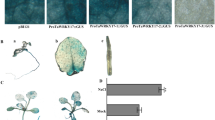
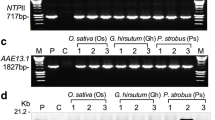
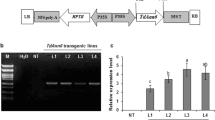
Abstract
Nicotianamine synthase (NAS) plays a pivotal role in balancing the concentrations of heavy metals in plants, but its characteristics and functions in salt stress responses are not completely understood, particularly in wheat. In this study, the salt-induced gene TaNAS-D was cloned from wheat and characterized. TaNAS-D, localized throughout the cell, is mainly expressed in developed vascular bundle tissues and is responsive to NaCl, ABA, and H2O2 stresses. Overexpression of TaNAS-D in Arabidopsis led to elevated NA levels and enhanced salt stress tolerance, which was demonstrated by higher germination rates and improved growth of TaNAS-D transgenic Arabidopsis plants compared with WT when exposed to salt stress. Further investigation revealed that TaNAS-D transgenic Arabidopsis plants displayed higher K+/Na+ ratios, lower malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, and less ion leakage (IL) consistently accompanied by increased peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) activities, thereby reducing membrane injury. Moreover, TaNAS-D overexpression under salt stress increased AtSOS1, AtSOS2, AtSOS3, AtFAD5, and AtSAD1 transcript levels. These findings indicate that TaNAS-D plays a positive role in salt tolerance by improving the antioxidant defense system and upregulating salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway genes.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NAS:
-
Nicotianamine synthase
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- IL:
-
Ion leakage
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- SOS:
-
Salt overly sensitive
References
Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Salem MA, Nabi G, Sharma S (2010) Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:161–175. doi:10.3109/07388550903524243
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptations to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7:1099–1111. doi:10.1105/tpc.7.7.1099
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J-K (2006) Salt stress signaling and mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. In: Genetic engineering. Springer, pp 141–177
Cho K, O’Neill CM, Kwon SJ, Yang TJ, Smooker AM, Fraser F, Bancroft I (2010) Sequence-level comparative analysis of the Brassica napus genome around two stearoyl-ACP desaturase loci. Plant J 61:591–599. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04084.x
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Deng X et al (2013) Ectopic expression of wheat TaCIPK14, encoding a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, confers salinity and cold tolerance in tobacco. Physiol Plant 149:367–377. doi:10.1111/ppl.12046
Douchkov D, Gryczka C, Stephan U, Hell R, Bäumlein H (2005) Ectopic expression of nicotianamine synthase genes results in improved iron accumulation and increased nickel tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Environ 28:365–374
Flowers T (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Guan LM, Zhao J, Scandalios JG (2000) Cis-elements and trans-factors that regulate expression of the maize Cat1 antioxidant gene in response to ABA and osmotic stress: H2O2 is the likely intermediary signaling molecule for the response. Plant J 22:87–95
Haydon MJ, Kawachi M, Wirtz M, Hillmer S, Hell R, Krämer U (2012) Vacuolar nicotianamine has critical and distinct roles under iron deficiency and for zinc sequestration in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:724–737
Higuchi K, Suzuki K, Nakanishi H, Yamaguchi H, Nishizawa N-K, Mori S (1999a) Cloning of nicotianamine synthase genes, novel genes involved in the biosynthesis of phytosiderophores. Plant Physiol 119:471–480
Higuchi K, Suzuki K, Nakanishi H, Yamaguchi H, Nishizawa N-K, Mori S (1999b) Cloning of nicotianamine synthase genes, novel genes involved in the biosynthesis of phytosiderophores. Plant Physiol 119:471–480
Higuchi K, Tani M, Nakanishi H, Yoshiwara T, Goto F, NISHIZAWA NK, Mori S (2001) The expression of a barley HνNAS1 nicotianamine synthase gene promoter-gus fusion gene in transgenic tobacco is induced by Fe-deficiency in roots. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:1692–1696
Hua S, Sun Z (2001) Support vector machine approach for protein subcellular localization prediction. Bioinformatics 17:721–728
Hugly S, Somerville C (1992) A role for membrane lipid polyunsaturation in chloroplast biogenesis at low temperature. Plant Physiol 99:197–202
Hussain TM, Hazara M, Sultan Z, Saleh BK, Gopal GR (2008) Recent advances in salt stress biology a review. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 3:8–13
Johnson AA, Kyriacou B, Callahan DL, Carruthers L, Stangoulis J, Lombi E, Tester M (2011) Constitutive overexpression of the OsNAS gene family reveals single-gene strategies for effective iron-and zinc-biofortification of rice endosperm. PLoS One 6:e24476
Kim S et al (2005a) Increased nicotianamine biosynthesis confers enhanced tolerance of high levels of metals, in particular nickel, to plants. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1809–1818
