Abstract
Key message
The chitinase-mediated defense system in higher plants has been intensively studied from physiological and structural viewpoints. However, the defense system in the most primitive plant species, such as green algae, has not yet been elucidated in details. In this study, we solved the crystal structure of a family CBM-50 LysM module attached to the N-terminus of chitinase from Volvox carteri, and successfully analyzed its chitin-binding ability by NMR spectroscopy and isothermal titration calorimetry. Trp96 of the LysM module appeared to make a CH-π stacking interaction with the reducing end sugar residue of the ligand. We believe the data included in this manuscript provide novel insights into the molecular basis of chitinase-mediated defense system in green algae.
Abstract
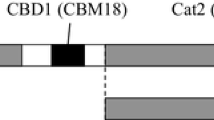
A chitinase from the multicellular green alga, Volvox carteri, contains two N-terminal lysin motifs (VcLysM1 and VcLysM2), that belong to the CBM-50 family, in addition to a catalytic domain. We produced a recombinant protein of VcLysM2 in order to examine its structure and function. The X-ray crystal structure of VcLysM2 was successfully solved at a resolution of 1.2 Å, and revealed that the protein adopts the βααβ fold typical of members belonging to the CBM-50 family. NMR spectra of 13C- and 15N-labeled proteins were analyzed in order to completely assign the main chain resonances of the 1H,15N-HSQC spectrum in a sequential manner. NMR-based titration experiments of chitin oligosaccharides, (GlcNAc)n (n = 3–6), revealed the ligand-binding site of VcLysM2, in which the Trp96 side chain appeared to interact with the terminal GlcNAc residue of the ligand. We then mutated Trp96 to alanine (VcLysM2-W96A), and the mutant protein was characterized. Based on isothermal titration calorimetry, the affinity of (GlcNAc)6 toward VcLysM2 (−6.9 kcal/mol) was found to be markedly higher than that of (GlcNAc)3 (−4.1 kcal/mol), whereas the difference in affinities between (GlcNAc)6 and (GlcNAc)3 in VcLysM2-W96A (−5.1 and −4.0 kcal/mol, respectively) was only moderate. This suggests that the Trp96 side chain of VcLysM2 interacts with the sugar residue of (GlcNAc)6 not with (GlcNAc)3. VcLysM2 appears to preferentially bind (GlcNAc)n with longer chains and plays a major role in the degradation of the chitinous components of enzyme targets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott DW, van Bueren AL (2014) Using structure to inform carbohydrate binding module function. Curr Opin Struct Biol 28:32–40
Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Zwart PH, Adams PD (2012) Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 68:352–367
Amon P, Haas E, Sumper M (1998) The sex-inducing pheromone and wounding trigger the same set of genes in the multicellular green alga Volvox. Plant Cell 10:781–789
Andre G, Leenhouts K, Hols P, Dufrêne YF (2008) Detection and localization of single LysM-peptidoglycan interactions. J Bacteriol 190:7079–7086
Arakane Y, Taira T, Ohnuma T, Fukamizo T (2012) Chitin-related enzymes in agro-biosciences. Curr Drug Targets 13:442–470
Asensio JL, Ardá A, Cañada FJ, Jiménez-Barbero J (2013) Carbohydrate-aromatic interactions. Acc Chem Res 46:946–954
Bailey S (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50:760–763
Béliveau C, Potvin C, Trudel J, Asselin A, Bellemare G (1991) Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli of a Streptococcus faecalis autolysin. J Bacteriol 173:5619–5623
Boraston AB, Notenboom V, Warren RAJ, Kilburn DG, Rose DR, Davies G (2003) Structure and ligand binding of carbohydrate-binding module CsCBM6-3 reveals similarities with fucose-specific lectins and “galactose-binding” domains. J Mol Biol 327:659–669
Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2004) Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J 382:769–781
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Emsley P, Cowtan K (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60:2126–2132
Garvey KJ, Saedi MS, Ito J (1986) Nucleotide sequence of Bacillus phage phi 29 genes 14 and 15: homology of gene 15 with other phage lysozymes. Nucleic Acids Res 14:10001–10008
Grondin JM, Chitayat S, Ficko-Blean E, Houliston S, Arrowsmith CH, Boraston AB, Smith SP (2014) An unusual mode of galactose recognition by a family 32 carbohydrate-binding module. J Mol Biol 426:869–880
Grzesiek S, Bax A (1992) Correlating backbone amide and site chain resonances in larger proteins by multiple relayed triple resonance NMR. J Am Chem Soc 114:6291–6293
Gust AA, Willmann R, Desaki Y, Grabherr HM, Nürnberger T (2012) Plant LysM proteins: modules mediating symbiosis and immunity. Trends Plant Sci 17:495–502
Inamine S, Onaga S, Ohnuma T, Fukamizo T, Taira T (2015) Purification, cDNA cloning, and characterization of LysM-containing plant chitinase from horsetail (Equisetum arvense). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79:1296–1304
Kay LE, Ikura M, Tschudin R, Bax A (1990) Three-dimensional triple-resonance NMR spectroscopy of isotopically enriched proteins. J Magn Reson 89:496–514
Kirk DL, Kirk MM (1986) Heat shock elicits production of sexual inducer in Volvox. Science 231:51–54
Lehtio J, Sugiyama J, Gustavsson M, Fransson L, Linder M, Teeri TT (2003) The binding specificity and affinity determinants of family 1 and family 3 cellulose binding modules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:484–489
