Abstract
Background and aims
Aridity has increased in the past decades and will probably continue to increase in arid and semiarid regions. Here we decipher the plant and soil capacity to retain metal cations when climate evolves to more arid conditions.
Methods
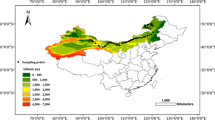
We analyzed K, Na, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu concentrations in 580 soil samples and 666 plant (shoot and root) samples along a 3600 km aridity gradient in northern China.
Results
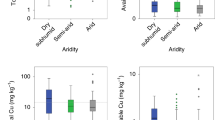
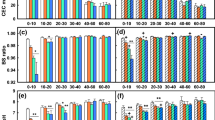
The concentrations of soil exchangeable K, Mg, Mn, Fe and Cu clearly decreased with increasing aridity due to the relationships of aridity with soil clay content and soil pH. Increases in exchangeable Na and Ca concentrations at mid- and high-aridity levels are probably due to the soil salinization, whereas increased exchangeable Fe concentrations at extreme levels of aridity may be more related to a reduced pH. Element concentrations in both plant shoots and roots were unrelated to soil exchangeable element concentrations; instead they increased monotonously with increasing aridity, corresponding with decreases in plant size and shoot/root ratios. The shoot/root mineralomass ratios in general increased with increasing aridity. The proportional higher element contents in shoots than in roots with increasing aridity are related to increased water uptake and/or use efficiency.
Conclusions
The extractability of soil elements in response to changing climate varied with the nature of specific elements that are controlled by biological and geochemical processes, i.e., some decreased linearly with increasing aridity, whereas others first decreased and then increased with different thresholds. These contrasting effects of aridity on nutrient availability could further constrain plant growth and should be incorporated into biogeochemical models. The prevailing paradigm of a positive relationship between concentrations of plant and soil elements needs to be reconsidered under changing climatic conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin AT (2011) Has water limited our imagination for aridland biogeochemistry? Trends Ecol Evol 26:229–235
Bloom PR (2000) Soil pH and pH buffering. In: Sumner M (ed) Handbook of soil science. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Chadwick OA, Gavenda RT, Kelly EF, Ziegler K, Olson CG, Elliott WC, Hendricks DM (2003) The impact of climate on the biogeochemical functioning of volcanic soils. Chem Geol 202:195–223
Chaves MM, Maroco JP, Pereira JS (2003) Understanding plant responses to drought—from genes to the whole plant. Funct Plant Biol 30:239–264
Clark JM, Chapman PJ, Adamson JK, Lane SN (2005) Influence of drought-induced acidification on the mobility of dissolved organic carbon in peat soils. Glob Chang Biol 11:791–809
Dahlgren R, Boettinger J, Huntington G, Amundson R (1997) Soil development along an elevational transect in the western sierra Nevada, California. Geoderma 78:207–236
Dai AG (2013) Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models. Nat Clim Chang 3:52–58
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Gallardo A, Bowker MA, Wallenstein MD, Quero JL, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, García-Gómez M, Soliveres S (2013) Decoupling of soil nutrient cycles as a function of aridity in global drylands. Nature 502:672–676
Duval BD, Dijkstra P, Drake BG, Johnson DW, Ketterer ME, Megonigal JP, Hungate BA (2013) Element pool changes within a scrub-oak ecosystem after 11 years of exposure to elevated CO2. PLoS One 8:e64386
Elamin EA, Hussein AH (2000) Cooper adsorption as affected by electrolyte concentration and sodium adsorption ratio in three major soil series in Sudan. An Arid Zone 39:137–143
Elser JJ, Acquisti C, Kumar S (2011) Stoichiogenomics: the evolutionary ecology of macromolecular elemental composition. Trends Ecol Evol 26:38–44