Kim S et al (2005b) Increased nicotianamine biosynthesis confers enhanced tolerance of high levels of metals, in particular nickel, to plants. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1809–1818. doi:10.1093/pcp/pci196
Klatte M, Schuler M, Wirtz M, Fink-Straube C, Hell R, Bauer P (2009) The analysis of Arabidopsis nicotianamine synthase mutants reveals functions for nicotianamine in seed iron loading and iron deficiency responses. Plant Physiol 150:257–271
Knight H, Knight MR (2001) Abiotic stress signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk. Trends Plant Sci 6:262–267
Koen E et al (2013) Arabidopsis thaliana nicotianamine synthase 4 is required for proper response to iron deficiency and to cadmium exposure. Plant Sci 209:1–11
Kojima I, Iida C (1986) Vapor phase digestion of botanical samples with acids in sealed polyterafluoroethlylene bomb. Anal Sci 2:567–570
Kong F, Mao S, Du K, Wu M, Zhou X, Chu C, Wang Y (2011a) Comparative proteomics analysis of OsNAS1 transgenic Brassica napus under salt stress. Chin Sci Bull 56:2343–2350
Kong F, Mao S, Du K, Wu M, Zhou X, Chu C, Wang Y (2011b) Comparative proteomics analysis of OsNAS1 transgenic Brassica napus under salt stress. Chin Sci Bull 56:2343–2350
Lee S et al (2009) Iron fortification of rice seeds through activation of the nicotianamine synthase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22014–22019
Ling HQ, Koch G, Baumlein H, Ganal MW (1999) Map-based cloning of chloronerva, a gene involved in iron uptake of higher plants encoding nicotianamine synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7098–7103
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Martin JL, McMillan FM (2002) SAM (dependent) I AM: the S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase fold. Curr Opin Struct Biol 12:783–793
Masuda H et al (2009) Overexpression of the barley nicotianamine synthase gene HvNAS1 increases iron and zinc concentrations in rice grains. Rice 2:155–166
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006a) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006b) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 60:324–349
Reddy AS, Ali GS, Celesnik H, Day IS (2011) Coping with stresses: roles of calcium-and calcium/calmodulin-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell Online 23:2010–2032
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Porcel R, Azcón C, Aroca R (2012) Regulation by arbuscular mycorrhizae of the integrated physiological response to salinity in plants: new challenges in physiological and molecular studies. J Exp Bot 63:4033–4044
Schuler M, Bauer P (2011) Heavy metals need assistance: the contribution of nicotianamine to metal circulation throughout the plant and the Arabidopsis NAS gene family. Front Plant Sci 2:69. doi:10.3389/fpls.2011.00069
Sears E (1966) Nullisomic-tetrasomic combinations in hexaploid wheat. In: Chromosome manipulations and plant genetics. Springer, pp 29–45
Shi H, Lee B-h, Wu S-J, Zhu J-K (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Shi H, Zhu J-K (2002) Regulation of expression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 by salt stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 50:543–550
Takahashi M, Terada Y, Nakai I, Nakanishi H, Yoshimura E, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2003) Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development. Plant Cell 15:1263–1280
Tian S, Mao X, Zhang H, Chen S, Zhai C, Yang S, Jing R (2013) Cloning and characterization of TaSnRK2. 3, a novel SnRK2 gene in common wheat. J Exp Bot 64:2063–2080
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotech 16:123–132
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu J-K (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell Online 14:S165–S183
Yang G et al (2015) Molecular cloning and characterization of MxNAS2, a gene encoding nicotianamine synthase in Malus xiaojinensis, with functions in tolerance to iron stress and misshapen flower in transgenic tobacco. Sci Hortic 183:77–86
Yang Q et al (2009) Overexpression of SOS (salt overly sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:22–31. doi:10.1093/mp/ssn058
Zhang H, Han B, Wang T, Chen S, Li H, Zhang Y, Dai S (2012) Mechanisms of plant salt response: insights from proteomics. J Proteome Res 11:49–67. doi:10.1021/pr200861w
Zhou X et al (2013) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression profiling of nicotianamine synthase (NAS) gene family in maize. BMC Genomics 14:238. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-238
Zhu J-K (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948
Zhu J-K (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329
Zhu JK (2007) Plant salt stress. In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. Wiley, Hoboken
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401309), Hebei Provincial Science and Technology Research and Development Project (16226320D and 13966305D), and China Agriculture Research System (CARS-03-01B).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Jie Han and Wei Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Zhang, W., Sun, L. et al. A Novel Wheat Nicotianamine Synthase Gene, TaNAS-D, Confers High Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis . Plant Mol Biol Rep 35, 252–264 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-016-1018-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-016-1018-7