Abstract
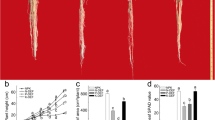
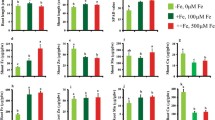
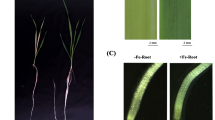
Plants are often subjected to iron (Fe)-deficiency stress because of its low solubility. Plants have evolved two distinct strategies to solubilize and transport Fe to acclimate to this abiotic stress condition. Transcriptomic profiling analysis was performed using Illumina digital gene expression to understand the mechanism underlying resistance responses of roots to Fe starvation in maize, an important Strategy II plant. A total of 3,427, 4,069, 4,881, and 2,610 genes had significantly changed expression levels after Fe-deficiency treatments of 1, 2, 4 or 7 days, respectively. Genes involved in 2′-deoxymugineic acid (DMA) synthesis, secretion, and Fe(III)–DMA uptake were significantly induced. Many genes related to plant hormones, protein kinases, and protein phosphatases responded to Fe-deficiency stress, suggesting their regulatory roles in response to the Fe-deficiency stress. Functional annotation clustering analysis, using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery, revealed maize root responses to Fe starvation. This resulted in 38 functional annotation clusters: 25 for up-regulated genes, and 13 for down-regulated ones. These included genes encoding enzymes involved in the metabolism of carboxylic acids, isoprenoids and aromatic compounds, transporters, and stress response proteins. Our work provides integrated information for understanding maize response to Fe-deficiency stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audic S, Claverie J-M (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7:986–995. doi:10.1101/gr.7.10.986
Bach L, Gissot L, Marion J et al (2011) Very-long-chain fatty acids are required for cell plate formation during cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Cell Sci 124:3223–3234. doi:10.1242/jcs.074575
Bashir K, Inoue H, Nagasaka S et al (2006) Cloning and characterization of deoxymugineic acid synthase genes from graminaceous plants. J Biol Chem 281:32395–32402. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604133200
Brosché M, Vinocur B, Alatalo ER et al (2005) Gene expression and metabolite profiling of Populus euphratica growing in the Negev desert. Genome Biol 6:R101. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-r101
Buckhout TJ, Yang TJ, Schmidt W (2009) Early iron-deficiency-induced transcriptional changes in Arabidopsis roots as revealed by microarray analyses. BMC Genom 10:147. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-147
Chen Y, Barak P (1982) Iron nutrition of plants in calcareous soils. Adv Agron 35:217–240
Curie C, Panaviene Z, Loulergue C et al (2001) Maize yellow stripe 1 encodes a membrane protein directly involved in Fe(III) uptake. Nature 409:346–349. doi:10.1038/35053080
Donnini S, Prinsi B, Negri AS et al (2010) Proteomic characterization of iron deficiency responses in Cucumis sativus L. roots. BMC Plant Biol 10:268. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-268
Draghici S, Khatri P, Eklund AC et al (2006) Reliability and reproducibility issues in DNA microarray measurements. Trends Genet 22:101–109. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2005.12.005
Eckardt NA (2008) Oxylipin signaling in plant stress responses. Plant Cell 20:495–497. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.059485
Farmer EE, Alméras E, Krishnamurthy V (2003) Jasmonates and related oxylipins in plant responses to pathogenesis and herbivory. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:372–378. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00045-1
Forde BG, Lea PJ (2007) Glutamate in plants: metabolism, regulation, and signalling. J Exp Bot 58:2339–2358. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm121
Forner-Giner M, Llosá M, Carrasco J et al (2010) Differential gene expression analysis provides new insights into the molecular basis of iron deficiency stress response in the citrus rootstock Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. J Exp Bot 61:483–490. doi:10.1093/jxb/erp328
Franke R, Höfer R, Briesen I et al (2009) The DAISY gene from Arabidopsis encodes a fatty acid elongase condensing enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of aliphatic suberin in roots and the chalaza-micropyle region of seeds. Plant J 57:80–95. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03674.x
Hansen NC, Hopkins BG, Ellsworth JW et al (2006) Iron nutrition in field crops. In: Barton LL, Abadia J (eds) Iron nutrition in plants and rhizospheric microorganisms. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 23–59
Hindt MN, Guerinot ML (2012) Getting a sense for signals: regulation of the plant iron deficiency response. BBA-Mol Cell Res 1823:1521–1530. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.03.010
