Abstract
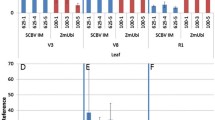
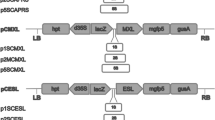
Enhancers are known to be capable of overriding the specificity of nearby promoters in a distance-dependent manner, which is problematic when multiple promoters coexist in a single transgene unit. In an attempt to determine whether enhancer activation function is inversely related to its distance from the target promoter, we inserted 1-, 2-, and 4-kb bacteriophage λ fragments, respectively, between the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S enhancer and a flower-specific AGAMOUS second intron-derived promoter (AGIP) fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region. In the absence of an insert sequence, the 35S enhancer activates AGIP-driven GUS expression in vegetative tissues of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana lines. Moreover, neither the 2-kb nor the 4-kb λ fragment was able to block GUS expression in transgenic leaves, implying that the 35S enhancer can override a distance barrier of at least 4 kb in our system. Unexpectedly, insertion of the 1-kb λ insert into the same site resulted in diminished GUS expression in transgenic leaves. Our data indicate that this fragment functions as a true enhancer-blocking insulator that could potentially be utilized to minimize enhancer–promoter interference between multiple transcriptional units within a plasmid vector during plant transformation experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao L, Zhou M, Cui Y (2008) CTCFBSDB: a CTCF-binding site database for characterization of vertebrate genomic insulators. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D83–D87
Belostotsky DA, Meagher RB (1996) A pollen-, ovule-, and early embryo-specific poly(A) binding protein from Arabidopsis complements essential functions in yeast. Plant Cell 8:1261–1275
Benfey PN, Ren L, Chua NH (1989) The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J 8:2195–2202
Benfey PN, Ren L, Chua NH (1990) Tissue-specific expression from CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains in early stages of plant development. EMBO J 9:1677–1684
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27:573–580
Bevan M (1984) Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8711–8721
Chung JH, Whiteley M, Felsenfeld G (1993) A 5′ element of the chicken β-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 74:505–514
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Dunn KL, Zhao H, Davie JR (2003) The insulator binding protein CTCF associates with the nuclear matrix. Exp Cell Res 288:218–223
Geyer PK, Spana C, Corces VG (1986) On the molecular mechanism of gypsy-induced mutations at the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 5:2657–2662
Goderis IJWM, De Bolle MFC, François IEJA, Wouters PFJ, Broekaert WF, Cammue BPA (2002) A set of modular plant transformation vectors allowing flexible insertion of up to six expression units. Plant Mol Biol 50:17–27
Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C (2007) CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W52–W57. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm360:1-6
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994
Hebbes TR, Clayton AL, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C (1994) Core histone hyperacetylation co-maps with generalized DNase I sensitivity in the chicken β-globin chromosomal domain. EMBO J 13:1823–1830
Hily JM, Liu Z (2009) A simple and sensitive high-throughput GFP screening in woody and herbaceous plants. Plant Cell Rep 28:493–501
Hily JM, Singer SD, Yang Y, Liu Z (2009) A transformation booster sequence (TBS) from Petunia hybrida functions as an enhancer-blocking insulator in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 28(7):1095–1104
Hirner B, Fischer WN, Rentsch D, Kwart M, Frommer WB (1998) Developmental control of H+/amino acid permease gene expression during seed development of Arabidopsis. Plant J 14:535–544
Jagannath A, Bandyopadhyay P, Arumugam N, Gupta V, Kumar P, Pental D (2001) The use of a Spacer DNA fragment insulates the tissue-specific expression of a cytotoxic gene (barnase) and allow high-frequency generation of transgenic male sterile lines in Brassica juncea L. Mol Breeding 8:11–23
Kellum R, Schedl P (1991) A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell 64:941–950
