M., deGruy, F. V., Dickinson, W. P., & Candib, L. M. (1999). Health-related quality of life and symptom profiles of female survivors of sexual abuse. Archives of Family Medicine, 8(1), 35–43.
Evren, C., Sar, V., Dalbudak, E., Cetin, R., Durkaya, M., Evren, B., et al. (2011). Lifetime PTSD and quality of life among alcohol-dependent men: Impact of childhood emotional abuse and dissociation. Psychiatry Research, 186(1), 85–90.
Rikhye, K., Tyrka, A. R., Kelly, M. M., Gagne, G. G, Jr, Mello, A. F., Mello, M. F., et al. (2008). Interplay between childhood maltreatment, parental bonding, and gender effects: Impact on quality of life. Child Abuse and Neglect, 32(1), 19–34.
Simon, N. M., Herlands, N. N., Marks, E. H., Mancini, C., Letamendi, A., Li, Z. H., et al. (2009). Childhood maltreatment linked to greater symptom severity and poorer quality of life and function in social anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety, 26(11), 1027–1032.
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., & Altman, D. G. (2001). Systematic reviews in health care: Meta-analysis in context (2nd ed.). London: BMJ Books.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. E. (2011). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 The Cochrane Collaboration.
Anderson, J. S. C., Sullivan, F., & Usherwood, T. P. (1990). The Medical Outcomes Study Instrument (MOSI)—Use of a new health status measure in Britain. Family Practice, 7(3), 205–218.
Ware, J. E, Jr, Kosinski, M., & Keller, S. D. (1996). A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: Construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Medical Care, 34(3), 220–233.
Hawthorne, G., Richardson, J., & Osborne, R. (1999). The Assessment of Quality of Life (AQoL) instrument: A psychometric measure of health-related quality of life. Quality of Life Research, 8(3), 209–224.
Fekkes, M., Theunissen, N. C., Brugman, E., Veen, S., Verrips, E. G., Koopman, H. M., et al. (2000). Development and psychometric evaluation of the TAPQOL: A health-related quality of life instrument for 1–5-year-old children. Quality of Life Research, 9(8), 961–972.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Auquier, P., Erhart, M., Gosch, A., Rajmil, L., Bruil, J., et al. (2007). The KIDSCREEN-27 quality of life measure for children and adolescents: Psychometric results from a cross-cultural survey in 13 European countries. Quality of Life Research, 16(8), 1347–1356.
Varni, J. W., Burwinkle, T. M., Seid, M., & Skarr, D. (2003). The PedsQL (TM) 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: Feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambulatory Pediatrics, 3(6), 329–341.
Lehman, A. F. (1995). Measuring quality of life in a reformed health system. Health Affairs, 14(3), 90–101.
Hays, R. D., Cunningham, W. E., Sherbourne, C. D., Wilson, I. B., Wu, A. W., Cleary, P. D., et al. (2000). Health-related quality of life in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection in the United States: Results from the HIV Cost and Services Utilization Study. The American Journal of Medicine, 108(9), 714–722.
Teicher, M. H., Andersen, S. L., Polcari, A., Anderson, C. M., Navalta, C. P., & Kim, D. M. (2003). The neurobiological consequences of early stress and childhood maltreatment. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 27(1), 33–44.
Filipas, H. H., & Ullman, S. E. (2006). Child sexual abuse, coping responses, self-blame, posttraumatic stress disorder, and adult sexual revictimization. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 21(5), 652–672.
Twardosz, S., & Lutzker, J. R. (2010). Child maltreatment and the developing brain: A review of neuroscience perspectives. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 15(1), 59–68.
Cicchetti, D. (2002). The impact of social experience on neurobiological systems: Illustration from a constructivist view of child maltreatment. Cognitive Development, 17(3), 1407–1428.
Mehta, M. A., Golembo, N. I., Nosarti, C., Colvert, E., Mota, A., Williams, S. C., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2009). Amygdala, hippocampal and corpus callosum size following severe early institutional deprivation: The English and Romanian Adoptees study pilot. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(8), 943–951.
Anderson, C. M., Teicher, M. H., Polcari, A., & Renshaw, P. F. (2002). Abnormal T2 relaxation time in the cerebellar vermis of adults sexually abused in childhood: Potential role of the vermis in stress-enhanced risk for drug abuse. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 27(1), 231–244.
De Bellis, M. D., Keshavan, M. S., Clark, D. B., Casey, B. J., Giedd, J. N., Boring, A. M., & Ryan, N. D. (1999). Developmental traumatology part II: Brain development. Biological Psychiatry, 45(10), 1271–1284.
Teicher, M. H., Dumont, N. L., Ito, Y., Vaituzis, C., Giedd, J. N., & Andersen, S. L. (2004). Childhood neglect is associated with reduced corpus callosum area. Biological Psychiatry, 56(2), 80–85.
Belsky, J., & de Haan, M. (2011). Annual Research Review: Parenting and children’s brain development: The end of the beginning. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(4), 409–428.
Wheeler, J. R., & Berliner, L. (1988). Treating the effects of sexual abuse on children. In G. E. Wyatt, & G. J. Powell (Eds.), Lasting effects of child sexual abuse. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Freeman, K. A., & Morris, T. L. (2001). A review of conceptual models explaining the effects of child sexual abuse. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 6(4), 357–373.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Reprint—Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Physical Therapy, 89(9), 873–880.
Trickett, P. K., Carlson, V., Aber, J. L., & Cicchetti, D. (1991). Relationship of socioeconomic-status to the etiology and developmental sequelae of physical child-abuse. Developmental Psychology, 27(1), 148–158.
Friedman, R. (1976). Child abuse: A review of the psycho-social research. In H. H. Company (Ed.), Four perspectives on the status of child abuse and neglect research. National Center on Child Abuse and Neglect: Washington, D.C.
Andersen, S. L., Tomada, A., Vincow, E. S., Valente, E., Polcari, A., & Teicher, M. H. (2008). Preliminary evidence for sensitive periods in the effect of childhood sexual abuse on regional brain development. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry & Clinical Neurosciences, 20(3), 292–301.
US Department of Health and Human Services, A. f. C. a. F., Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. (2012). Child Maltreatment 2012.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Perspectives Foundation, SwissLife, the Anna Mueller Grocholski Foundation the Olga Mayenfisch Foundation, and the Swiss Foundation for the Health of Children and Adolescents. We want to thank the following researchers who provided us with additional information about their published data (in alphabetical order): Agorastos Agorastos, Oswaldo Almeida, and Brian Draper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, S., Jud, A. & Landolt, M.A. Quality of life in maltreated children and adult survivors of child maltreatment: a systematic review. Qual Life Res 25, 237–255 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-1085-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-1085-5