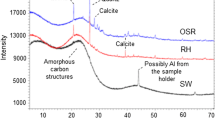
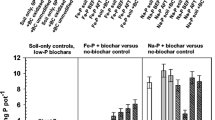
Abstract
Aims
The objectives of this study were to evaluate (1) the fertilizer potential of bone char, (2) the effects of wood biochar on plant-available phosphorus (P), and (3) the role of root-mycorrhizae-biochar interactions in plant P acquisition from a P-fixing soil.
Methods
Incubation and pot experiments were conducted with a P-fixing soil and maize with or without root hairs and arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM) inoculation. Olsen-, resin-P and plant P accumulation were used to estimate P availability from bone char, co-pyrolyzed bone char-wood biochar, and separate bone char and wood biochar additions produced at 60, 350 and 750 °C, and Triple Superphosphate (TSP).
Results
Maize inoculated with AM showed similar P accumulation when fertilized with either 750 °C bone char or TSP. Pyrolyzing bone did not increase extractable P in soil in comparison to unpyrolyzed bone, apart from a 67 % increase in resin-extractable P after additions of bone char pyrolyzed at 350 °C. Despite greater Olsen-P extractability, co-pyrolysis of bone with wood reduced maize P uptake. Wood biochars reduced resin-P from bone char by 14–26 %, whereas oven-dried wood increased resin-P by 23 %.
Conclusions
Bone char is an effective P fertilizer, especially if root-AM interactions are simultaneously considered. Biochar influences plant access to soil P and requires careful management to improve P availability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson PH (1999) A potential phosphate crisis. Science 283:2015
Akiyama K, Matsuzaki K, Hayashi H (2005) Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscual mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 435:824–827
Antelo JF, Arce F, Avena M, Fiol S, Lopez R, Macias F (2007) Adsorption of a soil humic acid at the surface of goethite and its competitive interaction with phosphate. Geoderma 138:12–19
Atkinson CJ, Fitzgerald JD, Hipps NA (2010) Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: a review. Plant Soil 337:1–18
Bates TR, Lynch JP (2001) Root hairs confer a competitive advantage under low phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 236:243–250
Benton Jones J (2001) Laboratory guide for conducting soil tests and plant analysis. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
Berta G, Fusconi A, Trotta A (1993) VA mycorrhizal infection and the morphology and function of root systems. Environ Exp Bot 33:159–173
Bolan NS, Naidu R, Mahimairaja S, Baskaran S (1994) Influence of low-molecular weight organic-acids on the solubilization of phosphates. Biol Fertil Soils 18:311–319
Brown WE, Patel PR, Chow LC (1975) Formation of CaHPO4 from enamel mineral and its relationship to caries mechniasm. J Dent Res 54:475–481
Buss W, Graham MC, Shepherd JG, Mašek O (2016) Suitability of marginal biomass-derived biochars for soil amendment. Sci Total Environ 547:314–322
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Chang 19:292–305
Cordell D, Rosamarin A, Schroder JJ, Smit AL (2011) Towards global phosphorus security: a systems framework for phosphorus recovery and reuse options. Chemosphere 84:747–758
Cornelissen G, Gustafsson O, Bucheli TD, Jonker MTO, Koelmans AA, Van Noort PCM (2005) Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environ Sci Technol 39:6881–6895
Cui MY, Caldwell MM (1996) Facilitation of plant phosphate acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizas from enriched soil patches II. Hyphae exploiting root-free soil. New Phytol 133:461–467
Cui HJ, Wang MK, Fu ML, Ci E (2011) Enhancing phosphorus availability in phosphorus-fertilized zones by reducing phosphate adsorbed on ferrihydrite using rice straw-derived biochar. J Soils Sediments 11:1135–1141
DeLuca TH, MacKanzie MD, Gundale MJ (2009) Bio-char effects on soil nutrient transformation. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan Publications Ltd, London, pp. 251–270
Deydier E, Guilet R, Sarda S, Sharrock P (2005) Physical and chemical characterisation of crude meat and bone meal combustion residue: “waste or raw material?”. J Hazard Mater 121:141–148