Kellum R, Schedl P (1992) A group of scs elements function as domain boundaries in an enhancer-blocking assay. Mol Cell Biol 12:2424–2431
Kim T, Abdullaev Z, Smith A, Ching K, Loukinov D, Green R, Zhang M, Lobanenkov V, Ren B (2007) Analysis of the vertebrate insulator protein CTCF-binding sites in the human genome. Cell 128:1231–1245
Kobayashi N, Horikoshi T, Katsuyama H, Handa T, Takayanagi K (1998) A simple and efficient DNA extraction method for plants, especially woody plants. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol 4:76–80
Koltunow AM, Truettner J, Cox KH, Wallroth M, Goldberg RB (1990) Different temporal and spatial gene expression patterns occur during anther development. Plant Cell 2:1201–1224
Lanfranco L (2003) Engineering crops, a deserving venture. Riv Biol 96:31–54
Li Z, Jayasankar S, Gray DJ (2001) Expression of a bifunctional green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion marker under the control of three constitutive promoters and enhanced derivatives in transgenic grape (Vitis vinifera). Plant Sci 160:877–887
Liu Z, Liu Z (2008) The second intron of AGAMOUS drives carpel- and stamen-specific expression sufficient to induce complete sterility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 27:855–863
Nabirochkin S, Ossokina M, Heidmann T (1998) A nuclear matrix/scaffold attachment region co-localizes with the gypsy retrotransposon insulator sequence. J Biol Chem 273:2473–2479
Namciu SJ, Blochlinger KB, Fournier REK (1998) Human matrix attachment regions insulate transgene expression from chromosomal position effects in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 18:2382–2391
Odell JT, Knowlton S, Lin W, Mauvais J (1988) Properties of an isolated transcription stimulating sequence derived from the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Plant Mol Biol 10:263–272
Ouwerkerk PBF, de Kam RJ, Hoge JHC, Meijer AH (2001) Glucocorticoid-inducible gene expression in rice. Planta 213:370–378
Prestridge DS (1995) Predicting pol II promoter sequences using transcription factor binding sites. J Mol Biol 249:923–932
Rosso MG, Li Y, Strizhov N, Reiss B, Dekker K, Weisshar B (2003) An Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA mutagenized population (GABI-Kat) for flanking sequence tag-based reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 53:247–259
Savidge B, Rounsley SD, Yanofsky MF (1995) Temporal relationship between the transcription of two Arabidopsis MADS box genes and the floral organ identity genes. Plant Cell 7:721–733
Singh GB, Kramer JA, Krawetz SA (1997) Mathematical model to predict regions of chromatin attachment to the nuclear matrix. Nucleic Acids Res 25:1419–1425
Smith DL, Fedoroff NV (1995) LRP1, a gene expressed in lateral and adventitious root primordia of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 7:735–745
Stief A, Winter DM, Strätling WH, Sippel AE (1989) A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature 341:343–345
van der Geest AHM, Hall TC (1997) The β-phaseolin 5′ matrix attachment region acts as an enhancer facilitator. Plant Mol Biol 33:553–557
Yoo SY, Bomblies K, Yoo SK, Yang JW, Choi MS, Lee JS, Weigel D, Ahn JH (2005) The 35S promoter used in a selectable marker gene of a plant transformation vector affects the expression of the transgene. Planta 221:523–530
Zheng X, Deng W, Luo K, Duan H, Chen Y, McAvoy R, Song S, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) The cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter sequence alters the level and patterns of activity of adjacent tissue- and organ-specific gene promoters. Plant Cell Rep 26:1195–1203
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Dennis Bennett for technical assistance. This study was funded by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)-Agricultural Research Service Headquarter 2005 and 2007 classes of postdoctoral grants and a USDA Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service Biotechnology Risk Assessment Research grant (2006-03701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singer, S.D., Hily, JM. & Liu, Z. A 1-kb Bacteriophage Lambda Fragment Functions as an Insulator to Effectively Block Enhancer–Promoter Interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Mol Biol Rep 28, 69–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0122-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0122-3