Abstract
Although the main genes in rice involved in the biosynthesis of secondary wall components have been characterized, the molecular mechanism underlying coordinated regulation of genes expression is not clear. In this study, we reported a new rice variety, cef1, showed the culm easily fragile (CEF) without other concomitant phenotypes. The CEF1 gene encodes a MYB family transcription factor OsMYB103L, was cloned based on map-based approach. Bioinformatics analyses indicated that CEF1 belongs to the R2R3-MYB subfamily and highly similar to Arabidopsis AtMYB103. Expression pattern analysis indicated that CEF1 is mainly expressed in internodes and panicles. Biochemical assays demonstrated that OsMYB103L is a nuclear protein and shows high transcriptional activation activity at C-terminus. OsMYB103L mediates cellulose biosynthesis and secondary walls formation mainly through directly binding the CESA4, CESA7, CESA9 and BC1 promoters and regulating their expression. OsMYB103L may also function as a master switch to regulate the expression of several downstream TFs, which involved in secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Furthermore, OsMYB103L physically interacts with SLENDER RICE1 (SLR1), a DELLA repressor of GA signaling, and involved in GA-mediated regulation of cellulose synthesis pathway. Our findings revealed that OsMYB103L plays an important role in GA-regulating secondary cell wall synthesis, and the manipulation of this gene provide a new strategy to help the straw decay in soil.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bracha-Drori K, Shichrur K, Katz A, Oliva M, Angelovici R, Yalovsky S, Ohad N (2004) Detection of protein-protein interactions in plants using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J 40:419–427
Cabiles DMS, Angeles OR, Johnson-Beebout SE, Sanchez PB, Buresh RJ (2008) Faster residue decomposition of brittle stem rice mutant due to finer breakage during threshing. Soil Tillage Res 98:211–216
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15:573–581
Fu X (2002) Gibberellin-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation of the barley DELLA protein SLN1 repressor. Plant Cell Online 14:3191–3200
Gunnarsson S, Marstorp H (2002) Carbohydrate composition of plant materials determines N mineralisation. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 62:175–183
Hirano K, Kotake T, Kamihara K, Tsuna K, Aohara T, Kaneko Y, Takatsuji H, Tsumuraya Y, Kawasaki S (2010) Rice BRITTLE CULM 3 (BC3) encodes a classical dynamin OsDRP2B essential for proper secondary cell wall synthesis. Planta 232:95–108
Hirano K, Aya K, Kondo M, Okuno A, Morinaka Y, Matsuoka M (2012) OsCAD2 is the major CAD gene responsible for monolignol biosynthesis in rice culm. Plant Cell Rep 31:91–101
Hirano K, Kondo M, Aya K, Miyao A, Sato Y, Antonio BA, Namiki N, Nagamura Y, Matsuoka M (2013) Identification of transcription factors involved in rice secondary cell wall formation. Plant Cell Physiol 54:1791–1802
Huang D, Wang S, Zhang B, Shang-Guan K, Shi Y, Zhang D, Liu X, Wu K, Xu Z, Fu X, Zhou Y (2015) A gibberellin-mediated DELLA-NAC signaling cascade regulates cellulose synthesis in rice. Plant Cell 27:1681–1696
Jin H, Martin C (1999) Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol Biol 41:577–585
Johnson SE, Angeles OR, Brar DS, Buresh RJ (2006) Faster anaerobic decomposition of a brittle straw rice mutant: implications for residue management. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1880–1892
Katiyar A, Smita S, Lenka SK, Rajwanshi R, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2012) Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genom 13:544
Keegstra K (2010) Plant cell walls. Plant Physiol 154:483–486
Kim WC, Ko JH, Kim JY, Kim JM, Bae HJ, Han KH (2013) MYB46 directly regulates the gene expression of secondary wall-associated cellulose synthases in Arabidopsis. Plant J 73:26–36
