Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of multidisciplinary treatment on obesity and health-related quality of life (HRQOL).
Methods
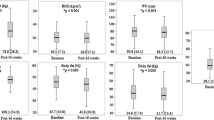
Obese children were randomized to a multidisciplinary lifestyle treatment, including medical, nutritional, physical, and psychological counseling during 3 months, (n = 40, BMI-SDS; 4.2 ± 0.7, age; 13.3 ± 2.0) or standard care, including an initial advice on nutrition and physical activity by the pediatrician (n = 39, BMI-SDS; 4.3 ± 0.7, age; 13.1 ± 1.9). At baseline, after 3 months of treatment and at 12 months follow-up, data were collected for BMI-SDS and a European validated questionnaire for assessing HRQOL (DISABKIDS).
Results
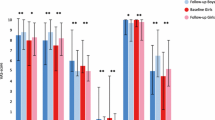
A significantly reduced BMI-SDS was found for the intervention group after 3 months treatment (4.0 ± 0.9 vs. 4.2 ± 0.7, P = 0.02) and at 12 months follow-up (3.8 ± 1.1 vs. 4.2 ± 0.7, P = 0.03). HRQOL in the intervention group was significantly improved at 12 months follow-up and unchanged in the obese control group. Agreement between child and parent report was moderate (67–85%), with parents reporting a lower HRQOL for their obese children than children themselves in both groups.
Conclusion
Multidisciplinary treatment is effective in reducing BMI-SDS and improving HRQOL after 12 months follow-up.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BMI-SDS:
-
Body mass index standard deviation score
- HRQOL:
-
Health-related quality of life
- ICC:
-
Inter-class correlation coefficient
- KINDL:
-
German questionnaire for measuring quality of life in children and adolescents
- PedsQOL:
-
Pediatric quality of life inventory
- PRISMA:
-
Pictorial representation of illness and self measure
- QOL:
-
Quality of life
References
Daniels, S. R., Arnett, D. K., Eckel, R. H., Gidding, S. S., Hayman, L. L., Kumanyika, S., et al. (2005). Overweight in children and adolescents: Pathophysiology, consequences, prevention, and treatment. Circulation, 111, 1999–2012.
Reilly, J. J., Methven, E., McDowell, Z. C., Alexander, D., Stewart, L., et al. (2003). Health consequences of obesity. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 88, 748–752.
Friedlander, S. L., Larkin, E. K., Rosen, C. L., Palermo, T. M., & Redline, S. (2003). Decreased quality of life associated with obesity in school-aged children. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 157, 1206–1211.
Robinson, S. (2006). Victimization of obese adolescents. Journal of School Nursing, 22, 201–206.
Schwimmer, J. B., Burwinkle, T. M., & Varni, J. W. (2003). Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. Journal of American Medical Association, 289, 1813–1819.
de Beer, M., Hofsteenge, G. H., Koot, H. M., Hirasing, R. A., Delemarre-van de Waal, H. A., & Gemke, R. J. (2007). Health-related-quality-of-life in obese adolescents is decreased and inversely related to BMI. Acta Paediatrica, 96, 710–714.
Hughes, A. R., Farewell, K., Harris, D., & Reilly, J. J. (2007). Quality of life in a clinical sample of obese children. International Journal of Obesity (London), 31, 39–44.
Kolotkin, R. L., Zeller, M., Modi, A. C., Samsa, G. P., Quinlan, N. P., Yanovski, J. A., et al. (2006). Assessing weight-related quality of life in adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring), 14, 448–457.
Pinhas-Hamiel, O., Singer, S., Pilpel, N., Fradkin, A., Modan, D., & Reichman, B. (2006). Health-related quality of life among children and adolescents: Associations with obesity. International Journal of Obesity (London), 30, 267–272.
Swallen, K. C., Reither, E. N., Haas, S. A., & Meier, A. M. (2005). Overweight, obesity, and health-related quality of life among adolescents: The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Pediatrics, 115, 340–347.
Williams, J., Wake, M., Hesketh, K., Maher, E., & Waters, E. (2005). Health-related quality of life of overweight and obese children. Journal of American Medical Association, 293, 70–76.
Zeller, M. H., & Modi, A. C. (2006). Predictors of health-related quality of life in obese youth. Obesity (Silver Spring), 14, 122–130.
Tsiros, M. D., Olds, T., Buckley, J. D., Grimshaw, P., Brennan, L., Walkley, J., et al. (2009). Health-related quality of life in obese children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity (London), 33, 387–400.
