Abstract
The objective of this study is to examine the relationship between military factors and international tourism indicators in the panel of 18 tourists and non tourists-oriented countries, over the period of 1995–2014. The results are robust by using the several panels econometric techniques including Hausman test for model specifications, panel random effect model and panel generalized method of moments estimations. The results show that arms export and military expenditures both significantly correlated with the international tourism indicators, while per capita GDP increases international tourism expenditures and it decreases international tourism receipts. The gross fixed capital formation and health care expenditures increase international tourism indicators while the incidence of tuberculosis affected the international tourism receipts in the region. Energy intensity although supports the international tourism growth, however, it does not uphold the international tourism receipts. The results confirm the bidirectional causality between international tourism indicators and domestic investment (and healthcare expenditures), while there is a unidirectional causality running from international tourism expenditures to arms export, from tourism expenditures to military spending, and from tourism growth to per capita income. The tourism led growth hypothesis and tourism induced military expenditures calls for the desirable policy attention in the region.

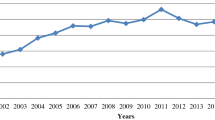
Source World Bank (2014)

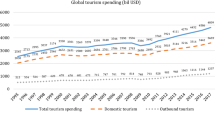
Source World Bank (2014). ‘D’ indicates first difference of the studied variables
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan Hye, Q.M., Ali Khan, R.E.: Tourism-led growth hypothesis: a case study of Pakistan. Asia Pacific J. Tour. Res. 18(4), 303–313 (2013)
Blake, A., Sinclair, M.T.: Tourism crisis management: US response to September 11. Ann. Tour. Res. 30(4), 813–832 (2003)
Botterill, D.: Dark tourism and crime. J. Tour. Hist. 7(3), 290–292 (2015)
Brida, J.G., Pereyra, J.S., Risso, W.A., Devesa, M.J.S., Aguirre, S.Z.: The tourism-led growth hypothesis: empirical evidence from Colombia. Tourismos: Int. Multidiscip. J. Tour. 4(2), 13–27 (2008)
Brown, C.B.: Tourism, crime and risk perception: an examination of broadcast media’s framing of negative Aruban sentiment in the Natalee Holloway case and its impact on tourism demand. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 16, 266–277 (2015)
Buultjens, J.W., Ratnayake, I., Gnanapala, W.A.C.: Post-conflict tourism development in Sri Lanka: implications for building resilience. Curr. Issues Tour. 19(4), 355–372 (2016)
Cárdenas-García, P.J., Pulido-Fernández, J.I.: Does the investment climate determine the transformation of tourism growth into economic development? Tour. Econ. 20(4), 669–694 (2014)
Chen, M.H., Lin, C.P., Chen, B.T.: Drivers of Taiwan’s tourism market cycle. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 32(3), 260–275 (2015)
Chin-Tsai, L., In-Fun, L., Ya-Ling, H.: Forecasting Thailand’s medical tourism demand and revenue from foreign patients. J. Grey Syst. 21(4), 369–376 (2009)
Deng, T., Ma, M., Cao, J.: Tourism resource development and long-term economic growth: a resource curse hypothesis approach. Tour. Econ. 20(5), 923–938 (2014)
Diedrich, A., Aswani, S.: Exploring the potential impacts of tourism development on social and ecological change in the Solomon Islands. Ambio 1–11 (2016)
Durbarry, R.: Tourism and economic growth: the case of Mauritius. Tour. Econ. 10(4), 389–401 (2004)
Feridun, M., Shahbaz, M.: Fighting terrorism: are military measures effective? Empirical evidence from Turkey. Def. Peace Econ. 21(2), 193–205 (2010)
Galtung, J.: Violence, peace, and peace research. J. Peace Res. 6(3), 167–191 (1969)
Greenwood, V.A., Dwyer, L.: Consumer protection legislation: a neglected determinant of destination competitiveness? J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 24, 1–8 (2015)
Gu, D., Zhu, H., Brown, T., Hoenig, H., Zeng, Y.: Tourism experiences and self-rated health among older adults in China. J. Aging Health, 0898264315609906 (2015)
Haessly, J.: Tourism and a culture of peace. In: Moufakkir, O., Kelly, I. (eds.) Tourism, Progress, and Peace, pp. 1–16. CABI, Wallingford (2010)
Hyndman, J.: The securitisation of Sri Lankan tourism in the absence of peace. Stability: Int. J. Secur. Dev. 4(1), 1–16 (2015)
Jackman, M.: Revisiting the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Barbados: a disaggregated market approach. Reg. Sect. Econ. Studies 12(2), 15–26 (2012)
Jenkins, C. L. (2015). Tourism policy and planning for developing countries: some critical issues. Tour. Recreat. Res. (ahead-of-print), 1–13