Earl KD, Syers JK, McLaughlin JR (1979) Origin of the effects of citrate, tartrate and acetate on phosphate soprtion by soils and synthetic gels. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:674–678
Gilbert N (2009) The disappearing nutrient. Nature 461:33–143
Guppy CN, Menzies NW, Moody PW, Blamey FPC (2005) Competitive sorption reactions between phosphorus and organic matter in soil: a review. Aust J Soil Res 43:189–202
Haynes RJ, Mokolobate MS (2001) Amelioration of Al toxicity and P deficiency in acid soils by additions of organic residues: a critical review of the phenomenon and the mechanisms involved. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 59:47–63
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hochholdinger F, Wen TJ, Zimmerman R, Chimot-Marolle P, da Costa e Silva O, Bruce W, Lamkey KR, Wienand U, Scnable PS (2008) The maize (Zea mays L.) roothairless3 gene encodes a putative GPI-anchored, monocot-specific, COBRA-like protein that significantly affects grain yield. Plant J 54:888–898
Hodge A, Berta G, Doussan C, Merchan F, Crespi M (2009) Plant root growth, architecture and function. Plant Soil 321:153–187
Hollister CC, Bisogni JJ, Lehmann J (2013) Ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate sorption to and solute leaching from biochars prepared from corn stover (Zea mays L.) and oak wood (Quercus spp.). J Environ Qual 42:137–144
Hunt JF, Ohno T, He Z, Honeycutt CW, Dail DB (2007) Inhibition of phosphorus sorption to goethite, gibbsite, and kaolin by fresh and decomposed organic matter. Biol Fertil Soils 44:277–288
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rhizosphere - a critical review. Plant Soil 205:25–44
Kaldorf M, Ludwig-Muller J (2000) AM fungi might affect the root morphology of maize by increasing indole-3-butyric acid biosynthesis. Physiol Plant 109:58–67
Koske RE, Gemma JN (1989) A modified procedure for staining roots to detect VA-mycorrhizas. Mycol Res 92:486–505
Kucey RMN, Janzen HH, Leggett ME (1989) Microbially mediated increases in plant-available phosphorus. Adv Agron 42:199–228
Kuo S (1996) Phosphorus. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis - Part 3 chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Inc. & American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp. 895–997
LeCroy C, Masiello CA, Rudgers JA, Hockaday WC, Silberg JJ (2013) Nitrogen, biochar, and mycorrhizae: alteration of the symbiosis and oxidation of the char surface. Soil Biol Biochem 58:248–254
Lehmann JJ, da Silva P, Steiner C, Nehls T, Zech W, Glaser B (2003) Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 249:343–357
Lynch JP (2011) Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant Physiol 156:1041–1049
Lynch JP, Beebe SE (1995) Adaptation of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L) to low phosphorus availability. Hortscience 30:1165–1171
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Matsumoto T, Okazaki M, Inoue M, Hamada Y, Taira M, Takahashi J (2002) Crystallinity and solubility characteristics of hydroxyapatite adsorbed amino acid. Biomaterials 23:2241–2247
Mosse B (1962) Establishment of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza under aseptic conditions. J. Gen Microbiol 27:509–520
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Parfitt RL, Atkinson RJ, Smart RSC (1975) Mechanism of phosphate fixation by iron oxides. Soil Sci Soc Am J 39:837–841
Qayyam MF, Ashraf I, Abid M, Steffens D (2015) Effect of biochar, lime, and compost application on phosphorus adsorption in a Ferralsol. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:576–581
Raghothama KG, Karthikeyan AS (2005) Phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil 274:37–49
Rajan SSS, Watkinson JH, Sinclair AG (1996) Phosphate rocks for direct application to soils. Adv Agron 57:77–159
Ramaekers L, Remans R, Rao IM, Blair MW, Vanderleyden J (2010) Strategies for improving phosphorus acquisition efficiency of crop plants. Field Crop Res 117:169–176
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Simpson RJ (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156