Ko JH, Jeon HW, Kim WC, Kim JY, Han KH (2014) The MYB46/MYB83-mediated transcriptional regulatory programme is a gatekeeper of secondary wall biosynthesis. Ann Bot 114:1099–1107
Kotake T, Aohara T, Hirano K, Sato A, Kaneko Y, Tsumuraya Y, Takatsuji H, Kawasaki S (2011) Rice Brittle culm 6 encodes a dominant-negative form of CesA protein that perturbs cellulose synthesis in secondary cell walls. J Exp Bot 62:2053–2062
Kubo M, Udagawa M, Nishikubo N, Horiguchi G, Yamaguchi M, Ito J, Mimura T, Fukuda H, Demura T (2005) Transcription switches for protoxylem and metaxylem vessel formation. Genes Dev 19:1855–1860
Li Y (2003) BRITTLE CULM1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein, affects the mechanical properties of rice plants. Plant Cell Online 15:2020–2031
Li M, Xiong G, Li R, Cui J, Tang D, Zhang B, Pauly M, Cheng Z, Zhou Y (2009a) Rice cellulose synthase-like D4 is essential for normal cell-wall biosynthesis and plant growth. Plant J 60:1055–1069
Li X, Yang Y, Yao J, Chen G, Li X, Zhang Q, Wu C (2009b) FLEXIBLE CULM 1 encoding a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase controls culm mechanical strength in rice. Plant Mol Biol 69:685–697
Li J, Jiang J, Qian Q, Xu Y, Zhang C, Xiao J, Du C, Luo W, Zou G, Chen M, Huang Y, Feng Y, Cheng Z, Yuan M, Chong K (2011) Mutation of rice BC12/GDD1, which encodes a kinesin-like protein that binds to a GA biosynthesis gene promoter, leads to dwarfism with impaired cell elongation. Plant Cell 23:628–640
Liu L, Shang-Guan K, Zhang B, Liu X, Yan M, Zhang L, Shi Y, Zhang M, Qian Q, Li J, Zhou Y (2013a) Brittle Culm1, a COBRA-like protein, functions in cellulose assembly through binding cellulose microfibrils. PLoS Genet 9:e1003704
Liu Z, Wu Y, Yang F, Zhang Y, Chen S, Xie Q, Tian X, Zhou JM (2013b) BIK1 interacts with PEPRs to mediate ethylene-induced immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:6205–6210
McCarthy RL, Zhong R, Ye ZH (2009) MYB83 is a direct target of SND1 and acts redundantly with MYB46 in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1950–1964
McCarthy RL, Zhong R, Fowler S, Lyskowski D, Piyasena H, Carleton K, Spicer C, Ye ZH (2010) The poplar MYB transcription factors, PtrMYB3 and PtrMYB20, are involved in the regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1084–1090
Ohman D, Demedts B, Kumar M, Gerber L, Gorzsas A, Goeminne G, Hedenstrom M, Ellis B, Boerjan W, Sundberg B (2013) MYB103 is required for FERULATE-5-HYDROXYLASE expression and syringyl lignin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis stems. Plant J 73:63–76
Ohta M, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H (2000) Three ethylene-responsive transcription factors in tobacco with distinct transactivation functions. Plant J 22:29–38
Rahn C, Bending G, Turner M, Lillywhite R (2003) Management of N mineralization from crop residues of high N content using amendment materials of varying quality. Soil Use Manag 19:193–200
Raineri D, Bottino P, Gordon M, Nester E (1990) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Nat Biotechnol 8:33–38
Riechmann JL (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110
Romero I, Fuertes A, Benito MJ, Malpica JM, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (1998) More than 80R2R3-MYB regulatory genes in the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 14:273–284
Song XQ, Liu LF, Jiang YJ, Zhang BC, Gao YP, Liu XL, Lin QS, Ling HQ, Zhou YH (2013) Disruption of secondary wall cellulose biosynthesis alters cadmium translocation and tolerance in rice plants. Mol Plant 6:768–780
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456
Sun H, Qian Q, Wu K, Luo J, Wang S, Zhang C, Ma Y, Liu Q, Huang X, Yuan Q, Han R, Zhao M, Dong G, Guo L, Zhu X, Gou Z, Wang W, Wu Y, Lin H, Fu X (2014) Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate nitrogen-use efficiency in rice. Nat Genet 46:652–656