Kim, S.S., Prideaux, B., Prideaux, J.: Using tourism to promote peace on the Korean Peninsula. Ann. Tour. Res. 34(2), 291–309 (2007)
Lee, C.C., Chang, C.P.: Tourism development and economic growth: a closer look at panels. Tour. Manag. 29(1), 180–192 (2008)
Lee, C.G.: Health care and tourism: evidence from Singapore. Tour. Manag. 31(4), 486–488 (2010)
Lee, Y.-S.: The Korean war and tourism: legacy of the war on the development of the tourism industry in South Korea. Int. J. Tour. Res. 8, 157–170 (2006)
Mehmood, S., Ahmad, Z., Khan, A.A.: Dynamic relationships between tourist arrivals, immigrants, and crimes in the United States. Tour. Manag. 54, 383–392 (2016)
Moyo, B., Ziramba, E.: The impact of crime on inbound tourism to South Africa: an application of the bounds test. Afr. Secur. Rev. 22(1), 4–18 (2013)
Narayan, P.K.: Did Rabuka’s military coups have a permanent effect or a transitory effect on tourist expenditure in Fiji: evidence from Vogelsang’s structural break test. Tour. Manag. 26(4), 509–515 (2005)
Omri, A., Shahbaz, M., Chaibi, A., Rault, C.: A panel analysis of the effects of oil consumption, international tourism, environmental quality and political instability on economic growth in MENA region. IPAG Working Paper Series No. 2015-613, Paris, France (2015)
Ozturk, I.: The relationships among tourism development, energy demand, and growth factors in developed and developing countries. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. (2015a). doi:10.1080/13504509.2015.1092000
Ozturk, I.: Sustainability in the food-energy-water nexus: evidence from BRICS (Brazil, the Russian Federation, India, China, and South Africa) countries. Energy 93, 999–1010 (2015b)
Pérez-Rodríguez, J.V., Ledesma-Rodríguez, F., Santana-Gallego, M.: Testing dependence between GDP and tourism’s growth rates. Tour. Manag. 48, 268–282 (2015)
Pizam, A., Mansfeld, Y.: Toward a theory of tourism security. In: Tourism, Security & Safety: From Theory to Practice, pp. 1–27. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2006)
Po, W.C., Huang, B.N.: Tourism development and economic growth—a nonlinear approach. Phys. A 387(22), 5535–5542 (2008)
Pratt, S.: The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Ann. Tour. Res. 52, 148–160 (2015)
Pratt, S., Liu, A.: Does tourism really lead to peace? A global view. Int. J. Tour. Res. 18(1), 82–90 (2016)
Ramakrishnan, S., Hishan, S. S., Nabi, A. A., Arshad, Z., Kanjanapathy, M., Zaman, K., Khan, F.: An interactive environmental model for economic growth: evidence from a panel of countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 1–13 (2016)
Ridderstaat, J., Croes, R., Nijkamp, P.: Tourism and long-run economic growth in Aruba. Int. J. Tour. Res. 16(5), 472–487 (2014)
Saha, S., Yap, G.: The moderation effects of political instability and terrorism on tourism development: a cross-country panel analysis. J. Travel Res. 54(4), 509–521 (2014)
Santana-Gallego, M., RossellÃ-Nadal, J., Fourie, J.: The effects of terrorism, crime and corruption on tourism. ERSA working paper 59. http://www.econrsa.org/system/files/publications/working_papers/working_paper_595.pdf (2016). Accessed on 17th May 2016
Tang, C.F.: Medical Tourism and Its Implication on Malaysia’s Economic Growth. Online available at: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/63365/ (2015). Accessed on 3rd Dec 2015)
Tang, C.F., Abosedra, S.: Does tourism expansion effectively spur economic growth in Morocco and Tunisia? Evidence from time series and panel data. J. Policy Res. Tour. Leisure Events 8(2), 127–145 (2016)
Teye, V., Sirakaya, E., Sönmez, S.F.: Residents’ attitudes toward tourism development. Ann. Tour. Res. 29(3), 668–688 (2002)
Wöltering, F.: War as tourism attraction: approaching a segment in tourism research. Mob. Hist. 7(1), 58–68 (2016)
World Bank: World Development Indicators, World Bank, Washington DC (2014)
Zaman, K., Moemen, M.A., Islam, T.: Dynamic linkages between tourism transportation expenditures, carbon dioxide emission, energy consumption and growth factors: evidence from the transition economies. Curr. Issues Tour. (2016a). doi:10.1080/13683500.2015.1135107
Zaman, K., Shahbaz, M., Loganathan, N., Raza, S.A.: Tourism development, energy consumption and Environmental Kuznets Curve: trivariate analysis in the panel of developed and developing countries. Tour. Manag. 54, 275–283 (2016b)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding this Research group No. (RG-1436-037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassani, A.A., Zaman, K., Aldakhil, A.M. et al. War economy and pleasure: assessing the effects of military expenditure on tourism growth. Qual Quant 51, 1733–1754 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-016-0362-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-016-0362-x