Falkowski PG, Fenchel T, Delong EF (2008) The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 320:1034–1039
Foulds W (1993) Nutrient concentrations of foliage and soil in South-Western Australia. New Phytol 125:529–546
Han WX, Fang JY, Reich PB, Ian Woodward F, Wang ZH (2011) Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol Lett 14:788–796
Hansch R, Mendel RR (2009) Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:259–266
Howarth R, Chan F, Conley DJ, Garnier J, Doney SC, Marino R, Billen G (2011) Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 9:18–26
Jarrell W, Beverly R (1981) The dilution effect in plant nutrition studies. Adv Agron 34:197–224
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2004) The uplift of soil nutrients by plants: biogeochemical consequences across scales. Ecology 85:2380–2389
Kopittke GR, Tietema A, Verstraten JM (2012) Soil acidification occurs under ambient conditions but is retarded by repeated drought: results of a field-scale climate manipulation experiment. Sci Total Environ 439:332–342
Lenton TM, Held H, Kriegler E, Hall JW, Lucht W, Rahmstorf S, Schellnhuber HJ (2008) Tipping elements in the Earth’s climate system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1786–1793
Luo WT, Jiang Y, Lü XT, Wang X, Li MH, Bai E, Han XG, Xu ZW (2013) Patterns of plant biomass allocation in temperate grasslands across a 2500-km transect in northern China. PLoS One 8. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071749
Luo WT, Elser JJ, Lü XT, Wang ZW, Bai E, Yan CF, Wang C, Li MH, Zimmermann NE, Han XG, Xu ZW, Li H, Wu YN, Jiang Y (2015a) Plant nutrients do not covary with soil nutrients under changing climatic conditions. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 29. doi:10.1002/2015GB005089
Luo WT, Nelson PN, Li MH, Cai JP, Zhang Y, Yang S, Wang RZ, Han XG, Jiang Y (2015b) Contrasting pH buffering patterns in neutral-alkaline soils along a 3600 km transect in northern China. Biogeosciences 12:7047–7056
Luo WT, Dijkstra FA, Bai E, Feng J, Lü XT, Wang C, Wu HH, Li MH, Han XG, Jiang Y (2016) A threshold reveals decoupled relationship of sulfur with carbon and nitrogen in soils across arid and semi-arid grasslands in northern China. Biogeochemistry 127:141–153
Martinez CE, Motto HL (2000) Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ Pollut 107:153–158
Moyano FE, Manzoni S, Chenu C (2013) Responses of soil heterotrophic respiration to moisture availability: an exploration of processes and models. Soil Biol Biochem 59:72–85
Peñuelas J, Sardans J (2009) Ecology: elementary factors. Nature 460:803–804
Peñuelas J, Sardans J, Rivas-ubach A, Janssens IA (2012) The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth’s life system. Glob Chang Biol 18:3–6
Ramezanian BA (2013) Influence of soil amendments and soil properties on macro-and micronutrient availability to microorganisms and plants. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Sueciae 30:1652–6880
Rodriguez-Navarro C, Doehne E (1999) Salt weathering: influence of evaporation rate, supersaturation and crystallization pattern. Earth Surf Process Landf 24:191–209
Roscoe R, Buurman P, Velthorst EJ (2000) Disruption of soil aggregates by varied amounts of ultrasonic energy in fractionation of organic matter of a clay Latosol: carbon, nitrogen and delta C-13 distribution in particle-size fractions. Eur J Soil Sci 51:445–454
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2007) Drought changes the dynamics of trace element accumulation in a Mediterranean Quercus ilex forest. Environ Pollut 147:567–583
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2015) Potassium: a neglected nutrient in global change. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 24:261–275
Sardans J, Janssens IA, Alonso R, Veresoglou SD, Rillig MC, Sanders TG, Carnicer J, Filella I, Farré-Armengol G, Peñuelas J (2015) Foliar elemental composition of European forest tree species associated with evolutionary traits and present environmental and competitive conditions. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 24:240–255