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanaka K (2003) Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol 133:73–83
Taylor NG, Scheible WR, Cutler S, Somerville CR, Turner SR (1999) The irregular xylem3 locus of Arabidopsis encodes a cellulose synthase required for secondary cell wall synthesis. Plant Cell 11:769–780
Taylor NG, Laurie S, Turner SR (2000) Multiple cellulose synthase catalytic subunits are required for cellulose synthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2529–2540
Taylor NG, Howells RM, Huttly AK, Vickers K, Turner SR (2003) Interactions among three distinct CesA proteins essential for cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1450–1455
Tian G, Kang B, Brussaard L (1992) Biological effects of plant residues with contrasting chemical compositions under humid tropical conditions—decomposition and nutrient release. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1051–1060
Updegraff DM (1969) Semimicro determination of cellulose inbiological materials. Anal Biochem 32:420–424
Vega-Sanchez ME, Verhertbruggen Y, Christensen U, Chen X, Sharma V, Varanasi P, Jobling SA, Talbot M, White RG, Joo M, Singh S, Auer M, Scheller HV, Ronald PC (2012) Loss of cellulose synthase-like F6 function affects mixed-linkage glucan deposition, cell wall mechanical properties, and defense responses in vegetative tissues of rice. Plant Physiol 159:56–69
Wadsworth GJ, Redinbaugh MG, Scandalios JG (1988) A procedure for the small-scale isolation of plant RNA suitable for RNA blot analysis. Anal Biochem 172:279–283
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954
Wu B, Zhang B, Dai Y, Zhang L, Shang-Guan K, Peng Y, Zhou Y, Zhu Z (2012) Brittle culm15 encodes a membrane-associated chitinase-like protein required for cellulose biosynthesis in rice. Plant Physiol 159:1440–1452
Xiong G, Li R, Qian Q, Song X, Liu X, Yu Y, Zeng D, Wan J, Li J, Zhou Y (2010) The rice dynamin-related protein DRP2B mediates membrane trafficking, and thereby plays a critical role in secondary cell wall cellulose biosynthesis. Plant J 64:56–70
Yan C, Yan S, Zeng X, Zhang Z, Gu M (2007) Fine mapping and isolation of Bc7(t), allelic to OsCesA4. J Genet Genomics 34:1019–1027
Yang C, Li D, Liu X, Ji C, Hao L, Zhao X, Li X, Chen C, Cheng Z, Zhu L (2014) OsMYB103L, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, influences leaf rolling and mechanical strength in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:158
Zhang ZB, Zhu J, Gao JF, Wang C, Li H, Li H, Zhang HQ, Zhang S, Wang DM, Wang QX, Huang H, Xia HJ, Yang ZN (2007) Transcription factor AtMYB103 is required for anther development by regulating tapetum development, callose dissolution and exine formation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:528–538
Zhang B, Deng L, Qian Q, Xiong G, Zeng D, Li R, Guo L, Li J, Zhou Y (2009) A missense mutation in the transmembrane domain of CESA4 affects protein abundance in the plasma membrane and results in abnormal cell wall biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 71:509–524
Zhang J, Li W, Xiang T, Liu Z, Laluk K, Ding X, Zou Y, Gao M, Zhang X, Chen S, Mengiste T, Zhang Y, Zhou JM (2010a) Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell Host Microbe 7:290–301
Zhang M, Zhang B, Qian Q, Yu Y, Li R, Zhang J, Liu X, Zeng D, Li J, Zhou Y (2010b) Brittle Culm 12, a dual-targeting kinesin-4 protein, controls cell-cycle progression and wall properties in rice. Plant J 63:312–328
Zhang S, Fang Z, Zhu J, Gao J, Yang Z (2010c) OsMYB103 is required for rice anther development by regulating tapetum development and exine formation. Chin Sci Bull 55:3288–3297
Zhang B, Liu X, Qian Q, Liu L, Dong G, Xiong G, Zeng D, Zhou Y (2011) Golgi nucleotide sugar transporter modulates cell wall biosynthesis and plant growth in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5110–5115