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Bull 347:36–39
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2008) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1–13. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn923
Inoue H, Kobayashi T, Nozoye T et al (2009) Rice OsYSL15 is an iron-regulated iron (III)–deoxymugineic acid transporter expressed in the roots and is essential for iron uptake in early growth of the seedlings. J Biol Chem 284:3470–3479. doi:10.1074/jbc.M806042200
Ivanov R, Brumbarova T, Bauer P (2012) Fitting into the harsh reality: regulation of iron-deficiency responses in dicotyledonous plants. Mol Plant 5:27–42. doi:10.1093/mp/ssr065
Kachroo A, Kachroo P (2009) Fatty acid-derived signals in plant defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:153–176. doi:10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081820
Kishor PBK, Sangam S, Amrutha RN et al (2005) Regulation of praline biosynthesis, degradation, uptake and transport in higher plants: its implications in plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. Curr SCI India 88:424–438
Kobayashi T, Nishizawa NK (2012) Iron uptake, translocation, and regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:131–152. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105522
Kobayashi T, Suzuki M, Inoue H et al (2005) Expression of iron-acquisition-related genes in iron-deficient rice is co-ordinately induced by partially conserved iron-deficiency-responsive elements. J Exp Bot 56:1305–1316. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri131
Kobayashi T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2010) Recent insights into iron homeostasis and their application in graminaceous crops. Proc Jpn Acad, Ser B 86:900–913. doi:10.2183/pjab.86.900
Lan P, Li W, Wen T-N et al (2011) iTRAQ protein profile analysis of Arabidopsis roots reveals new aspects critical for iron homeostasis. Plant Physiol 155:821–834. doi:10.1104/pp.110.169508
Lan P, Li W, Schmidt W (2013) A digital compendium of genes mediating the reversible phosphorylation of proteins in Fe-deficient Arabidopsis roots. Front Plant Sci 4:173. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00173
Landsberg EC (1982) Transfer cell formation in the root epidermis: a prerequisite for Fe-efficiency? J Plant Nutr 5:415–432
Li J, Wu XD, Hao ST et al (2008) Proteomic response to iron deficiency in tomato root. Proteomics 8:2299–2311. doi:10.1002/pmic.200700942
Lin B, Wechsler J, Hood L (2010) Signal sequencing for gene expression profiling. In: Yegnasubramanian S, Isaacs WB (eds) Modern molecular biology: approaches for unbiased discovery in cancer research. Springer, New York, pp 87–115
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lugan R, Niogret MF, Leport L et al (2010) Metabolome and water homeostasis analysis of Thellungiella salsuginea suggests that dehydration tolerance is a key response to osmotic stress in this halophyte. Plant J 64:215–229. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04323.x
Marschner H, Römheld V (1994) Strategies of plants for acquisition of iron. Plant Soil 165:261–274. doi:10.1007/BF00008069
Maurer F, Müller S, Bauer P (2011) Suppression of Fe deficiency gene expression by jasmonate. Plant Physiol Bioch 49:530–536. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.01.025
Müller M, Schmidt W (2004) Environmentally induced plasticity of root hair development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:409–419. doi:10.1104/pp.103.029066
Murata Y, Ma JF, Yamaji N et al (2006) A specific transporter for iron (III)–phytosiderophore in barley roots. Plant J 46:563–572. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02714.x
Nagasaka S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi-Itai R et al (2009) Time course analysis of gene expression over 24 hours in Fe-deficient barley roots. Plant Mol Biol 69:621–631. doi:10.1007/s11103-008-9443-0
Negishi T, Nakanishi H, Yazaki J et al (2002) cDNA microarray analysis of gene expression during Fe-deficiency stress in barley suggests that polar transport of vesicles is implicated in phytosiderophore secretion in Fe-deficient barley roots. Plant J 30:83–94. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01270.x
Nozoye T, Nagasaka S, Kobayashi T et al (2011) Phytosiderophore efflux transporters are crucial for iron acquisition in graminaceous plants. J Biol Chem 286:5446–5454. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.180026
Nozoye T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2013) Characterizing the crucial components of iron homeostasis in the maize mutants ys1 and ys3. PLoS ONE 8:e62567. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062567
