Abstract
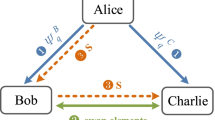
Side-channel attack is a serious impairment for the key generation processing in the continuous-variable quantum digital signature protocol. Based on measurement-device-independent components, we present a continuous-variable quantum digital signature protocol, so that the topology removes the loopholes of the practical detectors and eliminates all side-channel attacks. Without loss of generality, we consider the protocol involving three participants, whom independently decides whether to send a quantum pulse or a local oscillator pulse to the intermediate station at any time window. What’s more, we propose to employ phase-encoding and state-encoding strategies simultaneously that performing once key generation processing can obtain twin signatures. We hope the proposed protocol could further improve the performance of quantum digital signature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, C.S., Liao, H.Y.M.: Structural digital signature for image authentication: an incidental distortion resistant scheme. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 5, 161–173 (2003)
Micali, S., Reyzin, L.: Improving the exact security of digital signature schemes. J. Cryptol. 15, 1–18 (2002)
Yen, S.M., Laih, C.S.: New digital signature scheme based on discrete logarithm. Electron. Lett. 29, 396–398 (1993)
Goldwasser, S., Micali, S., Rivest, R.L.: A digital signature scheme secure against adaptive chosen-message attacks. SIAM J. Comput. 17, 281–308 (1988)
Koblitz, N.: Elliptic curve cryptosystems. Math. Comput. 48, 203–209 (1987)
ELGamal, T.: A public key cryptosystem and a signature scheme based on discrete logarithms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 31, 469–472 (1985)
Rivest, R.L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21, 120–126 (1978)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22, 644–654 (1976)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 26, 1484–1509 (1997)
Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P.: Quantum computations with cold trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4091–4094 (1995)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring, foundations of computer science, pp. 124–134 (1994)
Andersson, E., Curty, M., Jex, I.: Experimentally realizable quantum comparison of coherent states and its applications. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022323 (2006)
Clarke, P.J., Collins, R.J., Dunjko, V., Andersson, E., Jeffers, J., Buller, G.S.: Experimental demonstration of quantum digital signatures using phase-encoded coherent states of light. Nat. Commun. 3, 1174 (2012)
Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Andersson, E.: Quantum digital signatures without quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 040502 (2014)
Collins, R.J., Donaldson, R.J., Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Clarke, P.J., Andersson, E., Jeffers, J., Buller, G.S.: Realization of quantum digital signatures without the requirement of quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 040502 (2014)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum digital signatures. arXiv:quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Wallden, P., Dunjko, V., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Quantum digital signatures with quantum-key-distribution components. Phys. Rev. A 89, 042304 (2015)
Croal, C., Peuntinger, C., Heim, B., Khan, I., Marquardt, C., Leuchs, G., Korolkova, N.: Free-space quantum signatures using heterodyne measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 100503 (2016)
Amiri, R., Andersson, E.: Unconditionally secure quantum signatures. Entropy 17, 5635–5659 (2015)
Roberts, G.L., Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z.L., Dynes, J.F., Comandar, L.C., Sharpe, A.W., Shields, A.J., Curty, M., Puthoor, I.V., Andersson, E.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum digital signatures. Nat. Commun. 8, 1098 (2017)
Collins, R.J., Amiri, R., Fujiwara, M., Honjo, T., Shimizu, K., Tamaki, K.: Experimental demonstration of quantum digital signatures over 43 db channel loss using differential phase shift quantum key distribution. Sci. Rep. 7, 3235 (2017)
Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Secure quantum signatures using insecure quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 93, 032325 (2016)
Yin, H., Fu, Y., Chen, Z.: Practical quantum digital signature. Phys. Rev. A 93, 032316 (2016)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441–444 (2000)
Pomerene, A., Starbuck, A.L., Lentine, A.L., Long, C.M., Derose, C.T., Trotter, D.C.: Silicon photonic transceiver circuit for high-speed polarization-based discrete variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 25, 12282 (2017)
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Duek, M., Lutkenhaus, N., Peev, A.M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301–1350 (2009)
Ma, X., Qi, B., Zhao, Y., Lo, H.K.: Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012326 (2005)
Thornton, M., Scott, H., Croal, C., Korolkova, N.: Continuous-variable quantum digital signatures over insecure channels. Phys. Rev. A 99, 032341 (2019)
Zhang, G., Haw, J.Y., Cai, H., Xu, F., Assad, S.M., Fitzsimons, J.F., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, S., Wu, J., Ser, W., Kwek, L.C., Liu, A.Q.: An integrated silicon photonic chip platform for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 9, 1–4 (2019)
Huang, D., Huang, P., Lin, D.K., Zeng, G.H.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 6, 19201 (2016)
Jouguet, P., Kunzjacques, S., Leverrier, A., Grangier, P., Diamanti, E.: Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 7, 378–381 (2013)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J.: Unconditional optimality of Gaussian attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190503 (2006)
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002)
Pirandola, S., Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Weedbrook, C., Braunstein, S.L., Lloyd, S.L., Andersen, U.L.: High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 9, 397–402 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Weedbrook, C., Marshall, K., Pirandola, S., Yu, S., Guo, H.: Noiseless linear amplifiers in entanglement-based continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Entropy 17, 4547–4562 (2015)
Zhang, Y.C., Li, Z., Yu, S., Gu, W., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052325 (2014)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution protocols with a non-Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 83, 042312 (2011)
Donaldson, R.J., Collins, R.J., Kleczkowska, K., Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Dunjko, V., Jeffers, J., Andersson, E., Buller, G.S.: Experimental demonstration of kilometer-range quantum digital signatures. Phys. Rev. A 93, 012329 (2016)
Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Xu, F., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052301 (2014)
Ma, H.X., Huang, P., Bai, D.Y., Wang, T., Wang, S.Y., Bao, W.S.: Long-distance continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. A 99, 022322 (2018)
Swanson, C.M., Stinson, D.R.: Unconditionally secure signature schemes revisited. In: International Conference on Information Theoretic Security, pp. 100–116. Springer (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (Grant No. 2021zzts0202), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61801522), and National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2019JJ40352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Shi, R., Shi, J. et al. Quantum digital signature based on measurement-device-independent continuous-variable scheme. Quantum Inf Process 20, 222 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03152-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03152-7