Abstract
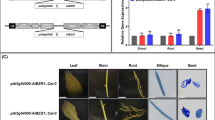
Soybean (Glycine max) is one of the most important crops in the world, and its yield is largely determined by grain weight and grain size. However, the genes that regulate soybean seed size have not been identified. CYP78A, which is highly conserved within terrestrial plants, regulates organ development. In Arabidopsis, AtCYP78A5/KLU has been shown to determine seed size. In the present study, soybean CYP78A72 (GmCYP78A72), one of the orthologs of KLU, was over-expressed in both Arabidopsis and soybean to examine its function in plant development. GmCYP78A72 heterologous expression in Arabidopsis resulted in enlarged sepals, petals, seeds and carpel. Over-expression of GmCYP78A72 in soybean resulted in increased pea size, which is an extremely desirable trait for enhancing productivity. Moreover, knock-down of GmCYP78A72 does not reduce grain size. However, silencing of GmCYP78A57, GmCYP78A70 and GmCYP78A72 genes in triplet reduces the seed size significantly indicating functional redundancy of these three GmCYP78A genes. In conclusion, we investigated the role of CYP78A in soybean seed regulation, and our strategy can be effectively used to engineer large seed traits in soybean varieties as well as other crops.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affolter M, Basler K (2007) The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat Rev Genet 8:663–674
Ainsworth EA, Yendrek CR, Skoneczka JA, Long SP (2012) Accelerating yield potential in soybean: potential targets for biotechnological improvement. Plant Cell Environ 35:38–52
Anastasiou E, Kenz S, Gerstung M, MacLean D, Timmer J, Fleck C, Lenhard M (2007) Control of plant organ size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent intercellular signaling. Dev Cell 13:843–856
Bak S, Beisson F, Bishop G, Hamberger B, Höfer R, Paquette S, Werck-Reichhart D (2011) Cytochromes P450. The Arabidopsis book. ASPB, Rockville
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Coen ES, Romero JM, Doyle S, Elliott R, Murphy G, Carpenter R (1990) Floricaula: a homeotic gene required for flower development in antirrhinum majus. Cell 63:1311–1322
Coomes DA, Grubb PJ (2003) Colonization, tolerance, competition and seed-size variation within functional groups. Trends Ecol Evol 18:283–291
Day SJ, Lawrence PA (2000) Measuring dimensions: the regulation of size and shape. Development 127:2977–2987
Disch S, Anastasiou E, Sharma VK, Laux T, Fletcher JC, Lanhard M (2006) The E3 ubiquitin ligase BIG BROTHER controls Arabidopsis organ size in a dosage-dependent manner. Curr Biol 16:272–279
Fang W, Wang Z, Cui R, Li J, Li Y (2012) Maternal control of seed size by EOD3/CYP78A6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 70:929–939
Gómez JM (2004) Bigger is not always better: conflicting selective pressures on seed size in Quercus ilex. Evolution 58:71–80
Halliday KJ (2004) Plant hormones: the interplay of brassinosteroids and auxin. Curr Biol 14:1008–1010
Horiguchi G, Ferjani A, Fujikura U, Tsukaya H (2006) Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion in the control of leaf size in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 119:37–42
Hu Z, Zhang H, Kan G, Ma D, Zhang D, Shi G, Hong D, Zhang G, Yu D (2013) Determination of the genetic architecture of seed size and shape via linkage and association analysis in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Genetica 141:247–254
Imaishi H, Matsuo S, Swai E, Ohawa H (2000) CYP78A1 preferentially expressed in developing inflorescences of Zea mays encoded a cytochrome P450-dependent lauric acid 12-monooxygenase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1696–1701
Joshi N, Fass J (2011) Sickle: A sliding-window, adaptive, quality-based trimming tool for FastQ files (version 1.33) [software]
Kandoth PK, Heinz R, Yeckel G, Gross NW, Juvale PS, Hill J, Whitham SA, Baum TJ, Mitchum MG (2013) A virus-induced gene silencing method to study soybean cyst nematode parasitism in Glycine max. BMC Res Notes 6:255. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-6-255
Katsumata T, Fukazawa J, Magome H, Jikumaru Y, Kamiya Y, Natsume M, Kawaide H, Yamaguchi S (2011) Involvement of the CYP78A subfamily of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in protonema growth and gametophore formation in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:331–336
Lam HM et al (2010) Resequencing of 31 wild and cultivated soybean genomes identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection. Nat Genet 42:1053–1059
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D302–D305