Zhao Q, Dixon RA (2011) Transcriptional networks for lignin biosynthesis: more complex than we thought? Trends Plant Sci 16:227–233
Zhong R, Ye ZH (2012) MYB46 and MYB83 bind to the SMRE sites and directly activate a suite of transcription factors and secondary wall biosynthetic genes. Plant Cell Physiol 53:368–380
Zhong R, Demura T, Ye ZH (2006) SND1, a NAC domain transcription factor, is a key regulator of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:3158–3170
Zhong R, Richardson EA, Ye ZH (2007a) The MYB46 transcription factor is a direct target of SND1 and regulates secondary wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2776–2792
Zhong R, Richardson EA, Ye ZH (2007b) Two NAC domain transcription factors, SND1 and NST1, function redundantly in regulation of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Planta 225:1603–1611
Zhong R, Lee C, Zhou J, McCarthy RL, Ye ZH (2008) A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:2763–2782
Zhong R, Lee C, McCarthy RL, Reeves CK, Jones EG, Ye ZH (2011) Transcriptional activation of secondary wall biosynthesis by rice and maize NAC and MYB transcription factors. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1856–1871
Zhou Y, Li S, Qian Q, Zeng D, Zhang M, Guo L, Liu X, Zhang B, Deng L, Liu X, Luo G, Wang X, Li J (2009) BC10, a DUF266-containing and Golgi-located type II membrane protein, is required for cell-wall biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J 57:446–462
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 31301297), The Science and Technology Service program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant KFJ-EW-STS-083), the State Key Laboratory of Plant Cell and Chromosome Engineering(Grant PCCE-KF-2014-03) and the Ministry of Agriculture of China for Transgenic Research (Grant 2014ZX08009-35B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yafeng Ye and Binmei Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
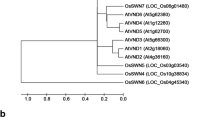
CEF1 is a R2R3-MYB family transcription factor. A, Prediction of the domain structure of CEF1. B, Phylogenetic tree of the CEF1 homologs in Arabidopsis and rice. CEF1 and AtMYB103 have a very high homology. C, CEF1/MYB103L is a Nuclear-localized protein. A rice protoplast cell expressing MYB103L-GFP, indicating that CEF1/MYB103L is a Nuclear-localized protein. DAPI is a Nuclear dye (TIFF 542 kb)
Supplemental Figure 2
Transcriptional activation of CEF1/MYB103L. A, Transactivation activity of MYB103L in a yeast assay. Transformants harbouring pBD-MYB103L, the positive control pGAL4 and the negative control pBD were streaked onto SD-Trp or SD-Trp, His, Ade medium to determine growth. B, Effector and reporter constructs used in the Arabidopsis protoplast transient assay (TIFF 645 kb)
Supplemental Figure 3
Expression of cellulose synthesis related genes. A, the expression of OsCESA genes in NIL-CEF1 and NIL-cef1. B, the expression of CESA4, 7, 9 in NIL-CEF1 and NIL-cef1 p35S::myc-MYB103L transgenic plants. The Actin1 was used as internal control. All data given as mean ± SE (n = 3) (TIFF 436 kb)
Supplemental Figure 4
CEF1/OsMYB103L expression in overexpression (OX) transgenic plants (NIL-cef1 p35S::myc-MYB103L) as determined by qRT-PCR. The Actin was used as internal control. Error bars, SE of three biological replicates (TIFF 157 kb)
Supplemental Figure 5
MYB103L can’t binding SND2, MYB42/85, MYB52/54 promoters. Yeast one-hybrid assay showing the activity of LacZ reporters driven by BC1, SND2, MYB42/85, MYB52/54 promoters and activated by activation domain (AD) fusion effectors. The empty pB42AD and pLacZi were used as negative control (TIFF 469 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Liu, B., Zhao, M. et al. CEF1/OsMYB103L is involved in GA-mediated regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 89, 385–401 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0376-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0376-0