Sanchez P (1976) Properties and management of acid soils in the tropics. John Wiley, New York
Siebers NF, Leinweber P (2013) Bone char: a clean and renewable phosphorus fertilizer with cadmium immobilization capability. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:405–411
Siebers NF, Godlinski F, Leinweber P (2012) The phosphorus fertilizer value of bone char for potatoes, wheat and onions: first results. Landbauforsch Volk 62:59–64
Siebers NF, Godlinski F, Leinweber P (2014) Bone char as phosphorus fertilizer involved in cadmium immobilization in lettuce, wheat, and potato cropping. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 177:75–83
Singh BB, Jones JP (1976) Phosphorus sorption and desorption characteristics of soil as affected by organic residues. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40:389–394
Smil V (2000) Phosphorus in the environment: natural flows and human interferences. Annu Rev Energy 25:53–88
Smits MM, Bonneville S, Benning LG, Banwart SA, Leake JR (2012) Plant-driven weathering of apatite - the role of an ectomycorrhizal fungus. Geobiology 10:445–456
Tiessen H, Moir J (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential fractionation. In: Carter M (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp. 75–78
Tuominen L, Kairesalo T, Hartikainen H (1994) Comparison of methods for inhibiting bacterial-activity in sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3454–3457
Van Zwieten L, Kimber S, Morris S, Chan KY, Downie A, Rust J, Joseph S, Cowie A (2009) Effect of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 327:235–246
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447
Vanek S, Lehmann J (2015) Phosphorus availability to beans via interactions between mycorrhizas and biochar. Plant Soil 395:105–123
Vassilev N, Martos E, Mendes G, Martos V, Vassileva M (2013) Biochar of animal origin: a sustainable solution ot the global problem of high-grade rock phosphate scarcity? J Sci Food Agric 93:1799–1804
Vierheilig H (2004) Regulatory mechanisms during the plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus interaction. Can J Bot 82:1166–1176
Warnock DD, Lehmann J, Kuyper TW, Rillig MC (2007) Mycorrhizal responses to biochar in soil - concepts and mechanisms. Plant Soil 300:9–20
Warren GP, Robinson JS, Someus E (2009) Dissolution of phosphorus from animal bone char in 12 soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 84:167–178
Wen TJ, Schnable (1994) Analyses of mutrants of 3 genes that influence root hair development in Zea mays (Gramineae) suggest that root hairs are dispensable. Am J Bot 81:833–842
Wopenka B, Pasteris J (2003) Biological apatites: a comparison of bone and tooth mineralization. J Vertebr Paleontol 23:112A–112A
Wopenka B, Pasteris JD (2005) A mineralogical perspective on the apatite in bone. Mater Sci Eng C 25:131–143
Zhu J, Zhang C, Lynch JP (2010) The utility of phenotypic plasticity of root hair length for phosphorus acquisition. Funct Plant Biol 37:313–322
Zwetsloot MJ, Lehmann J, Solomon D (2015) Recycling slaughterhouse waste into fertilizer: how do pyrolysis temperature and biomass additions affect phosphorus availability and chemistry? J Sci Food Agric 95:281–288
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for support from the Towards Sustainability Foundation, CARE-Cornell Impact through Innovations Fund, McKnight Foundation, Bradfield Award, Fulbright and Huygens Talent Scholarship Program. We would also like to thank Cornell Center for Materials Research for help with X-ray Diffraction Analysis under NSF award number DMR-0520404, Berhanu Belay and Gebermedihin Ambaw for support in procuring the soil, and Dawit Solomon for help with data interpretation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Andreas Meyer-aurich.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zwetsloot, M.J., Lehmann, J., Bauerle, T. et al. Phosphorus availability from bone char in a P-fixing soil influenced by root-mycorrhizae-biochar interactions. Plant Soil 408, 95–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2905-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2905-2