McGovern, L., Johnson, J. N., Paulo, R., Hettinger, A., Singhal, V., Kamath, C., et al. (2008). Clinical review: Treatment of pediatric obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 93, 4600–4605.
Oude, L. H., Baur, L., Jansen, H., Shrewsbury, V. A., O’Malley, C., Stolk, R. P., & Summerbell C. D. (2009). Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database System Review, 21(1), CD001872.
Knopfli, B. H., Radtke, T., Lehmann, M., Schatzle, B., Eisenblatter, J., Gachnang, A., et al. (2008). Effects of a multidisciplinary inpatient intervention on body composition, aerobic fitness, and quality of life in severely obese girls and boys. Journal of Adolescent Health, 42, 119–127.
Warschburger, P., Fromme, C., Petermann, F., Wojtalla, N., & Oepen, J. (2001). Conceptualisation and evaluation of a cognitive-behavioural training programme for children and adolescents with obesity. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 25(Suppl 1), S93–S95.
Fullerton, G., Tyler, C., Johnston, C. A., Vincent, J. P., Harris, G. E., & Foreyt, J. P. (2007). Quality of life in Mexican-American children following a weight management program. Obesity (Silver Spring), 15, 2553–2556.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Redegeld, M., & Bullinger, M. (2001). Quality of life after in-patient rehabilitation in children with obesity. International Jouranl of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 25(Suppl 1), S63–S65.
Vos, R. C., Wit, J. M., Pijl, H., Kruyff, C. C., & Houdijk, E. C. (2011). The effect of family-based multidisciplinary cognitive behavioral treatment in children with obesity: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 12, 110.
Cole, T. J., Bellizzi, M. C., Flegal, K. M., & Dietz, W. H. (2000). Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ, 320, 1240–1243.
Epstein, L. H., Wing, R. R., & Valoski, A. (1985). Childhood obesity. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 32, 363–379.
Cole, T. J., & Roede, M. J. (1999). Centiles of body mass index for Dutch children aged 0–20 years in 1980: A baseline to assess recent trends in obesity. Annals of Human Biology, 1999(26), 303–308.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Schmidt, S., Gosch, A., Erhart, M., Petersen, C., & Bullinger, M. (2007) Measuring subjective health in children and adolescents: results of the European KIDSCREEN/DISABKIDS Project. Psychosoc Med 4: Doc08.
Streiner, D. L., & Norman, G. R. (2008). Health measurements scales; a practical guide to their development and use (4th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Twisk, J. W. R. (2003). Applied longitudinal data analysis for epidemiology: A practical guide. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lazzer, S., Vermorel, M., Montaurier, C., Meyer, M., & Boirie, Y. (2005). Changes in adipocyte hormones and lipid oxidation associated with weight loss and regain in severely obese adolescents. International Journal of Obesity (London), 29, 1184–1191.
Kirk, S., Zeller, M., Claytor, R., Santangelo, M., Khoury, P. R., & Daniels, S. R. (2005). The relationship of health outcomes to improvement in BMI in children and adolescents. Obesity Research, 13, 876–882.
Weigel, C., Kokocinski, K., Lederer, P., Dotsch, J., Rascher, W., & Knerr, I. (2008). Childhood obesity: concept, feasibility, and interim results of a local group-based, long-term treatment program. J Nutr Educ Behav, 40, 369–373.
Reinehr, T., Kleber, M., & Toschke, A. M. (2009). Lifestyle intervention in obese children is associated with a decrease of the metabolic syndrome prevalence. Atherosclerosis, 207, 174–180.
Vos, R. C., Wit, J. M., Pijl, H., & Houdijk, E. C. (2011). Long-term effect of lifestyle intervention on adiposity, metabolic parameters, inflammation and physical fitness in obese children: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrition and Diabetes, 1, e9. doi:10.1038/nutd.2011.5.
Acknowledgments
The study was partly funded by an unrestricted educational grant by Pfizer and an unrestricted educational grant by a non-profit foundation (“de Stichting Vrienden van het JKZ”). We acknowledge and appreciated the helpful advice about the DISABKIDS questionnaire by Dr. H.M. Koopman. We also thank N. Kist for her help with implementing data for analysis. In addition, we thank all members of the multidisciplinary team for their time and patience in treating the children, and the participating children and their families.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vos, R.C., Huisman, S.D., Houdijk, E.C.A.M. et al. The effect of family-based multidisciplinary cognitive behavioral treatment on health-related quality of life in childhood obesity. Qual Life Res 21, 1587–1594 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-0079-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-0079-1