Li Y, Zheng L, Corke F, Smith C, Bevan MW (2008) Control of final seed and organ size by the DA1 gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Denes Dev 22:1331–1336
McKenna A et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a map reduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Miyoshi K, Ahn BO, Kawakatsu T, Ito Y, Itoh J, Nagato Y, Kurata N (2004) PLASTOCHRON1, a timekeeper of leaf initiation in rice, encodes cytochrome P450. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:875–880
Nadeau JA, Zhang XS, Li J, O’Neill SD (1996) Ovule development: identification of stage-specific and tissue-specific cDNAs. Plant Cell 8:213–239
Nagasawa N, Hibara K, Heppard EP, Vander Velden KA, Luck S, Beatty M, Nagato Y, Sakai H (2013) GIANT EMBRYO encodes CYP78A13, required for proper size balance between embryo and endosperm in rice. Plant J 75:592–605
Nelson DR (2006) Plant cytochrome P450s from moss to poplar. Phytochem Rev 5:193–204
Niu Y, Xu Y, Liu XF, Yang SX, Wei SP, Xie FT, Zhang YM (2013) Association mapping for seed size and shape traits in soybean cultivars. Mol Breed 31:785–794
Rech EL, Vianna GR, Aragao FJ (2008) High-efficiency transformation by biolistics of soybean, common bean and cotton transgenic plants. Nat Protoc 3:410–418
Rensing SA et al (2008) The Physcomitrella genome reveals evolutionary insights into the conquest of land by plants. Science 319:64–69
Schuler MA, Werck-Reichhart D (2003) Functional genomics of P450s. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:629–667
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008) Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1023–1028
Silvertown JW (1981) Seed size, life span, and germination date as coadapted features of plant life history. Am Nat 118:860–864
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Sotelo-Silveira M, Cucinotta M, Chauvin AL, Chavez Montes RA, Colombo L, Marsch-Martinez N, de Folter S (2013) Cytochrome P450 CYP78A9 is involved in Arabidopsis reproductive development. Plant Physiol 162:779–799
Sundaresan V (2005) Control of seed size in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:17887–17888
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D (2008) Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20:1231–1243
Wang X, Li Y, Zhang H, Sun G, Zhang W, Qiu L (2015) Evolution and association analysis of GmCYP78A10 gene with seed size/weight and pod number in soybean. Mol Biol Rep 42:489–496
Weir BS, Hill WG (2002) Estimating F-statistics. Annu Rev Genet 36:721–750
Xia T, Li N, Jack D, Li J, Andrei K, Michael WB, Gao F, Li Y (2013) The Ubiquitin receptor DA1 Interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase DA2 to regulate seed and organ size in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3347–3359
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. CABIOS 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AM (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Ye M, Zhang M, Yang S, Shao Q, An H, Cao Z, Feng X (2011) (2010) Optimization of biolistics transformation of embryonic tips of soybean (Glycine max) mature seeds. Soybean Sci 30:20–23
Zhang C, Ghabrial SA (2006) Development of bean pod mottle virus-based vectors for stable protein expression and sequence-specific virus-induced gene silencing in soybean. Virology 344:401–411
Zhang C, Yang C, Whitham SA, Hill JH (2009) Development and use of an efficient DNA-based viral gene silencing vector for soybean. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:123–131
Acknowledgments
We thank Stefan Cerbin (Michigan State University) for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31171571 and 91131008) and the China National Transgenic Major Program (Grant No. 2014ZX0800943B) and was also supported by One Hundred Person Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to be declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2015_392_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figs. 1. Expression pattern of GmCYP78A in soybean. Total RNA was separately extracted from root, root nodules, inflorescence (3-5 mm young inflorescence), petals and sepals, leaf bud, mature leaves and tender pods (5 mm green pod) of soybean ecotype Williams82. We designated GmCYP78A70 expression in the mature leaves as the benchmark (a value of 1)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Dai, A., Wei, H. et al. Arabidopsis KLU homologue GmCYP78A72 regulates seed size in soybean. Plant Mol Biol 90, 33–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0392-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0392-0