Lovell SC, Davis IW, Arendall WB 3rd, de Bakker PI, Word JM, Prisant MG, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2003) Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi, psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins 50:437–450
McCoy AJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Storoni LC, Read RJ (2005) Likelihood-enhanced fast translation functions. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:458–464
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618
Mulder L, Lefebvre B, Cullimore J, Imberty A (2006) LysM domains of Medicago truncatula NFP protein involved in Nod factor perception. Glycosylation state, molecular modeling and docking of chitooligosaccharides and Nod factors. Glycobiology 16:801–809
Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ (1997) Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr D 53:240–255
Notenboom V, Boraston AB, Chiu P, Freelove AC, Kilburn DG, Rose DR (2001) Recognition of cello-oligosaccharides by a family 17 carbohydrate-binding module: an X-ray crystallographic, thermodynamic and mutagenic study. J Mol Biol 314:797–806
Ohnuma T, Onaga S, Murata K, Taira T, Katoh E (2008) LysM domains from Pteris ryukyuensis chitinase-A: a stability study and characterization of the chitin-binding site. J Biol Chem 283:5178–5187
Ohnuma T, Sørlie M, Fukuda T, Kawamoto N, Taira T, Fukamizo T (2011) Chitin oligosaccharide binding to a family GH19 chitinase from the moss Bryum coronatum. FEBS J 278:3991–4001
Ohnuma T, Numata T, Osawa T, Mizuhara M, Lampela O, Juffer AH, Skriver K, Fukamizo T (2011) A class V chitinase from Arabidopsis thaliana: gene responses, enzymatic properties, and crystallographic analysis. Planta 234:123–137
Onaga S, Taira T (2008) A new type of plant chitinase containing LysM domains from a fern (Pteris ryukyuensis): roles of LysM domains in chitin binding and antifungal activity. Glycobiology 18:414–423
Otwinowski, Minor W Z (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 276:307–326
Pace CN, Vajdos F, Fee L, Grimsley G, Gray T (1995) How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci. 4: 2411–2423
Pell G, Williamson MP, Walters C, Du H, Gilbert HJ, Bolam DN (2003) Importance of hydrophobic and polar residues in ligand binding in the family 15 carbohydrate-binding module from Cellvibrio japonicus Xyn10C. BioChemistry 42:9316–9323
Petutschnig EK, Jones AM, Serazetdinova L, Lipka U, Lipka V (2010) The lysin motif receptor-like kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 is a major chitin-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and subject to chitin-induced phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 285:28902–28911
Prochnik SE, Umen J, Nedelcu AM, Hallmann A, Miller SM, Nishii I, Ferris P, Kuo A, Mitros T, Fritz-Laylin LK, Hellsten U, Chapman J, Simakov O, Rensing SA, Terry A, Pangilinan J, Kapitonov V, Jurka J, Salamov A, Shapiro H, Schmutz J, Grimwood J, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Grigoriev IV, Schmitt R, Kirk D, Rokhsar DS (2010) Genomic analysis of organismal complexity in the multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Science 329:223–226
Rupley JA (1964) The hydrolysis of chitin by concentrated hydrochloric acid, and the prepration of low-molecular-weight substrates for lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta 83:245–255
Schägger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:368–379
Takenaka Y, Nakano S, Tamoi M, Sakuda S, Fukamizo T (2009) Chitinase gene expression in response to environmental stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana: chitinase inhibitor allosamidin enhances stress tolerance. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1066–1071
Tormo J, Lamed R, Chirino AJ, Morag E, Bayer EA, Shoham Y, Steitz TA (1996) Crystal structure of a bacterial family-III cellulose-binding domain: a general mechanism for attachment to cellulose. EMBO J 15:5739–5751
Umen JG, Olson BJ (2012) Genomics of volvocine algae. Adv Bot Res 64:185–243
Wishart DS, Bigam CG, Yao J, Abildgaard F, Dyson HJ, Oldfield E, Markley JL, Sykes BD (1995) 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shift referencing in biomolecular NMR. J Biomol NMR 6:135–140
Wong JE, Midtgaard SR, Gysel K, Thygesen MB, Sørensen KK, Jensen KJ, Stougaard J, Thirup S, Blaise M (2015) An intermolecular binding mechanism involving multiple LysM domains mediates carbohydrate recognition by an endopeptidase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71:592–605
Funding
This work was supported by “Strategic Project to Support the Formation of Research Bases at Private Universities: Matching Fund Subsidy from MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan)”, 2011–2015 (S1101035), to TF. YK was supported by a Research Fellowship for Young Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (16J10483).
Author contributions
YK and TO designed research; YK performed research; YK, TF, TN, and TO analyzed data; and YK and TF wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitaoku, Y., Fukamizo, T., Numata, T. et al. Chitin oligosaccharide binding to the lysin motif of a novel type of chitinase from the multicellular green alga, Volvox carteri . Plant Mol Biol 93, 97–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0549-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0549-5