Scheffer M, Bascompte J, Brock WA, Brovkin V, Carpenter SR, Dakos V, Held H, van Nes EH, Rietkerk M, Sugihara G (2009) Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature 461:53–59
Scheffer M, Carpenter SR, Lenton TM, Bascompte J, Brock W, Dakos V, van de Koppel J, van de Leemput IA, Levin SA, van Nes EH, Pascual M, Vandermeer J (2012) Anticipating critical transitions. Science 338:344–348
Schlesinger WH, Bernhardt ES (2013) Biogeochemistry: an analysis of global change. Academic press
Schroter D, Cramer W, Leemans R, Prentice IC, Araujo MB, Arnell NW, Bondeau A, Bugmann H, Carter TR, Gracia CA, de la Vega-Leinert AC, Erhard M, Ewert F, Glendining M, House JI, Kankaanpaa S, Klein RJT, Lavorel S, Lindner M, Metzger MJ, Meyer J, Mitchell TD, Reginster I, Rounsevell M, Sabate S, Sitch S, Smith B, Smith J, Smith P, Sykes MT, Thonicke K, Thuiller W, Tuck G, Zaehle S, Zierl B (2005) Ecosystem service supply and vulnerability to global change in Europe. Science 310:1333–1337
Stael S, Wurzinger B, Mair A, Mehlmer N, Vothknecht UC, Teige M (2012) Plant organellar calcium signaling: an emerging field. J Exp Bot 63:1525–1542
Tiller KG, Gerth J, Brümmer G (1984) The relative affinities of Cd, Ni and Zn for different soil clay fractions and goethite. Geoderma 34:17–35
van Groenigen KJ, Six J, Hungate BA, de Graaff MA, van Breemen N, Van Kessel C (2006) Element interactions limit soil carbon storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:6571–6574
Vicente-Serrano SM, Zouber A, Lasanta T, Pueyo Y (2012) Dryness is accelerating degradation of vulnerable shrublands in semiarid Mediterranean environments. Ecol Monogr 82:407–428
Vitousek PM, Chadwick OA (2013) Pedogenic thresholds and soil process domains in basalt-derived soils. Ecosystems 16:1379–1395
Wang S, Wan C, Wang Y, Chen H, Zhou Z, Fu H, Sosebee RE (2004) The characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Wang C, Wang XB, Liu DW, Wu HH, Lü XT, Fang YT, Cheng WX, Luo WT, Jiang P, Shi J, Yin H, Zhou JZ, Han XG, Bai E (2014) Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nat Commun 5. doi:10.1038/ncomms5799
West NE (1981) Nutrient cycling in desert ecosystems. In: Goodall DW, Perry RA, Howes KMW (eds) Arid-land ecosystems: structure, functioning and management. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Whitehead DC (2000) Nutrient elements in grassland. In: Soil-plant-animal relationships. Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing
Xoconostle-Cazares B, Ramirez-Ortega FA, Flores-Elenes L, Ruiz-Medrano R (2010) Drought tolerance in crop plants. Am J Plant Physiol 5:241–256
Zhang SB, Zhang JL, Slik JWF, Cao KF (2012) Leaf element concentrations of terrestrial plants across China are influenced by taxonomy and the environment. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 21:809–818
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of the Field Expedition Team from the Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for assistance with field data collection. We also thank the Erguna Forest-Steppe Ecotone Research Station, Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371251), by the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB403204), and State Key Laboratory of Forest and Soil Ecology (LFSE2013-01). JP and JS acknowledge funding from the European Research Council Synergy grant ERC-2013-SyG-610028 IMBALANCE-P, the Spanish Government grant CGL2013-48074-P and the Catalan Government grant SGR 2014-274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elizabeth M Baggs.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, W., Sardans, J., Dijkstra, F.A. et al. Thresholds in decoupled soil-plant elements under changing climatic conditions. Plant Soil 409, 159–173 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2955-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2955-5