O’Rourke J, Charlson D, Gonzalez D et al (2007) Microarray analysis of iron deficiency chlorosis in near-isogenic soybean lines. BMC Genom 8:476. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-476
O’Rourke JA, Nelson RT, Grant D et al (2009) Integrating microarray analysis and the soybean genome to understand the soybeans iron deficiency response. BMC Genom 10:376. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-376
Park Y-S, Kunze S, Ni X et al (2010) Comparative molecular and biochemical characterization of segmentally duplicated 9-lipoxygenase genes ZmLOX4 and ZmLOX5 of maize. Planta 231:1425–1437. doi:10.1007/s00425-010-1143-8
Prasad P (2003) Iron chlorosis. In: Thomas B, Murphy DJ, Murray BG (eds) Encyclopedia of applied plant sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 649–656
Pulido P, Perello C, Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2012) New insights into plant isoprenoid metabolism. Mol Plant 5:964–967. doi:10.1093/mp/sss088
Rellán-Álvarez R, Andaluz S, Rodríguez-Celma J et al (2010) Changes in the proteomic and metabolic profiles of Beta vulgaris root tips in response to iron deficiency and resupply. BMC Plant Biol 10:120. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-120
Rodó AP, Brugière N, Vankova R et al (2008) Over-expression of a zeatin O-glucosylation gene in maize leads to growth retardation and tasselseed formation. J Exp Bot 59:2673–2686. doi:10.1093/jxb/ern137
Rodríguez-Celma J, Lattanzio G, Grusak MA et al (2011) Root responses of Medicago truncatula plants grown in two different iron deficiency conditions: changes in root protein profile and riboflavin biosynthesis. J Proteome Res 10:2590–2601. doi:10.1021/pr2000623
Rodríguez-Celma J, Lattanzio G, Jiménez S et al (2013) Changes induced by Fe deficiency and Fe resupply in the root protein profile of a peach-almond hybrid rootstock. J Proteome Res 12:1162–1172. doi:10.1021/pr300763c
Roudier F, Gissot L, Beaudoin F et al (2010) Very-long-chain fatty acids are involved in polar auxin transport and developmental patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:364–375. doi:10.1105/tpc.109.071209
Schreiber L, Franke R, Lessire R (2005) Biochemical characterization of elongase activity in corn (Zea mays L.) roots. Phytochemistry 66:131–138. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.11.022
Strasser O, Köhl K, Römheld V (1999) Overestimation of apoplastic Fe in roots of soil grown plants. Plant Soil 210:179–187. doi:10.1023/A:1004650506592
‘t Hoen PAC, Ariyurek Y, Thygesen HH et al (2008) Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e141. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn705
Usadel B, Bläsing OE, Gibon Y et al (2008) Multilevel genomic analysis of the response of transcripts, enzyme activities and metabolites in Arabidopsis rosettes to a progressive decrease of temperature in the non-freezing range. Plant, Cell Environ 31:518–547. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01763.x
Vickers CE, Gershenzon J, Lerdau MT et al (2009) A unified mechanism of action for volatile isoprenoids in plant abiotic stress. Nat Chem Biol 5:283–291. doi:10.1038/nchembio.158
Walch-Liu P, Liu L-H, Remans T et al (2006) Evidence that L-glutamate can act as an exogenous signal to modulate root growth and branching in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1045–1057. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcj075
Wang B, Li Y, Zhang W-H (2012) Brassinosteroids are involved in response of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) to iron deficiency. Ann Bot 110:681–688. doi:10.1093/aob/mcs126
Yang TJ, Lin W-D, Schmidt W (2010) Transcriptional profiling of the Arabidopsis iron deficiency response reveals conserved transition metal homeostasis networks. Plant Physiol 152:2130–2141. doi:10.1104/pp.109.152728
Zamboni A, Zanin L, Tomasi N et al (2012) Genome-wide microarray analysis of tomato roots showed defined responses to iron deficiency. BMC Genom 13:101. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-101
Zheng L, Huang F, Narsai R et al (2009) Physiological and transcriptome analysis of iron and phosphorus interaction in rice seedlings. Plant Physiol 151:262–274. doi:10.1104/pp.109.141051
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101160), Shandong Postdoctoral Innovation Foundation (201102038), and Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Crop Biology (2011KF01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, N., Zhao, F. et al. Changes in the transcriptomic profiles of maize roots in response to iron-deficiency stress. Plant Mol Biol 85, 349–363 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0189-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0189-6